Yaser Faghan
Adversarial Attacks on Deep Algorithmic Trading Policies
Oct 22, 2020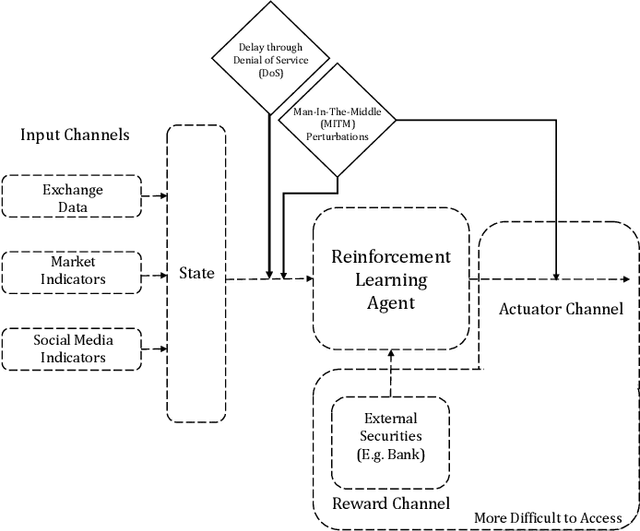

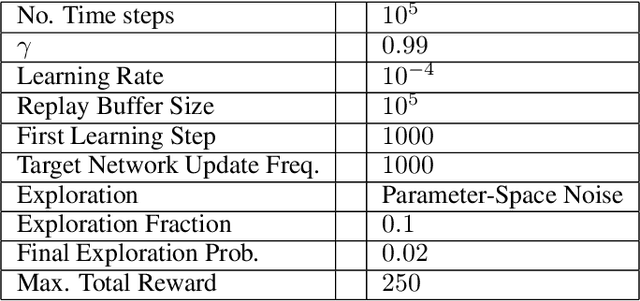
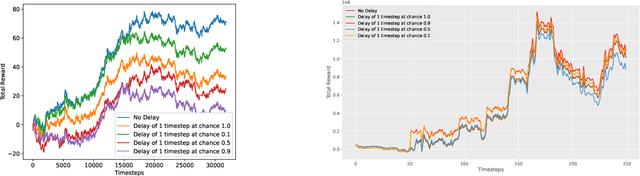
Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has become an appealing solution to algorithmic trading such as high frequency trading of stocks and cyptocurrencies. However, DRL have been shown to be susceptible to adversarial attacks. It follows that algorithmic trading DRL agents may also be compromised by such adversarial techniques, leading to policy manipulation. In this paper, we develop a threat model for deep trading policies, and propose two attack techniques for manipulating the performance of such policies at test-time. Furthermore, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed attacks against benchmark and real-world DQN trading agents.
Comprehensive Review of Deep Reinforcement Learning Methods and Applications in Economics
Mar 21, 2020



Abstract:The popularity of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) methods in economics have been exponentially increased. DRL through a wide range of capabilities from reinforcement learning (RL) and deep learning (DL) for handling sophisticated dynamic business environments offers vast opportunities. DRL is characterized by scalability with the potential to be applied to high-dimensional problems in conjunction with noisy and nonlinear patterns of economic data. In this work, we first consider a brief review of DL, RL, and deep RL methods in diverse applications in economics providing an in-depth insight into the state of the art. Furthermore, the architecture of DRL applied to economic applications is investigated in order to highlight the complexity, robustness, accuracy, performance, computational tasks, risk constraints, and profitability. The survey results indicate that DRL can provide better performance and higher accuracy as compared to the traditional algorithms while facing real economic problems at the presence of risk parameters and the ever-increasing uncertainties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge