Yasamin Jafarian
Pro-Pose: Unpaired Full-Body Portrait Synthesis via Canonical UV Maps
Dec 19, 2025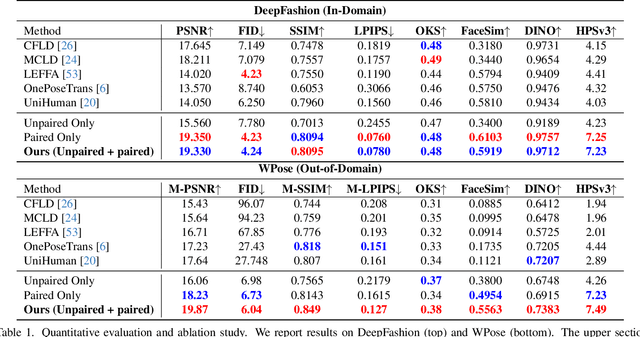
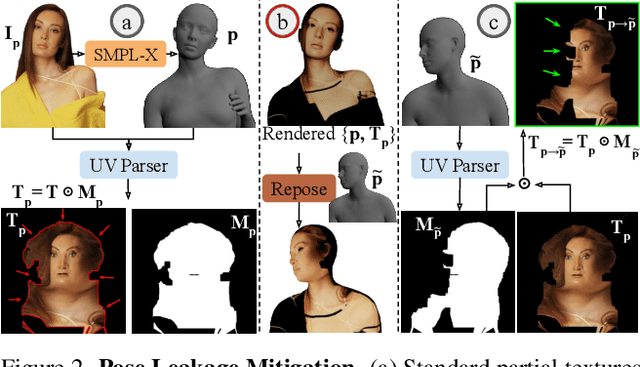
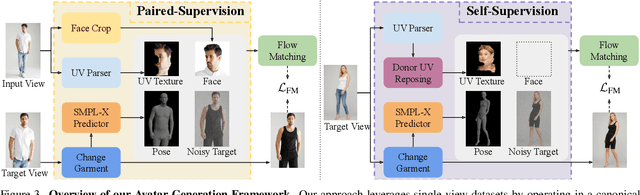
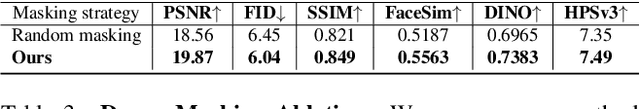
Abstract:Photographs of people taken by professional photographers typically present the person in beautiful lighting, with an interesting pose, and flattering quality. This is unlike common photos people can take of themselves. In this paper, we explore how to create a ``professional'' version of a person's photograph, i.e., in a chosen pose, in a simple environment, with good lighting, and standard black top/bottom clothing. A key challenge is to preserve the person's unique identity, face and body features while transforming the photo. If there would exist a large paired dataset of the same person photographed both ``in the wild'' and by a professional photographer, the problem would potentially be easier to solve. However, such data does not exist, especially for a large variety of identities. To that end, we propose two key insights: 1) Our method transforms the input photo and person's face to a canonical UV space, which is further coupled with reposing methodology to model occlusions and novel view synthesis. Operating in UV space allows us to leverage existing unpaired datasets. 2) We personalize the output photo via multi image finetuning. Our approach yields high-quality, reposed portraits and achieves strong qualitative and quantitative performance on real-world imagery.
Test-Time Anchoring for Discrete Diffusion Posterior Sampling
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:We study the problem of posterior sampling using pretrained discrete diffusion foundation models, aiming to recover images from noisy measurements without retraining task-specific models. While diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in generative modeling, most advances rely on continuous Gaussian diffusion. In contrast, discrete diffusion offers a unified framework for jointly modeling categorical data such as text and images. Beyond unification, discrete diffusion provides faster inference, finer control, and principled training-free Bayesian inference, making it particularly well-suited for posterior sampling. However, existing approaches to discrete diffusion posterior sampling face severe challenges: derivative-free guidance yields sparse signals, continuous relaxations limit applicability, and split Gibbs samplers suffer from the curse of dimensionality. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Anchored Posterior Sampling (APS) for masked diffusion foundation models, built on two key innovations -- quantized expectation for gradient-like guidance in discrete embedding space, and anchored remasking for adaptive decoding. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance among discrete diffusion samplers across linear and nonlinear inverse problems on the standard benchmarks. We further demonstrate the benefits of our approach in training-free stylization and text-guided editing.
Normal-guided Garment UV Prediction for Human Re-texturing
Mar 11, 2023



Abstract:Clothes undergo complex geometric deformations, which lead to appearance changes. To edit human videos in a physically plausible way, a texture map must take into account not only the garment transformation induced by the body movements and clothes fitting, but also its 3D fine-grained surface geometry. This poses, however, a new challenge of 3D reconstruction of dynamic clothes from an image or a video. In this paper, we show that it is possible to edit dressed human images and videos without 3D reconstruction. We estimate a geometry aware texture map between the garment region in an image and the texture space, a.k.a, UV map. Our UV map is designed to preserve isometry with respect to the underlying 3D surface by making use of the 3D surface normals predicted from the image. Our approach captures the underlying geometry of the garment in a self-supervised way, requiring no ground truth annotation of UV maps and can be readily extended to predict temporally coherent UV maps. We demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art human UV map estimation approaches on both real and synthetic data.
Explainable Ensemble Machine Learning for Breast Cancer Diagnosis based on Ultrasound Image Texture Features
Jan 17, 2022



Abstract:Image classification is widely used to build predictive models for breast cancer diagnosis. Most existing approaches overwhelmingly rely on deep convolutional networks to build such diagnosis pipelines. These model architectures, although remarkable in performance, are black-box systems that provide minimal insight into the inner logic behind their predictions. This is a major drawback as the explainability of prediction is vital for applications such as cancer diagnosis. In this paper, we address this issue by proposing an explainable machine learning pipeline for breast cancer diagnosis based on ultrasound images. We extract first- and second-order texture features of the ultrasound images and use them to build a probabilistic ensemble of decision tree classifiers. Each decision tree learns to classify the input ultrasound image by learning a set of robust decision thresholds for texture features of the image. The decision path of the model predictions can then be interpreted by decomposing the learned decision trees. Our results show that our proposed framework achieves high predictive performance while being explainable.
Learning High Fidelity Depths of Dressed Humans by Watching Social Media Dance Videos
Mar 04, 2021



Abstract:A key challenge of learning the geometry of dressed humans lies in the limited availability of the ground truth data (e.g., 3D scanned models), which results in the performance degradation of 3D human reconstruction when applying to real-world imagery. We address this challenge by leveraging a new data resource: a number of social media dance videos that span diverse appearance, clothing styles, performances, and identities. Each video depicts dynamic movements of the body and clothes of a single person while lacking the 3D ground truth geometry. To utilize these videos, we present a new method to use the local transformation that warps the predicted local geometry of the person from an image to that of another image at a different time instant. This allows self-supervision as enforcing a temporal coherence over the predictions. In addition, we jointly learn the depth along with the surface normals that are highly responsive to local texture, wrinkle, and shade by maximizing their geometric consistency. Our method is end-to-end trainable, resulting in high fidelity depth estimation that predicts fine geometry faithful to the input real image. We demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art human depth estimation and human shape recovery approaches on both real and rendered images.
MONET: Multiview Semi-supervised Keypoint via Epipolar Divergence
May 31, 2018



Abstract:This paper presents MONET---an end-to-end semi-supervised learning framework for a pose detector using multiview image streams. What differentiates MONET from existing models is its capability of detecting general subjects including non-human species without a pre-trained model. A key challenge of such subjects lies in the limited availability of expert manual annotations, which often leads to a large bias in the detection model. We address this challenge by using the epipolar constraint embedded in the unlabeled data in two ways. First, given a set of the labeled data, the keypoint trajectories can be reliably reconstructed in 3D using multiview optical flows, resulting in considerable data augmentation in space and time from nearly exhaustive views. Second, the detection across views must geometrically agree with each other. We introduce a new measure of geometric consistency in keypoint distributions called epipolar divergence---a generalized distance from the epipolar lines to the corresponding keypoint distribution. Epipolar divergence characterizes when two view keypoint distributions produces zero reprojection error. We design a twin network that minimizes the epipolar divergence through stereo rectification that can significantly alleviate computational complexity and sampling aliasing in training. We demonstrate that our framework can localize customized keypoints of diverse species, e.g., humans, dogs, and monkeys.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge