Yansong Huang
A Comparative Visual Analytics Framework for Evaluating Evolutionary Processes in Multi-objective Optimization
Aug 10, 2023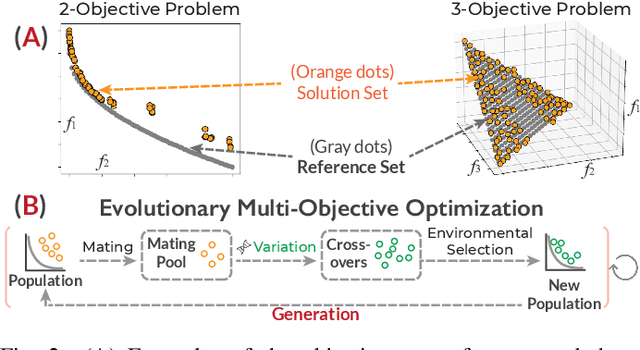
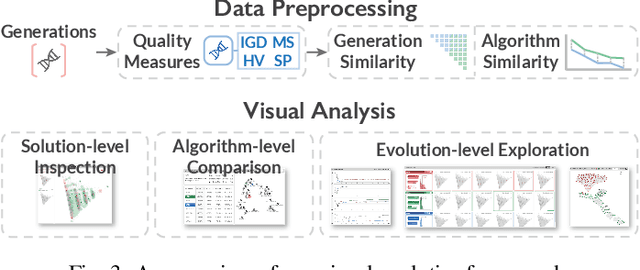
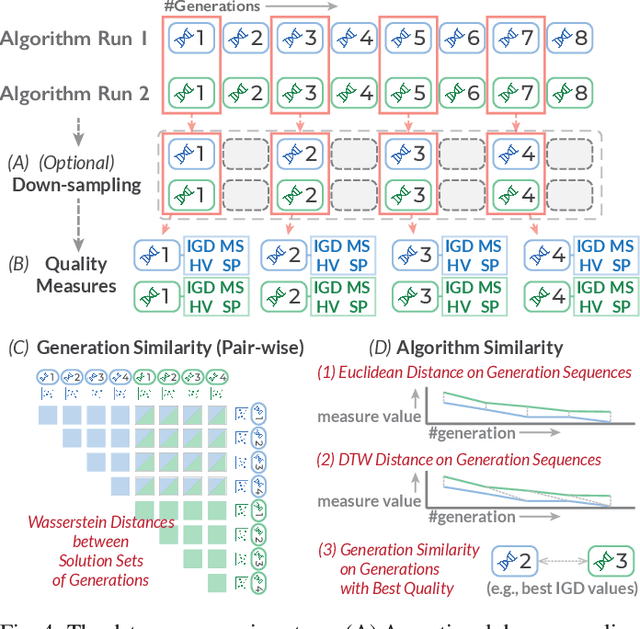
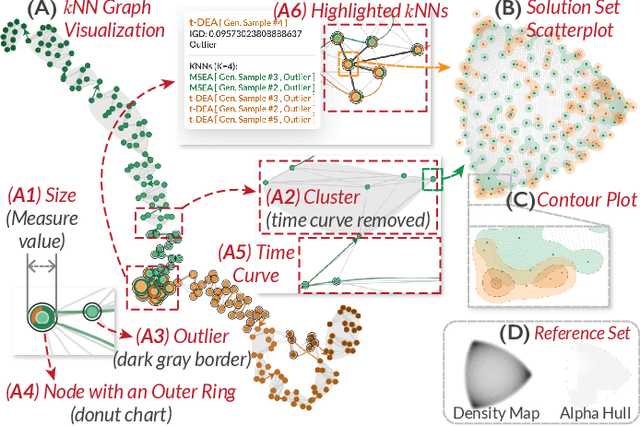
Abstract:Evolutionary multi-objective optimization (EMO) algorithms have been demonstrated to be effective in solving multi-criteria decision-making problems. In real-world applications, analysts often employ several algorithms concurrently and compare their solution sets to gain insight into the characteristics of different algorithms and explore a broader range of feasible solutions. However, EMO algorithms are typically treated as black boxes, leading to difficulties in performing detailed analysis and comparisons between the internal evolutionary processes. Inspired by the successful application of visual analytics tools in explainable AI, we argue that interactive visualization can significantly enhance the comparative analysis between multiple EMO algorithms. In this paper, we present a visual analytics framework that enables the exploration and comparison of evolutionary processes in EMO algorithms. Guided by a literature review and expert interviews, the proposed framework addresses various analytical tasks and establishes a multi-faceted visualization design to support the comparative analysis of intermediate generations in the evolution as well as solution sets. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework through case studies on benchmarking and real-world multi-objective optimization problems to elucidate how analysts can leverage our framework to inspect and compare diverse algorithms.
Video Sentiment Analysis with Bimodal Information-augmented Multi-Head Attention
Mar 09, 2021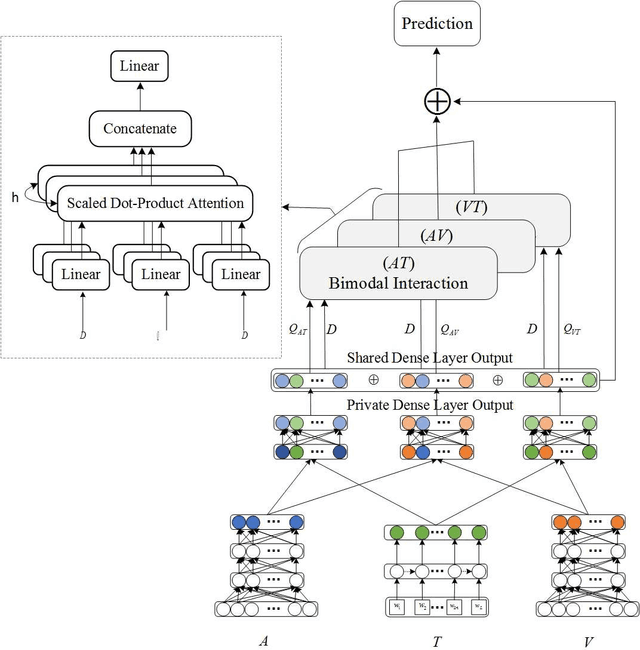
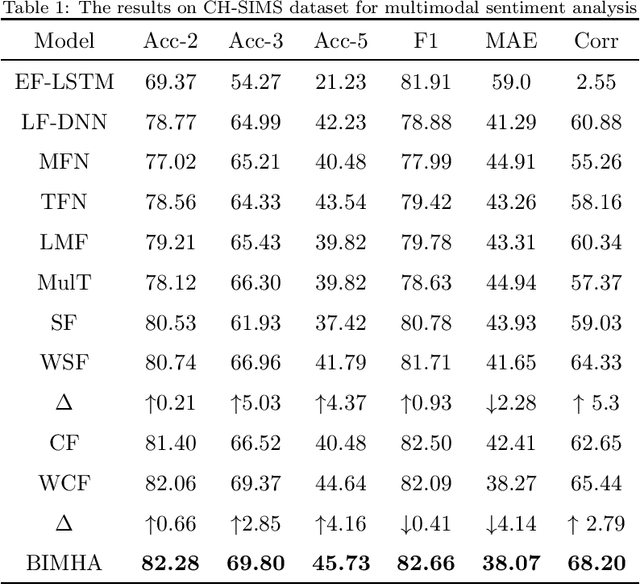

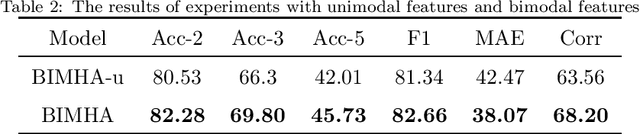
Abstract:Sentiment analysis is the basis of intelligent human-computer interaction. As one of the frontier research directions of artificial intelligence, it can help computers better identify human intentions and emotional states so that provide more personalized services. However, as human present sentiments by spoken words, gestures, facial expressions and others which involve variable forms of data including text, audio, video, etc., it poses many challenges to this study. Due to the limitations of unimodal sentiment analysis, recent research has focused on the sentiment analysis of videos containing time series data of multiple modalities. When analyzing videos with multimodal data, the key problem is how to fuse these heterogeneous data. In consideration that the contribution of each modality is different, current fusion methods tend to extract the important information of single modality prior to fusion, which ignores the consistency and complementarity of bimodal interaction and has influences on the final decision. To solve this problem, a video sentiment analysis method using multi-head attention with bimodal information augmented is proposed. Based on bimodal interaction, more important bimodal features are assigned larger weights. In this way, different feature representations are adaptively assigned corresponding attention for effective multimodal fusion. Extensive experiments were conducted on both Chinese and English public datasets. The results show that our approach outperforms the existing methods and can give an insight into the contributions of bimodal interaction among three modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge