Yankaiqi Li
Optimized Unet with Attention Mechanism for Multi-Scale Semantic Segmentation
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Semantic segmentation is one of the core tasks in the field of computer vision, and its goal is to accurately classify each pixel in an image. The traditional Unet model achieves efficient feature extraction and fusion through an encoder-decoder structure, but it still has certain limitations when dealing with complex backgrounds, long-distance dependencies, and multi-scale targets. To this end, this paper proposes an improved Unet model combined with an attention mechanism, introduces channel attention and spatial attention modules, enhances the model's ability to focus on important features, and optimizes skip connections through a multi-scale feature fusion strategy, thereby improving the combination of global semantic information and fine-grained features. The experiment is based on the Cityscapes dataset and compared with classic models such as FCN, SegNet, DeepLabv3+, and PSPNet. The improved model performs well in terms of mIoU and pixel accuracy (PA), reaching 76.5% and 95.3% respectively. The experimental results verify the superiority of this method in dealing with complex scenes and blurred target boundaries. In addition, this paper discusses the potential of the improved model in practical applications and future expansion directions, indicating that it has broad application value in fields such as autonomous driving, remote sensing image analysis, and medical image processing.
Graph Neural Network-Driven Hierarchical Mining for Complex Imbalanced Data
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:This study presents a hierarchical mining framework for high-dimensional imbalanced data, leveraging a depth graph model to address the inherent performance limitations of conventional approaches in handling complex, high-dimensional data distributions with imbalanced sample representations. By constructing a structured graph representation of the dataset and integrating graph neural network (GNN) embeddings, the proposed method effectively captures global interdependencies among samples. Furthermore, a hierarchical strategy is employed to enhance the characterization and extraction of minority class feature patterns, thereby facilitating precise and robust imbalanced data mining. Empirical evaluations across multiple experimental scenarios validate the efficacy of the proposed approach, demonstrating substantial improvements over traditional methods in key performance metrics, including pattern discovery count, average support, and minority class coverage. Notably, the method exhibits superior capabilities in minority-class feature extraction and pattern correlation analysis. These findings underscore the potential of depth graph models, in conjunction with hierarchical mining strategies, to significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of imbalanced data analysis. This research contributes a novel computational framework for high-dimensional complex data processing and lays the foundation for future extensions to dynamically evolving imbalanced data and multi-modal data applications, thereby expanding the applicability of advanced data mining methodologies to more intricate analytical domains.
Collaborative Optimization in Financial Data Mining Through Deep Learning and ResNeXt
Dec 23, 2024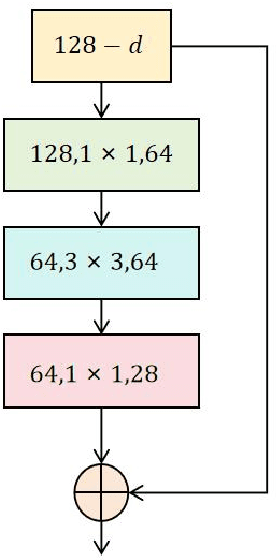

Abstract:This study proposes a multi-task learning framework based on ResNeXt, aiming to solve the problem of feature extraction and task collaborative optimization in financial data mining. Financial data usually has the complex characteristics of high dimensionality, nonlinearity, and time series, and is accompanied by potential correlations between multiple tasks, making it difficult for traditional methods to meet the needs of data mining. This study introduces the ResNeXt model into the multi-task learning framework and makes full use of its group convolution mechanism to achieve efficient extraction of local patterns and global features of financial data. At the same time, through the design of task sharing layers and dedicated layers, it is established between multiple related tasks. Deep collaborative optimization relationships. Through flexible multi-task loss weight design, the model can effectively balance the learning needs of different tasks and improve overall performance. Experiments are conducted on a real S&P 500 financial data set, verifying the significant advantages of the proposed framework in classification and regression tasks. The results indicate that, when compared to other conventional deep learning models, the proposed method delivers superior performance in terms of accuracy, F1 score, root mean square error, and other metrics, highlighting its outstanding effectiveness and robustness in handling complex financial data. This research provides an efficient and adaptable solution for financial data mining, and at the same time opens up a new research direction for the combination of multi-task learning and deep learning, which has important theoretical significance and practical application value.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge