Yanhao Chen
CoIRL-AD: Collaborative-Competitive Imitation-Reinforcement Learning in Latent World Models for Autonomous Driving
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving models trained solely with imitation learning (IL) often suffer from poor generalization. In contrast, reinforcement learning (RL) promotes exploration through reward maximization but faces challenges such as sample inefficiency and unstable convergence. A natural solution is to combine IL and RL. Moving beyond the conventional two-stage paradigm (IL pretraining followed by RL fine-tuning), we propose CoIRL-AD, a competitive dual-policy framework that enables IL and RL agents to interact during training. CoIRL-AD introduces a competition-based mechanism that facilitates knowledge exchange while preventing gradient conflicts. Experiments on the nuScenes dataset show an 18% reduction in collision rate compared to baselines, along with stronger generalization and improved performance on long-tail scenarios. Code is available at: https://github.com/SEU-zxj/CoIRL-AD.
HAUR: Human Annotation Understanding and Recognition Through Text-Heavy Images
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Vision Question Answering (VQA) tasks use images to convey critical information to answer text-based questions, which is one of the most common forms of question answering in real-world scenarios. Numerous vision-text models exist today and have performed well on certain VQA tasks. However, these models exhibit significant limitations in understanding human annotations on text-heavy images. To address this, we propose the Human Annotation Understanding and Recognition (HAUR) task. As part of this effort, we introduce the Human Annotation Understanding and Recognition-5 (HAUR-5) dataset, which encompasses five common types of human annotations. Additionally, we developed and trained our model, OCR-Mix. Through comprehensive cross-model comparisons, our results demonstrate that OCR-Mix outperforms other models in this task. Our dataset and model will be released soon .
A Synergistic Compilation Workflow for Tackling Crosstalk in Quantum Machines
Jul 19, 2022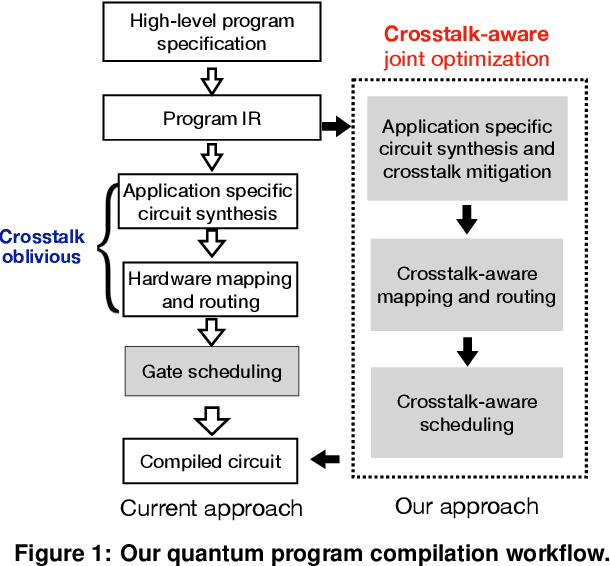
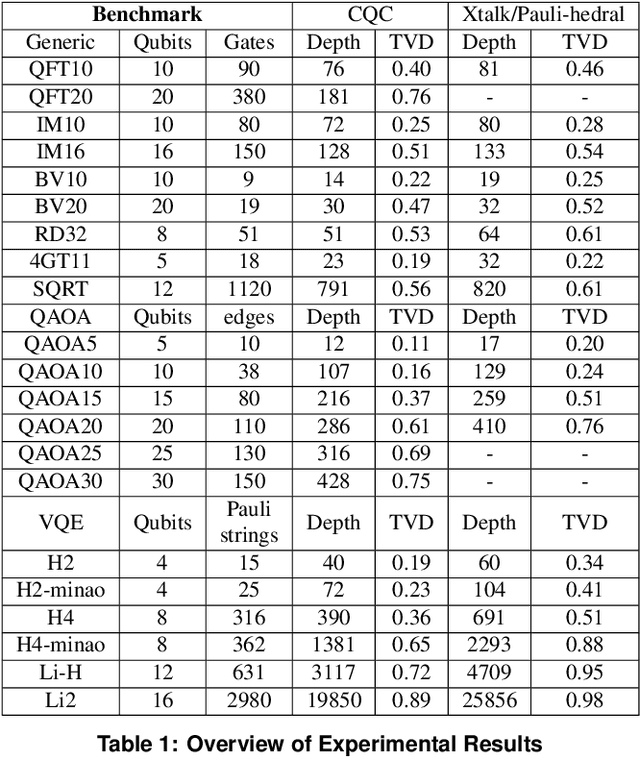
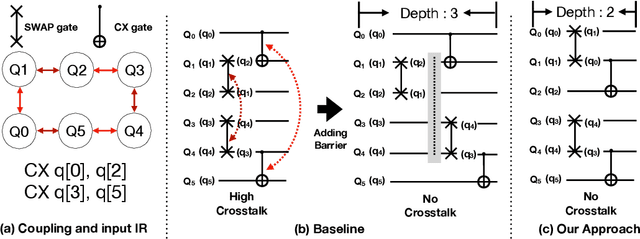
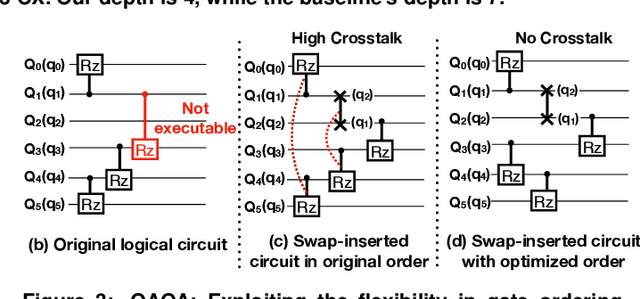
Abstract:Near-term quantum systems tend to be noisy. Crosstalk noise has been recognized as one of several major types of noises in superconducting Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices. Crosstalk arises from the concurrent execution of two-qubit gates on nearby qubits, such as \texttt{CX}. It might significantly raise the error rate of gates in comparison to running them individually. Crosstalk can be mitigated through scheduling or hardware machine tuning. Prior scientific studies, however, manage crosstalk at a really late phase in the compilation process, usually after hardware mapping is done. It may miss great opportunities of optimizing algorithm logic, routing, and crosstalk at the same time. In this paper, we push the envelope by considering all these factors simultaneously at the very early compilation stage. We propose a crosstalk-aware quantum program compilation framework called CQC that can enhance crosstalk mitigation while achieving satisfactory circuit depth. Moreover, we identify opportunities for translation from intermediate representation to the circuit for application-specific crosstalk mitigation, for instance, the \texttt{CX} ladder construction in variational quantum eigensolvers (VQE). Evaluations through simulation and on real IBM-Q devices show that our framework can significantly reduce the error rate by up to 6$\times$, with only $\sim$60\% circuit depth compared to state-of-the-art gate scheduling approaches. In particular, for VQE, we demonstrate 49\% circuit depth reduction with 9.6\% fidelity improvement over prior art on the H4 molecule using IBMQ Guadalupe. Our CQC framework will be released on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge