Yanbin Lin
Global Data Constraints: Ethical and Effectiveness Challenges in Large Language Model
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:The efficacy and ethical integrity of large language models (LLMs) are profoundly influenced by the diversity and quality of their training datasets. However, the global landscape of data accessibility presents significant challenges, particularly in regions with stringent data privacy laws or limited open-source information. This paper examines the multifaceted challenges associated with acquiring high-quality training data for LLMs, focusing on data scarcity, bias, and low-quality content across various linguistic contexts. We highlight the technical and ethical implications of relying on publicly available but potentially biased or irrelevant data sources, which can lead to the generation of biased or hallucinatory content by LLMs. Through a series of evaluations using GPT-4 and GPT-4o, we demonstrate how these data constraints adversely affect model performance and ethical alignment. We propose and validate several mitigation strategies designed to enhance data quality and model robustness, including advanced data filtering techniques and ethical data collection practices. Our findings underscore the need for a proactive approach in developing LLMs that considers both the effectiveness and ethical implications of data constraints, aiming to foster the creation of more reliable and universally applicable AI systems.
LLMGeo: Benchmarking Large Language Models on Image Geolocation In-the-wild
May 30, 2024



Abstract:Image geolocation is a critical task in various image-understanding applications. However, existing methods often fail when analyzing challenging, in-the-wild images. Inspired by the exceptional background knowledge of multimodal language models, we systematically evaluate their geolocation capabilities using a novel image dataset and a comprehensive evaluation framework. We first collect images from various countries via Google Street View. Then, we conduct training-free and training-based evaluations on closed-source and open-source multi-modal language models. we conduct both training-free and training-based evaluations on closed-source and open-source multimodal language models. Our findings indicate that closed-source models demonstrate superior geolocation abilities, while open-source models can achieve comparable performance through fine-tuning.
Smart Expert System: Large Language Models as Text Classifiers
May 17, 2024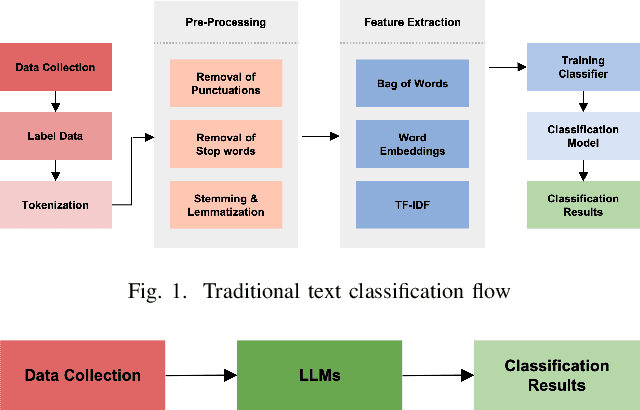
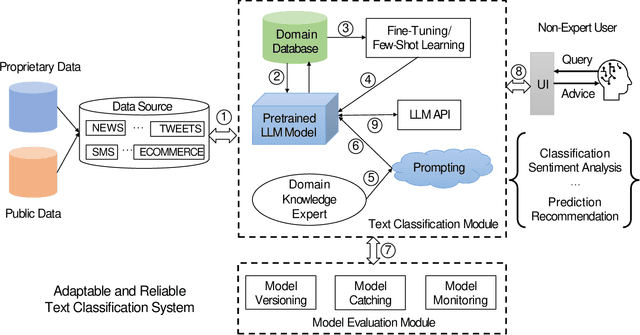
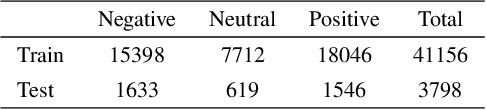
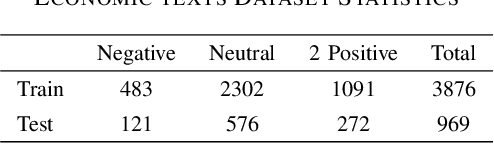
Abstract:Text classification is a fundamental task in Natural Language Processing (NLP), and the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized the field. This paper introduces the Smart Expert System, a novel approach that leverages LLMs as text classifiers. The system simplifies the traditional text classification workflow, eliminating the need for extensive preprocessing and domain expertise. The performance of several LLMs, machine learning (ML) algorithms, and neural network (NN) based structures is evaluated on four datasets. Results demonstrate that certain LLMs surpass traditional methods in sentiment analysis, spam SMS detection and multi-label classification. Furthermore, it is shown that the system's performance can be further enhanced through few-shot or fine-tuning strategies, making the fine-tuned model the top performer across all datasets. Source code and datasets are available in this GitHub repository: https://github.com/yeyimilk/llm-zero-shot-classifiers.
Large Language Models Are Zero-Shot Text Classifiers
Dec 02, 2023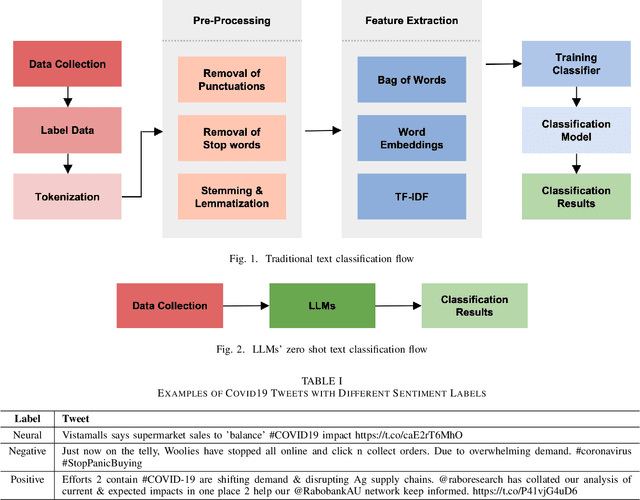
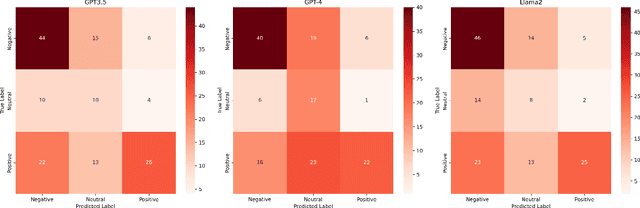

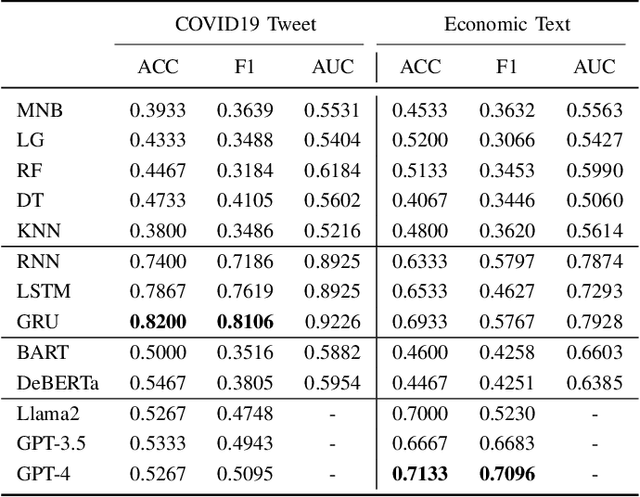
Abstract:Retrained large language models (LLMs) have become extensively used across various sub-disciplines of natural language processing (NLP). In NLP, text classification problems have garnered considerable focus, but still faced with some limitations related to expensive computational cost, time consumption, and robust performance to unseen classes. With the proposal of chain of thought prompting (CoT), LLMs can be implemented using zero-shot learning (ZSL) with the step by step reasoning prompts, instead of conventional question and answer formats. The zero-shot LLMs in the text classification problems can alleviate these limitations by directly utilizing pretrained models to predict both seen and unseen classes. Our research primarily validates the capability of GPT models in text classification. We focus on effectively utilizing prompt strategies to various text classification scenarios. Besides, we compare the performance of zero shot LLMs with other state of the art text classification methods, including traditional machine learning methods, deep learning methods, and ZSL methods. Experimental results demonstrate that the performance of LLMs underscores their effectiveness as zero-shot text classifiers in three of the four datasets analyzed. The proficiency is especially advantageous for small businesses or teams that may not have extensive knowledge in text classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge