Yahia Lebbah
Boosting the Learning for Ranking Patterns
Mar 05, 2022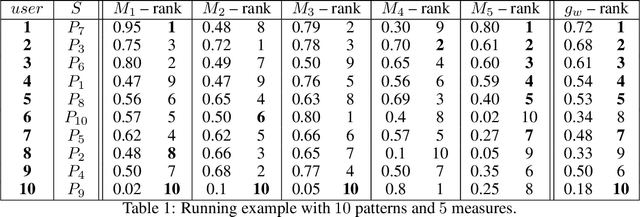
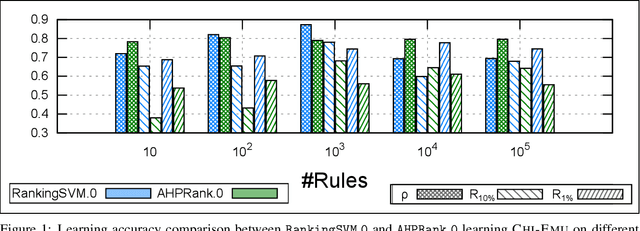

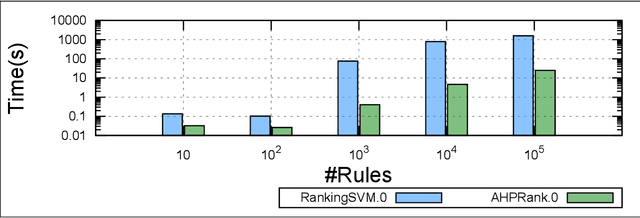
Abstract:Discovering relevant patterns for a particular user remains a challenging tasks in data mining. Several approaches have been proposed to learn user-specific pattern ranking functions. These approaches generalize well, but at the expense of the running time. On the other hand, several measures are often used to evaluate the interestingness of patterns, with the hope to reveal a ranking that is as close as possible to the user-specific ranking. In this paper, we formulate the problem of learning pattern ranking functions as a multicriteria decision making problem. Our approach aggregates different interestingness measures into a single weighted linear ranking function, using an interactive learning procedure that operates in either passive or active modes. A fast learning step is used for eliciting the weights of all the measures by mean of pairwise comparisons. This approach is based on Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), and a set of user-ranked patterns to build a preference matrix, which compares the importance of measures according to the user-specific interestingness. A sensitivity based heuristic is proposed for the active learning mode, in order to insure high quality results with few user ranking queries. Experiments conducted on well-known datasets show that our approach significantly reduces the running time and returns precise pattern ranking, while being robust to user-error compared with state-of-the-art approaches.
Users Constraints in Itemset Mining
Feb 08, 2018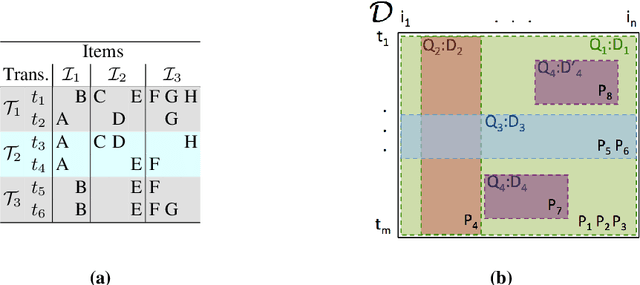
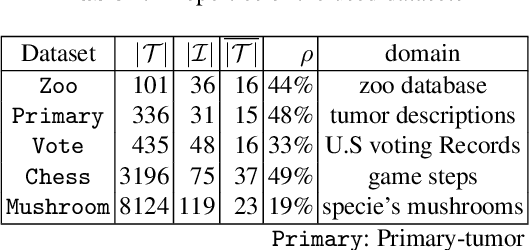
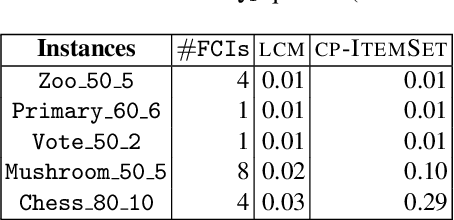
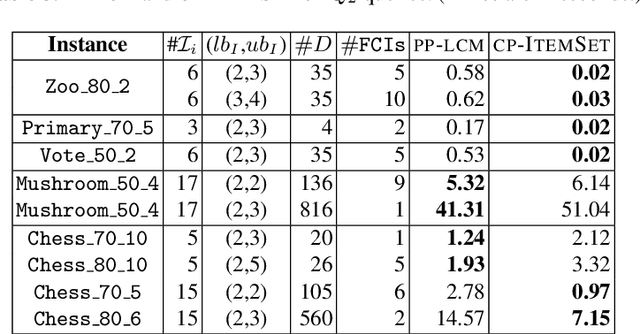
Abstract:Discovering significant itemsets is one of the fundamental problems in data mining. It has recently been shown that constraint programming is a flexible way to tackle data mining tasks. With a constraint programming approach, we can easily express and efficiently answer queries with users constraints on items. However, in many practical cases it is possible that queries also express users constraints on the dataset itself. For instance, asking for a particular itemset in a particular part of the dataset. This paper presents a general constraint programming model able to handle any kind of query on the items or the dataset for itemset mining.
A global constraint for closed itemset mining
Apr 17, 2016


Abstract:Discovering the set of closed frequent patterns is one of the fundamental problems in Data Mining. Recent Constraint Programming (CP) approaches for declarative itemset mining have proven their usefulness and flexibility. But the wide use of reified constraints in current CP approaches raises many difficulties to cope with high dimensional datasets. This paper proposes CLOSED PATTERN global constraint which does not require any reified constraints nor any extra variables to encode efficiently the Closed Frequent Pattern Mining (CFPM) constraint. CLOSED-PATTERN captures the particular semantics of the CFPM problem in order to ensure a polynomial pruning algorithm ensuring domain consistency. The computational properties of our constraint are analyzed and their practical effectiveness is experimentally evaluated.
A global Constraint for mining Sequential Patterns with GAP constraint
Nov 26, 2015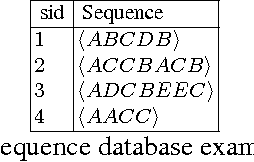
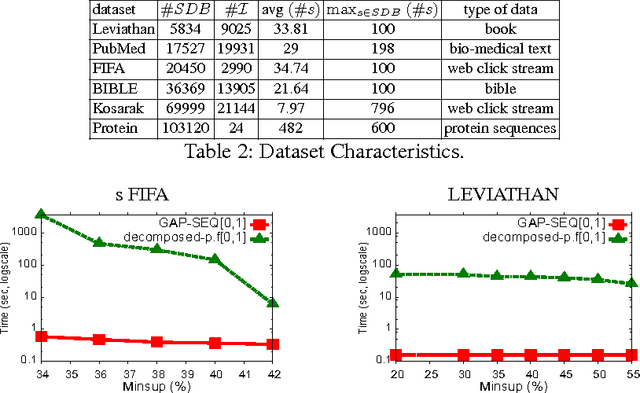
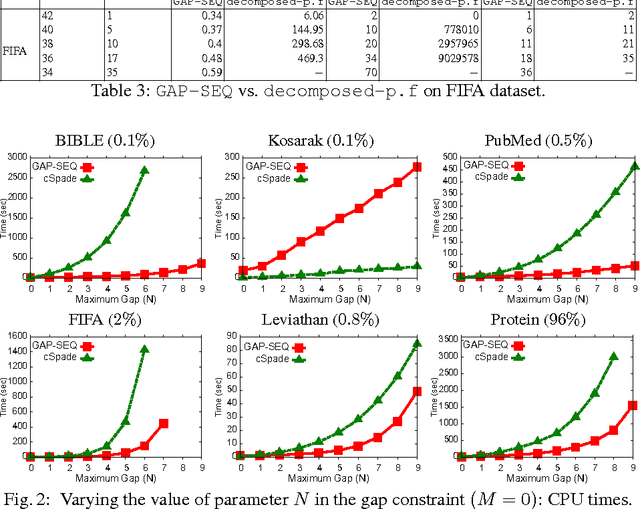
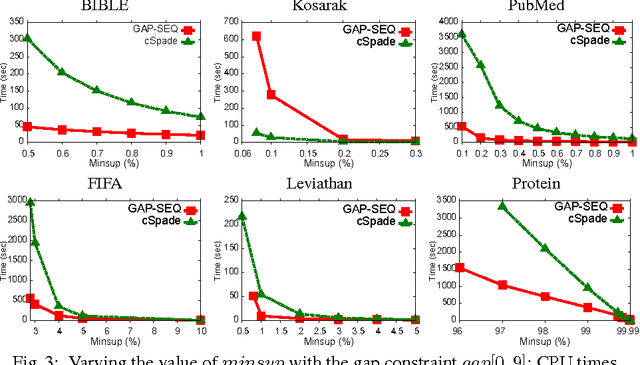
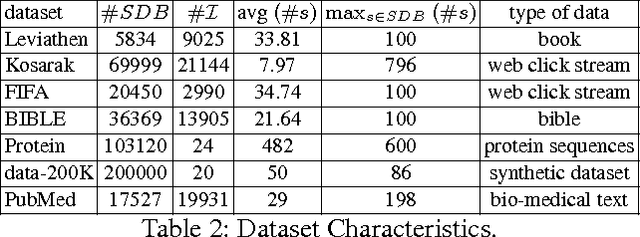
Abstract:Sequential pattern mining (SPM) under gap constraint is a challenging task. Many efficient specialized methods have been developed but they are all suffering from a lack of genericity. The Constraint Programming (CP) approaches are not so effective because of the size of their encodings. In[7], we have proposed the global constraint Prefix-Projection for SPM which remedies to this drawback. However, this global constraint cannot be directly extended to support gap constraint. In this paper, we propose the global constraint GAP-SEQ enabling to handle SPM with or without gap constraint. GAP-SEQ relies on the principle of right pattern extensions. Experiments show that our approach clearly outperforms both CP approaches and the state-of-the-art cSpade method on large datasets.
Prefix-Projection Global Constraint for Sequential Pattern Mining
Jun 23, 2015


Abstract:Sequential pattern mining under constraints is a challenging data mining task. Many efficient ad hoc methods have been developed for mining sequential patterns, but they are all suffering from a lack of genericity. Recent works have investigated Constraint Programming (CP) methods, but they are not still effective because of their encoding. In this paper, we propose a global constraint based on the projected databases principle which remedies to this drawback. Experiments show that our approach clearly outperforms CP approaches and competes well with ad hoc methods on large datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge