Yadong Ding
A Multi-Task Incremental Learning Framework with Category Name Embedding for Aspect-Category Sentiment Analysis
Oct 06, 2020


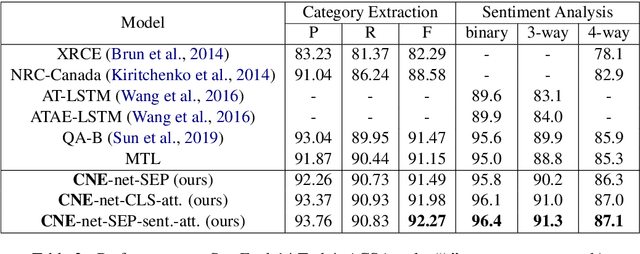
Abstract:(T)ACSA tasks, including aspect-category sentiment analysis (ACSA) and targeted aspect-category sentiment analysis (TACSA), aims at identifying sentiment polarity on predefined categories. Incremental learning on new categories is necessary for (T)ACSA real applications. Though current multi-task learning models achieve good performance in (T)ACSA tasks, they suffer from catastrophic forgetting problems in (T)ACSA incremental learning tasks. In this paper, to make multi-task learning feasible for incremental learning, we proposed Category Name Embedding network (CNE-net). We set both encoder and decoder shared among all categories to weaken the catastrophic forgetting problem. Besides the origin input sentence, we applied another input feature, i.e., category name, for task discrimination. Our model achieved state-of-the-art on two (T)ACSA benchmark datasets. Furthermore, we proposed a dataset for (T)ACSA incremental learning and achieved the best performance compared with other strong baselines.
Charge-Based Prison Term Prediction with Deep Gating Network
Aug 30, 2019

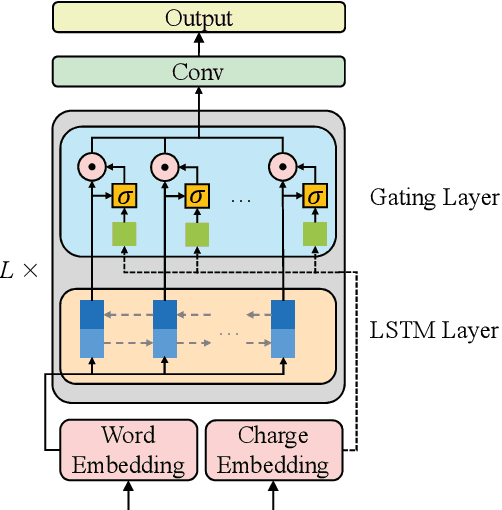

Abstract:Judgment prediction for legal cases has attracted much research efforts for its practice use, of which the ultimate goal is prison term prediction. While existing work merely predicts the total prison term, in reality a defendant is often charged with multiple crimes. In this paper, we argue that charge-based prison term prediction (CPTP) not only better fits realistic needs, but also makes the total prison term prediction more accurate and interpretable. We collect the first large-scale structured data for CPTP and evaluate several competitive baselines. Based on the observation that fine-grained feature selection is the key to achieving good performance, we propose the Deep Gating Network (DGN) for charge-specific feature selection and aggregation. Experiments show that DGN achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge