Xueyuan Zhang
Cross-Organ and Cross-Scanner Adenocarcinoma Segmentation using Rein to Fine-tune Vision Foundation Models
Sep 19, 2024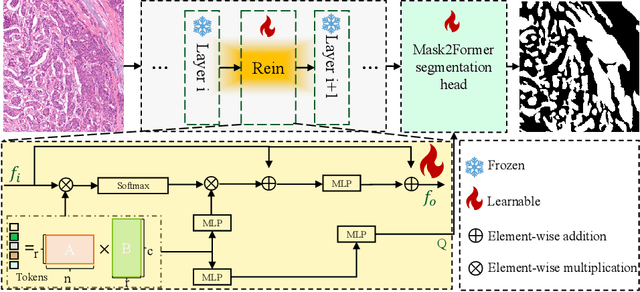

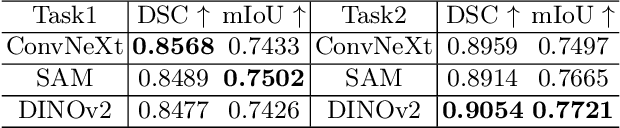
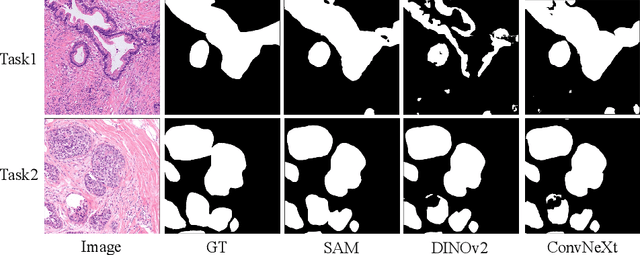
Abstract:In recent years, significant progress has been made in tumor segmentation within the field of digital pathology. However, variations in organs, tissue preparation methods, and image acquisition processes can lead to domain discrepancies among digital pathology images. To address this problem, in this paper, we use Rein, a fine-tuning method, to parametrically and efficiently fine-tune various vision foundation models (VFMs) for MICCAI 2024 Cross-Organ and Cross-Scanner Adenocarcinoma Segmentation (COSAS2024). The core of Rein consists of a set of learnable tokens, which are directly linked to instances, improving functionality at the instance level in each layer. In the data environment of the COSAS2024 Challenge, extensive experiments demonstrate that Rein fine-tuned the VFMs to achieve satisfactory results. Specifically, we used Rein to fine-tune ConvNeXt and DINOv2. Our team used the former to achieve scores of 0.7719 and 0.7557 on the preliminary test phase and final test phase in task1, respectively, while the latter achieved scores of 0.8848 and 0.8192 on the preliminary test phase and final test phase in task2. Code is available at GitHub.
Split Two-Tower Model for Efficient and Privacy-Preserving Cross-device Federated Recommendation
Jun 28, 2022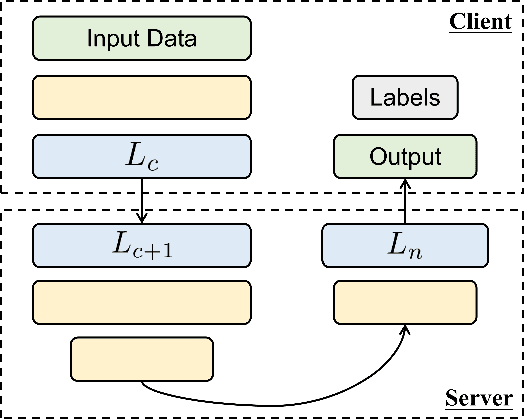

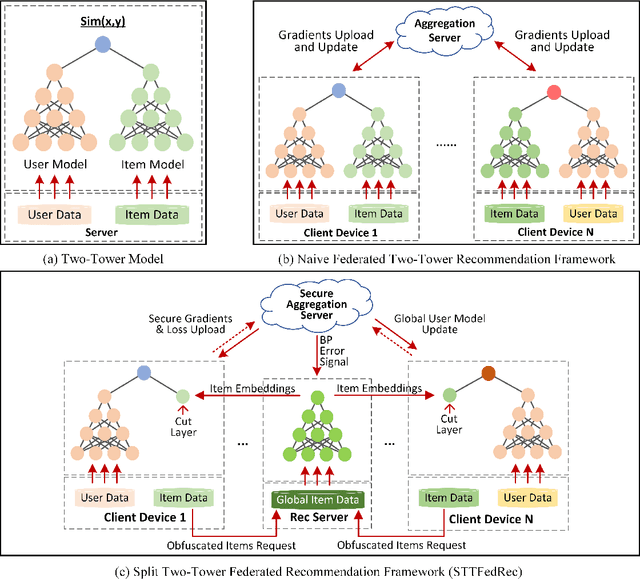

Abstract:Federated Recommendation can mitigate the systematical privacy risks of traditional recommendation since it allows the model training and online inferring without centralized user data collection. Most existing works assume that all user devices are available and adequate to participate in the Federated Learning. However, in practice, the complex recommendation models designed for accurate prediction and massive item data cause a high computation and communication cost to the resource-constrained user device, resulting in poor performance or training failure. Therefore, how to effectively compress the computation and communication overhead to achieve efficient federated recommendations across ubiquitous mobile devices remains a significant challenge. This paper introduces split learning into the two-tower recommendation models and proposes STTFedRec, a privacy-preserving and efficient cross-device federated recommendation framework. STTFedRec achieves local computation reduction by splitting the training and computation of the item model from user devices to a performance-powered server. The server with the item model provides low-dimensional item embeddings instead of raw item data to the user devices for local training and online inferring, achieving server broadcast compression. The user devices only need to perform similarity calculations with cached user embeddings to achieve efficient online inferring. We also propose an obfuscated item request strategy and multi-party circular secret sharing chain to enhance the privacy protection of model training. The experiments conducted on two public datasets demonstrate that STTFedRec improves the average computation time and communication size of the baseline models by about 40 times and 42 times in the best-case scenario with balanced recommendation accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge