Xueya Zhang
Graph Wasserstein Correlation Analysis for Movie Retrieval
Aug 06, 2020
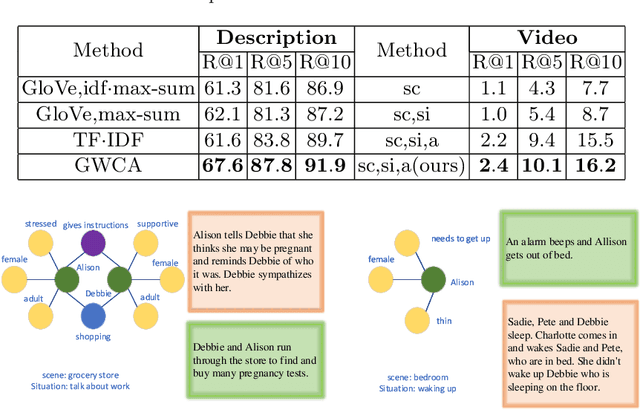
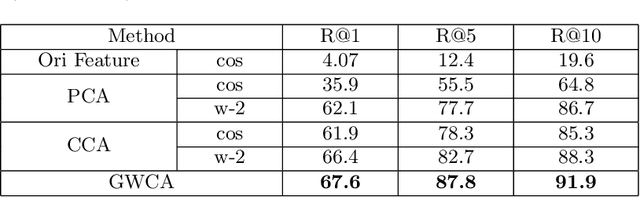

Abstract:Movie graphs play an important role to bridge heterogenous modalities of videos and texts in human-centric retrieval. In this work, we propose Graph Wasserstein Correlation Analysis (GWCA) to deal with the core issue therein, i.e, cross heterogeneous graph comparison. Spectral graph filtering is introduced to encode graph signals, which are then embedded as probability distributions in a Wasserstein space, called graph Wasserstein metric learning. Such a seamless integration of graph signal filtering together with metric learning results in a surprise consistency on both learning processes, in which the goal of metric learning is just to optimize signal filters or vice versa. Further, we derive the solution of the graph comparison model as a classic generalized eigenvalue decomposition problem, which has an exactly closed-form solution. Finally, GWCA together with movie/text graphs generation are unified into the framework of movie retrieval to evaluate our proposed method. Extensive experiments on MovieGrpahs dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our GWCA as well as the entire framework.
Dual-Attention Graph Convolutional Network
Nov 28, 2019



Abstract:Graph convolutional networks (GCNs) have shown the powerful ability in text structure representation and effectively facilitate the task of text classification. However, challenges still exist in adapting GCN on learning discriminative features from texts due to the main issue of graph variants incurred by the textual complexity and diversity. In this paper, we propose a dual-attention GCN to model the structural information of various texts as well as tackle the graph-invariant problem through embedding two types of attention mechanisms, i.e. the connection-attention and hop-attention, into the classic GCN. To encode various connection patterns between neighbour words, connection-attention adaptively imposes different weights specified to neighbourhoods of each word, which captures the short-term dependencies. On the other hand, the hop-attention applies scaled coefficients to different scopes during the graph diffusion process to make the model learn more about the distribution of context, which captures long-term semantics in an adaptive way. Extensive experiments are conducted on five widely used datasets to evaluate our dual-attention GCN, and the achieved state-of-the-art performance verifies the effectiveness of dual-attention mechanisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge