Xiqiao Li
Pseudo-labelling and Meta Reweighting Learning for Image Aesthetic Quality Assessment
Jan 08, 2022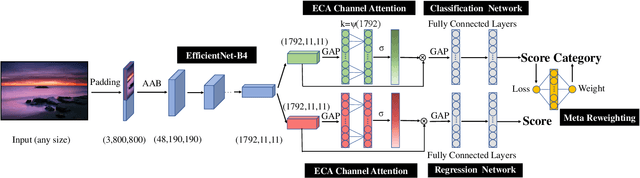

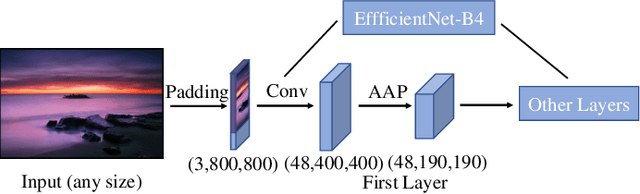
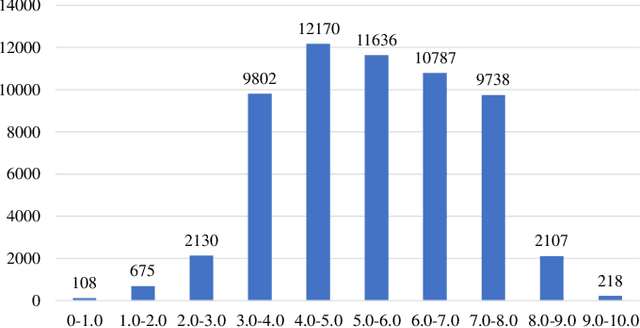
Abstract:In the tasks of image aesthetic quality evaluation, it is difficult to reach both the high score area and low score area due to the normal distribution of aesthetic datasets. To reduce the error in labeling and solve the problem of normal data distribution, we propose a new aesthetic mixed dataset with classification and regression called AMD-CR, and we train a meta reweighting network to reweight the loss of training data differently. In addition, we provide a training strategy acccording to different stages, based on pseudo labels of the binary classification task, and then we use it for aesthetic training acccording to different stages in classification and regression tasks. In the construction of the network structure, we construct an aesthetic adaptive block (AAB) structure that can adapt to any size of the input images. Besides, we also use the efficient channel attention (ECA) to strengthen the feature extracting ability of each task. The experimental result shows that our method improves 0.1112 compared with the conventional methods in SROCC. The method can also help to find best aesthetic path planning for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) and vehicles.
A Deep Drift-Diffusion Model for Image Aesthetic Score Distribution Prediction
Oct 15, 2020



Abstract:The task of aesthetic quality assessment is complicated due to its subjectivity. In recent years, the target representation of image aesthetic quality has changed from a one-dimensional binary classification label or numerical score to a multi-dimensional score distribution. According to current methods, the ground truth score distributions are straightforwardly regressed. However, the subjectivity of aesthetics is not taken into account, that is to say, the psychological processes of human beings are not taken into consideration, which limits the performance of the task. In this paper, we propose a Deep Drift-Diffusion (DDD) model inspired by psychologists to predict aesthetic score distribution from images. The DDD model can describe the psychological process of aesthetic perception instead of traditional modeling of the results of assessment. We use deep convolution neural networks to regress the parameters of the drift-diffusion model. The experimental results in large scale aesthetic image datasets reveal that our novel DDD model is simple but efficient, which outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in aesthetic score distribution prediction. Besides, different psychological processes can also be predicted by our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge