Xinghong Hu
Copy-Move Image Forgery Detection Based on Evolving Circular Domains Coverage
Sep 09, 2021



Abstract:The aim of this paper is to improve the accuracy of copy-move forgery detection (CMFD) in image forensics by proposing a novel scheme. The proposed scheme integrates both block-based and keypoint-based forgery detection methods. Firstly, speed-up robust feature (SURF) descriptor in log-polar space and scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) descriptor are extracted from an entire forged image. Secondly, generalized 2 nearest neighbor (g2NN) is employed to get massive matched pairs. Then, random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm is employed to filter out mismatched pairs, thus allowing rough localization of the counterfeit areas. To present more accurately these forgery areas more accurately, we propose an efficient and accurate algorithm, evolving circular domains coverage (ECDC), to cover present them. This algorithm aims to find satisfactory threshold areas by extracting block features from jointly evolving circular domains, which are centered on the matched pairs. Finally, morphological operation is applied to refine the detected forgery areas. The experimental results indicate that the proposed CMFD scheme can achieve better detection performance under various attacks compared with other state-of-the-art CMFD schemes.
Binocular Tone Mapping with Improved Overall Contrast and Local Details
Sep 17, 2018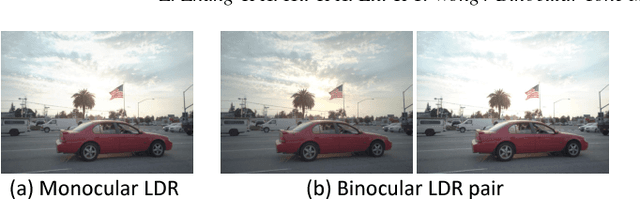
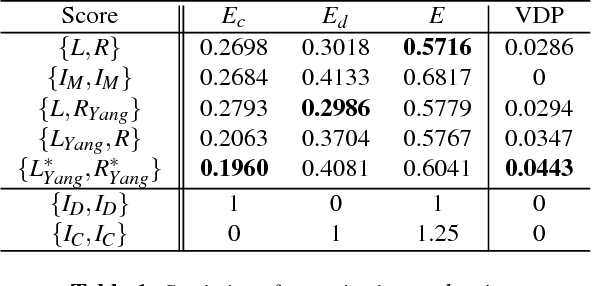
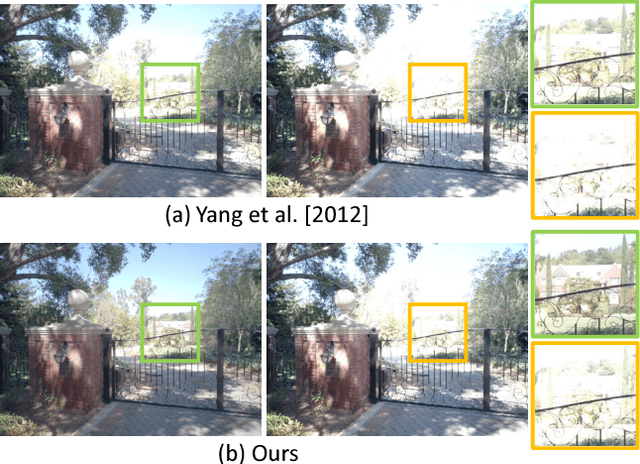
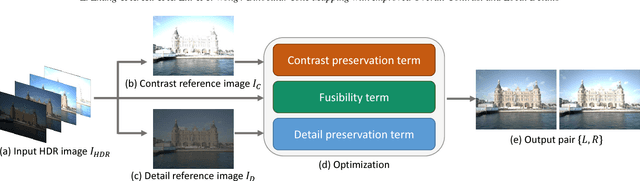
Abstract:Tone mapping is a commonly used technique that maps the set of colors in high-dynamic-range (HDR) images to another set of colors in low-dynamic-range (LDR) images, to fit the need for print-outs, LCD monitors and projectors. Unfortunately, during the compression of dynamic range, the overall contrast and local details generally cannot be preserved simultaneously. Recently, with the increased use of stereoscopic devices, the notion of binocular tone mapping has been proposed in the existing research study. However, the existing research lacks the binocular perception study and is unable to generate the optimal binocular pair that presents the most visual content. In this paper, we propose a novel perception-based binocular tone mapping method, that can generate an optimal binocular image pair (generating left and right images simultaneously) from an HDR image that presents the most visual content by designing a binocular perception metric. Our method outperforms the existing method in terms of both visual and time performance.
* Accepted by Pacific Graphics 2018
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge