Woochang Sim
GIFARC: Synthetic Dataset for Leveraging Human-Intuitive Analogies to Elevate AI Reasoning
May 27, 2025Abstract:The Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC) poses a stringent test of general AI capabilities, requiring solvers to infer abstract patterns from only a handful of examples. Despite substantial progress in deep learning, state-of-the-art models still achieve accuracy rates of merely 40-55% on 2024 ARC Competition, indicative of a significant gap between their performance and human-level reasoning. In this work, we seek to bridge that gap by introducing an analogy-inspired ARC dataset, GIFARC. Leveraging large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs), we synthesize new ARC-style tasks from a variety of GIF images that include analogies. Each new task is paired with ground-truth analogy, providing an explicit mapping between visual transformations and everyday concepts. By embedding robust human-intuitive analogies into ARC-style tasks, GIFARC guides AI agents to evaluate the task analogically before engaging in brute-force pattern search, thus efficiently reducing problem complexity and build a more concise and human-understandable solution. We empirically validate that guiding LLM with analogic approach with GIFARC affects task-solving approaches of LLMs to align with analogic approach of human.
Enhancing Analogical Reasoning in the Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus via Model-Based RL
Aug 27, 2024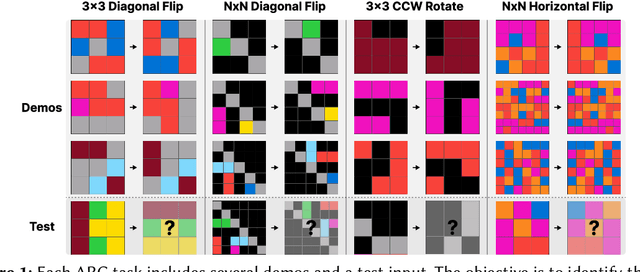
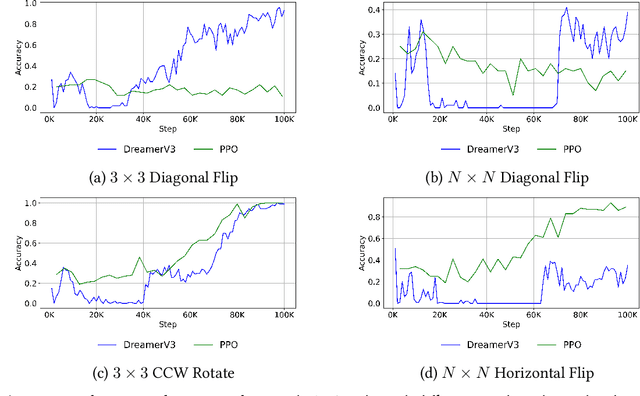

Abstract:This paper demonstrates that model-based reinforcement learning (model-based RL) is a suitable approach for the task of analogical reasoning. We hypothesize that model-based RL can solve analogical reasoning tasks more efficiently through the creation of internal models. To test this, we compared DreamerV3, a model-based RL method, with Proximal Policy Optimization, a model-free RL method, on the Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC) tasks. Our results indicate that model-based RL not only outperforms model-free RL in learning and generalizing from single tasks but also shows significant advantages in reasoning across similar tasks.
Reasoning Abilities of Large Language Models: In-Depth Analysis on the Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:The existing methods for evaluating the inference abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) have been results-centric, making it difficult to assess the inference process. We introduce a new approach using the Abstract and Reasoning Corpus (ARC) dataset to evaluate the inference and contextual understanding abilities of large language models in a process-centric manner. ARC demands rigorous logical structures for problem-solving, making it a benchmark that facilitates the comparison of model inference abilities with humans. Experimental results confirm that while large language models possess weak inference abilities, they still lag in terms of logical coherence, compositionality, and productivity. Our experiments highlight the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, proposing development paths for achieving human-level reasoning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge