Wolf De Wulf
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
Knowledge Graph Embeddings in the Biomedical Domain: Are They Useful? A Look at Link Prediction, Rule Learning, and Downstream Polypharmacy Tasks
May 31, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge graphs are powerful tools for representing and organising complex biomedical data. Several knowledge graph embedding algorithms have been proposed to learn from and complete knowledge graphs. However, a recent study demonstrates the limited efficacy of these embedding algorithms when applied to biomedical knowledge graphs, raising the question of whether knowledge graph embeddings have limitations in biomedical settings. This study aims to apply state-of-the-art knowledge graph embedding models in the context of a recent biomedical knowledge graph, BioKG, and evaluate their performance and potential downstream uses. We achieve a three-fold improvement in terms of performance based on the HITS@10 score over previous work on the same biomedical knowledge graph. Additionally, we provide interpretable predictions through a rule-based method. We demonstrate that knowledge graph embedding models are applicable in practice by evaluating the best-performing model on four tasks that represent real-life polypharmacy situations. Results suggest that knowledge learnt from large biomedical knowledge graphs can be transferred to such downstream use cases. Our code is available at https://github.com/aryopg/biokge.
LP2PB: Translating Answer Set Programs into Pseudo-Boolean Theories
Sep 22, 2020

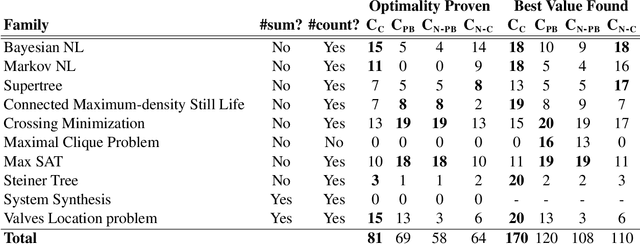
Abstract:Answer set programming (ASP) is a well-established knowledge representation formalism. Most ASP solvers are based on (extensions of) technology from Boolean satisfiability solving. While these solvers have shown to be very successful in many practical applications, their strength is limited by their underlying proof system, resolution. In this paper, we present a new tool LP2PB that translates ASP programs into pseudo-Boolean theories, for which solvers based on the (stronger) cutting plane proof system exist. We evaluate our tool, and the potential of cutting-plane-based solving for ASP on traditional ASP benchmarks as well as benchmarks from pseudo-Boolean solving. Our results are mixed: overall, traditional ASP solvers still outperform our translational approach, but several benchmark families are identified where the balance shifts the other way, thereby suggesting that further investigation into a stronger proof system for ASP is valuable.
* In Proceedings ICLP 2020, arXiv:2009.09158
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge