Wim Van Paesschen
SeizeIT2: Wearable Dataset Of Patients With Focal Epilepsy
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:The increasing technological advancements towards miniaturized physiological measuring devices have enabled continuous monitoring of epileptic patients outside of specialized environments. The large amounts of data that can be recorded with such devices holds significant potential for developing automated seizure detection frameworks. In this work, we present SeizeIT2, the first open dataset of wearable data recorded in patients with focal epilepsy. The dataset comprises more than 11,000 hours of multimodal data, including behind-the-ear electroencephalography, electrocardiography, electromyography and movement (accelerometer and gyroscope) data. The dataset contains 886 focal seizures recorded from 125 patients across five different European Epileptic Monitoring Centers. We present a suggestive training/validation split to propel the development of AI methodologies for seizure detection, as well as two benchmark approaches and evaluation metrics. The dataset can be accessed on OpenNeuro and is stored in Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) format.
Multimodal wearable EEG, EMG and accelerometry measurements improve the accuracy of tonic-clonic seizure detection in-hospital
Mar 19, 2024



Abstract:Objective: Most current wearable tonic-clonic seizure (TCS) detection systems are based on extra-cerebral signals, such as electromyography (EMG) or accelerometry (ACC). Although many of these devices show good sensitivity in seizure detection, their false positive rates (FPR) are still relatively high. Wearable EEG may improve performance; however, studies investigating this remain scarce. This paper aims 1) to investigate the possibility of detecting TCSs with a behind-the-ear, two-channel wearable EEG, and 2) to evaluate the added value of wearable EEG to other non-EEG modalities in multimodal TCS detection. Method: We included 27 participants with a total of 44 TCSs from the European multicenter study SeizeIT2. The multimodal wearable detection system Sensor Dot (Byteflies) was used to measure two-channel, behind-the-ear EEG, EMG, electrocardiography (ECG), ACC and gyroscope (GYR). First, we evaluated automatic unimodal detection of TCSs, using performance metrics such as sensitivity, precision, FPR and F1-score. Secondly, we fused the different modalities and again assessed performance. Algorithm-labeled segments were then provided to a neurologist and a wearable data expert, who reviewed and annotated the true positive TCSs, and discarded false positives (FPs). Results: Wearable EEG outperformed the other modalities in unimodal TCS detection by achieving a sensitivity of 100.0% and a FPR of 10.3/24h (compared to 97.7% sensitivity and 30.9/24h FPR for EMG; 95.5% sensitivity and 13.9 FPR for ACC). The combination of wearable EEG and EMG achieved overall the most clinically useful performance in offline TCS detection with a sensitivity of 97.7%, a FPR of 0.4/24 h, a precision of 43.0%, and a F1-score of 59.7%. Subsequent visual review of the automated detections resulted in maximal sensitivity and zero FPs.
Augmenting interictal mapping with neurovascular coupling biomarkers by structured factorization of epileptic EEG and fMRI data
Apr 29, 2020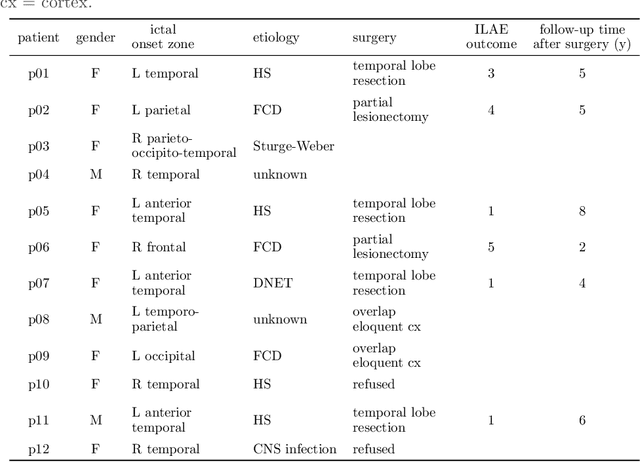



Abstract:EEG-correlated fMRI analysis is widely used to detect regional blood oxygen level dependent fluctuations that are significantly synchronized to interictal epileptic discharges, which can provide evidence for localizing the ictal onset zone. However, such an asymmetrical, mass-univariate approach cannot capture the inherent, higher order structure in the EEG data, nor multivariate relations in the fMRI data, and it is nontrivial to accurately handle varying neurovascular coupling over patients and brain regions. We aim to overcome these drawbacks in a data-driven manner by means of a novel structured matrix-tensor factorization: the single-subject EEG data (represented as a third-order spectrogram tensor) and fMRI data (represented as a spatiotemporal BOLD signal matrix) are jointly decomposed into a superposition of several sources, characterized by space-time-frequency profiles. In the shared temporal mode, Toeplitz-structured factors account for a spatially specific, neurovascular `bridge' between the EEG and fMRI temporal fluctuations, capturing the hemodynamic response's variability over brain regions. We show that the extracted source signatures provide a sensitive localization of the ictal onset zone, and, moreover, that complementary localizing information can be derived from the spatial variation of the hemodynamic response. Hence, this multivariate, multimodal factorization provides two useful sets of EEG-fMRI biomarkers, which can inform the presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. We make all code required to perform the computations available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge