William R. Mark
Low-Shot Validation: Active Importance Sampling for Estimating Classifier Performance on Rare Categories
Sep 13, 2021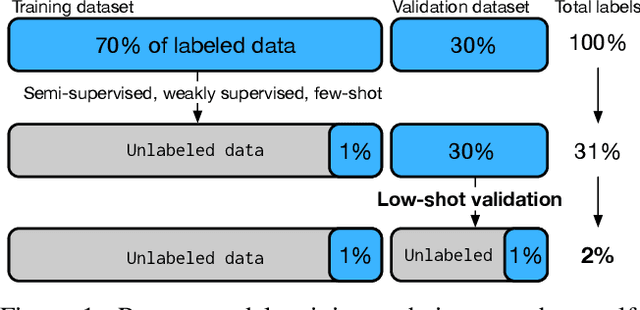
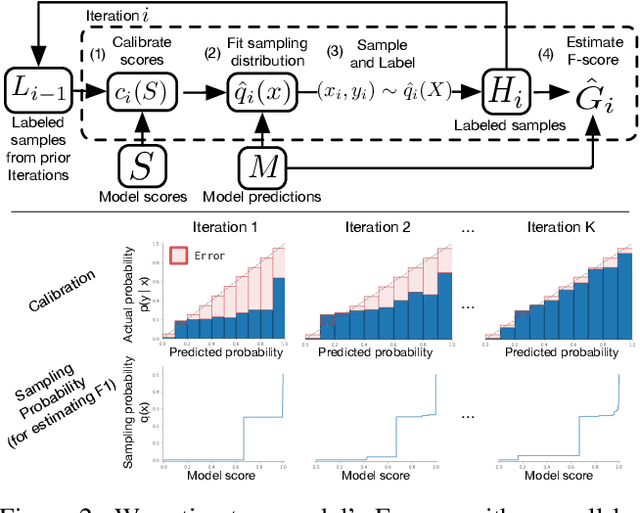
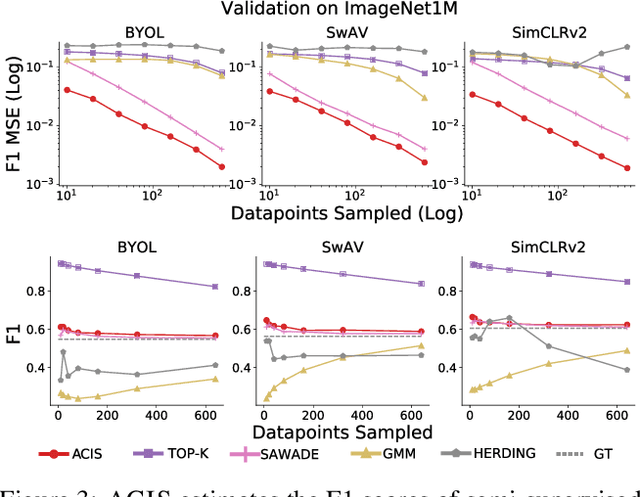
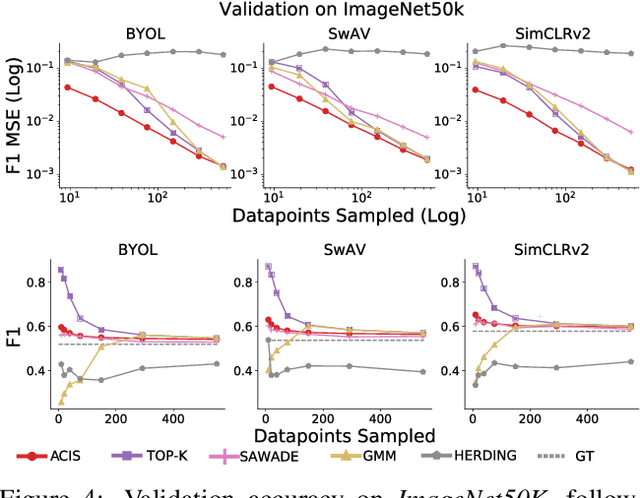
Abstract:For machine learning models trained with limited labeled training data, validation stands to become the main bottleneck to reducing overall annotation costs. We propose a statistical validation algorithm that accurately estimates the F-score of binary classifiers for rare categories, where finding relevant examples to evaluate on is particularly challenging. Our key insight is that simultaneous calibration and importance sampling enables accurate estimates even in the low-sample regime (< 300 samples). Critically, we also derive an accurate single-trial estimator of the variance of our method and demonstrate that this estimator is empirically accurate at low sample counts, enabling a practitioner to know how well they can trust a given low-sample estimate. When validating state-of-the-art semi-supervised models on ImageNet and iNaturalist2017, our method achieves the same estimates of model performance with up to 10x fewer labels than competing approaches. In particular, we can estimate model F1 scores with a variance of 0.005 using as few as 100 labels.
Background Splitting: Finding Rare Classes in a Sea of Background
Aug 28, 2020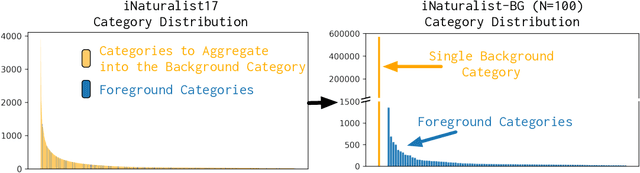
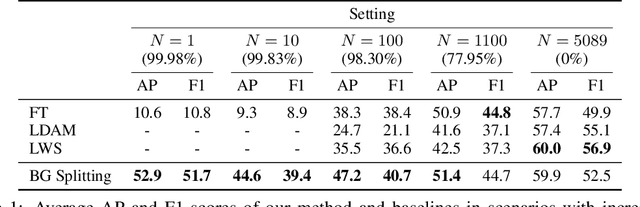
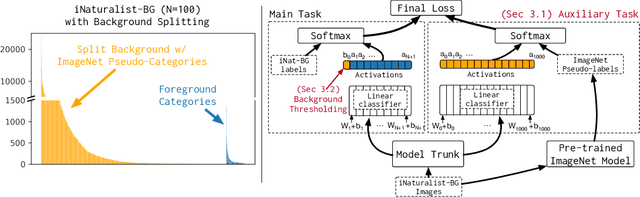

Abstract:We focus on the real-world problem of training accurate deep models for image classification of a small number of rare categories. In these scenarios, almost all images belong to the background category in the dataset (>95% of the dataset is background). We demonstrate that both standard fine-tuning approaches and state-of-the-art approaches for training on imbalanced datasets do not produce accurate deep models in the presence of this extreme imbalance. Our key observation is that the extreme imbalance due to the background category can be drastically reduced by leveraging visual knowledge from an existing pre-trained model. Specifically, the background category is "split" into smaller and more coherent pseudo-categories during training using a pre-trained model. We incorporate background splitting into an image classification model by adding an auxiliary loss that learns to mimic the predictions of the existing, pre-trained image classification model. Note that this process is automatic and requires no additional manual labels. The auxiliary loss regularizes the feature representation of the shared network trunk by requiring it to discriminate between previously homogeneous background instances and reduces overfitting to the small number of rare category positives. We also show that BG splitting can be combined with other background imbalance methods to further improve performance. We evaluate our method on a modified version of the iNaturalist dataset where only a small subset of rare category labels are available during training (all other images are labeled as background). By jointly learning to recognize ImageNet categories and selected iNaturalist categories, our approach yields performance that is 42.3 mAP points higher than a fine-tuning baseline when 99.98% of the data is background, and 8.3 mAP points higher than SotA baselines when 98.30% of the data is background.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge