Wenwei Zhao
A Survey of Semen Quality Evaluation in Microscopic Videos Using Computer Assisted Sperm Analysis
Feb 17, 2022
Abstract:The Computer Assisted Sperm Analysis (CASA) plays a crucial role in male reproductive health diagnosis and Infertility treatment. With the development of the computer industry in recent years, a great of accurate algorithms are proposed. With the assistance of those novel algorithms, it is possible for CASA to achieve a faster and higher quality result. Since image processing is the technical basis of CASA, including pre-processing,feature extraction, target detection and tracking, these methods are important technical steps in dealing with CASA. The various works related to Computer Assisted Sperm Analysis methods in the last 30 years (since 1988) are comprehensively introduced and analysed in this survey. To facilitate understanding, the methods involved are analysed in the sequence of general steps in sperm analysis. In other words, the methods related to sperm detection (localization) are first analysed, and then the methods of sperm tracking are analysed. Beside this, we analyse and prospect the present situation and future of CASA. According to our work, the feasible for applying in sperm microscopic video of methods mentioned in this review is explained. Moreover, existing challenges of object detection and tracking in microscope video are potential to be solved inspired by this survey.
PCB Component Detection using Computer Vision for Hardware Assurance
Feb 17, 2022
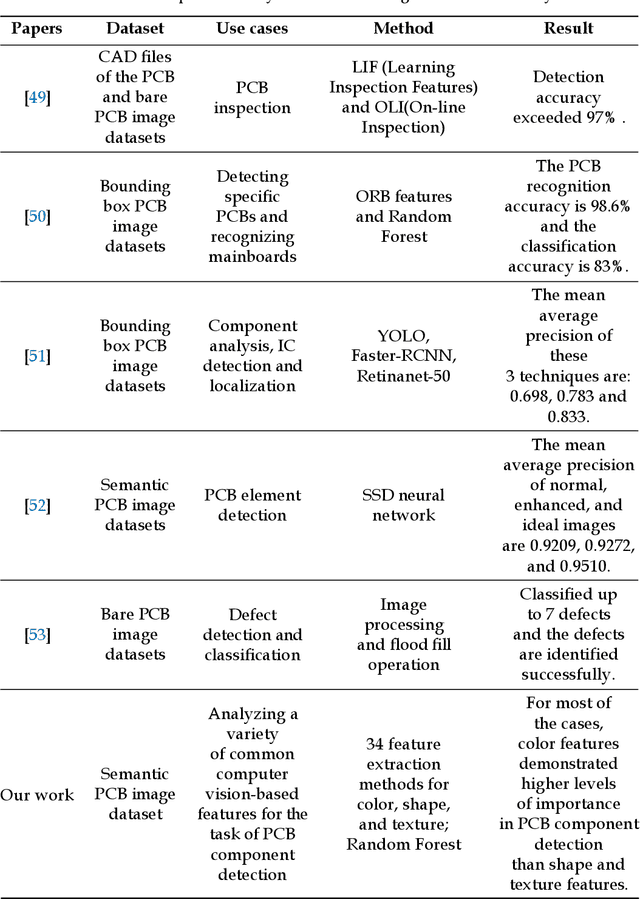
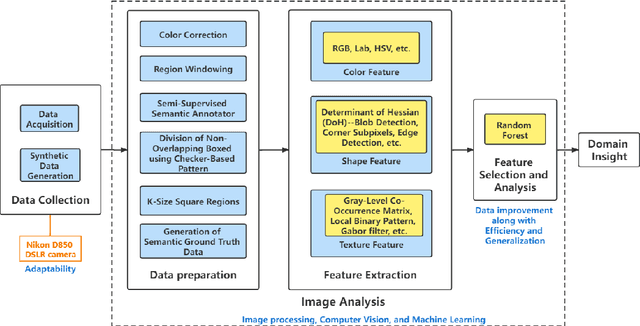
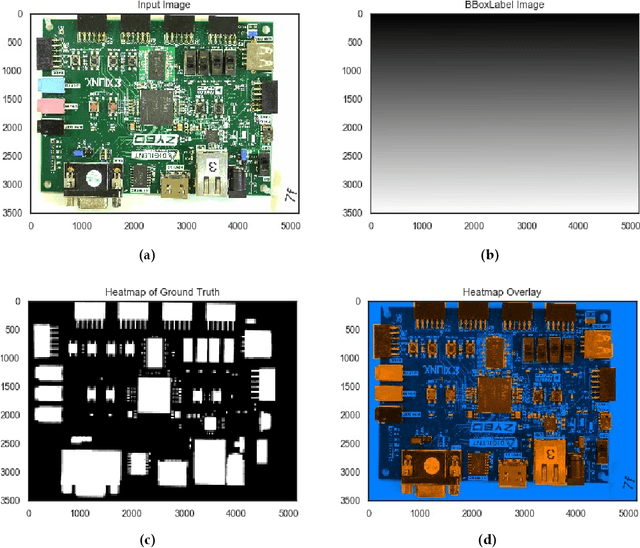
Abstract:Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assurance in the optical domain is a crucial field of study. Though there are many existing PCB assurance methods using image processing, computer vision (CV), and machine learning (ML), the PCB field is complex and increasingly evolving so new techniques are required to overcome the emerging problems. Existing ML-based methods outperform traditional CV methods, however they often require more data, have low explainability, and can be difficult to adapt when a new technology arises. To overcome these challenges, CV methods can be used in tandem with ML methods. In particular, human-interpretable CV algorithms such as those that extract color, shape, and texture features increase PCB assurance explainability. This allows for incorporation of prior knowledge, which effectively reduce the number of trainable ML parameters and thus, the amount of data needed to achieve high accuracy when training or retraining an ML model. Hence, this study explores the benefits and limitations of a variety of common computer vision-based features for the task of PCB component detection using semantic data. Results of this study indicate that color features demonstrate promising performance for PCB component detection. The purpose of this paper is to facilitate collaboration between the hardware assurance, computer vision, and machine learning communities.
Foldover Features for Dynamic Object Behavior Description in Microscopic Videos
Mar 21, 2020
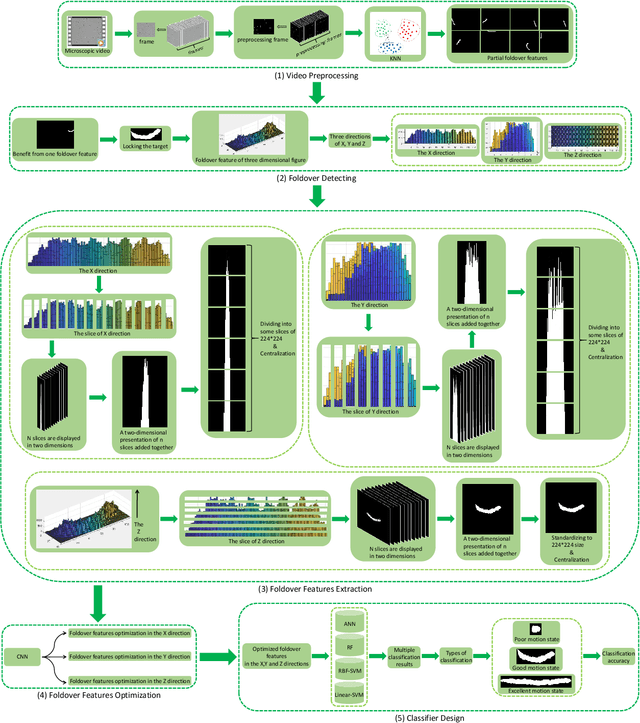
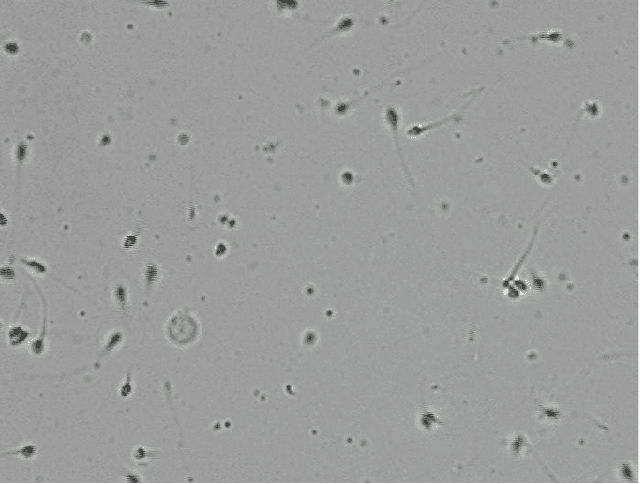

Abstract:Behavior description is conducive to the analysis of tiny objects, similar objects, objects with weak visual information and objects with similar visual information, playing a fundamental role in the identification and classification of dynamic objects in microscopic videos. To this end, we propose foldover features to describe the behavior of dynamic objects. First, we generate foldover for each object in microscopic videos in X, Y and Z directions, respectively. Then, we extract foldover features from the X, Y and Z directions with statistical methods, respectively. Finally, we use four different classifiers to test the effectiveness of the proposed foldover features. In the experiment, we use a sperm microscopic video dataset to evaluate the proposed foldover features, including three types of 1374 sperms, and obtain the highest classification accuracy of 96.5%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge