Shayan Taheri
EVHA: Explainable Vision System for Hardware Testing and Assurance -- An Overview
Jul 20, 2022



Abstract:Due to the ever-growing demands for electronic chips in different sectors the semiconductor companies have been mandated to offshore their manufacturing processes. This unwanted matter has made security and trustworthiness of their fabricated chips concerning and caused creation of hardware attacks. In this condition, different entities in the semiconductor supply chain can act maliciously and execute an attack on the design computing layers, from devices to systems. Our attack is a hardware Trojan that is inserted during mask generation/fabrication in an untrusted foundry. The Trojan leaves a footprint in the fabricated through addition, deletion, or change of design cells. In order to tackle this problem, we propose Explainable Vision System for Hardware Testing and Assurance (EVHA) in this work that can detect the smallest possible change to a design in a low-cost, accurate, and fast manner. The inputs to this system are Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images acquired from the Integrated Circuits (ICs) under examination. The system output is determination of IC status in terms of having any defect and/or hardware Trojan through addition, deletion, or change in the design cells at the cell-level. This article provides an overview on the design, development, implementation, and analysis of our defense system.
PCB Component Detection using Computer Vision for Hardware Assurance
Feb 17, 2022
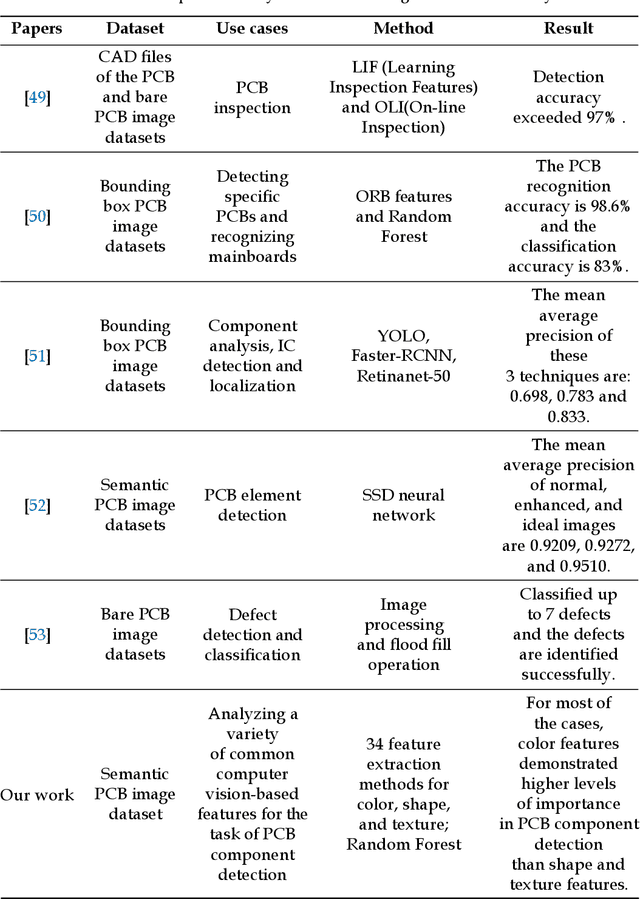
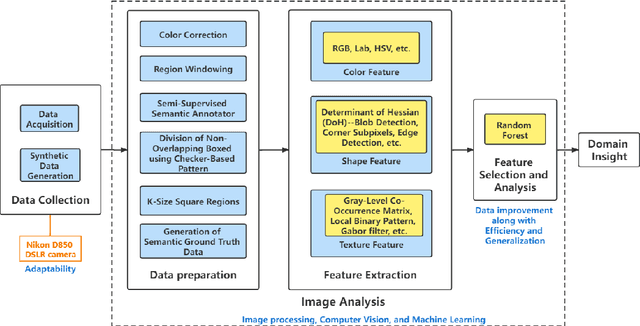
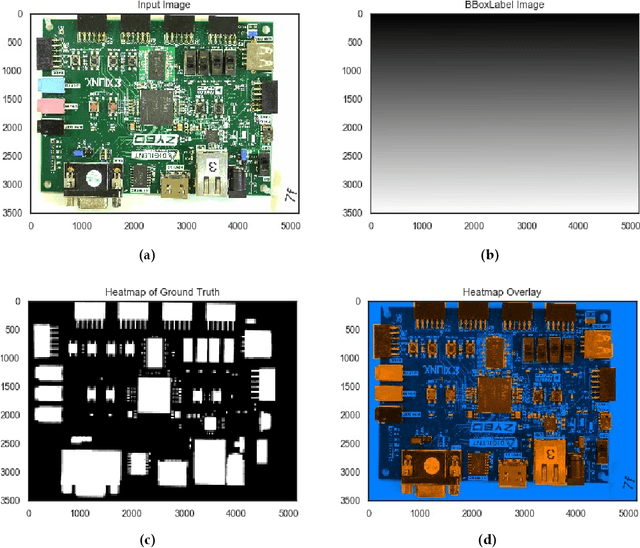
Abstract:Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assurance in the optical domain is a crucial field of study. Though there are many existing PCB assurance methods using image processing, computer vision (CV), and machine learning (ML), the PCB field is complex and increasingly evolving so new techniques are required to overcome the emerging problems. Existing ML-based methods outperform traditional CV methods, however they often require more data, have low explainability, and can be difficult to adapt when a new technology arises. To overcome these challenges, CV methods can be used in tandem with ML methods. In particular, human-interpretable CV algorithms such as those that extract color, shape, and texture features increase PCB assurance explainability. This allows for incorporation of prior knowledge, which effectively reduce the number of trainable ML parameters and thus, the amount of data needed to achieve high accuracy when training or retraining an ML model. Hence, this study explores the benefits and limitations of a variety of common computer vision-based features for the task of PCB component detection using semantic data. Results of this study indicate that color features demonstrate promising performance for PCB component detection. The purpose of this paper is to facilitate collaboration between the hardware assurance, computer vision, and machine learning communities.
Anomaly Generation using Generative Adversarial Networks in Host Based Intrusion Detection
Dec 11, 2018



Abstract:Generative adversarial networks have been able to generate striking results in various domains. This generation capability can be general while the networks gain deep understanding regarding the data distribution. In many domains, this data distribution consists of anomalies and normal data, with the anomalies commonly occurring relatively less, creating datasets that are imbalanced. The capabilities that generative adversarial networks offer can be leveraged to examine these anomalies and help alleviate the challenge that imbalanced datasets propose via creating synthetic anomalies. This anomaly generation can be specifically beneficial in domains that have costly data creation processes as well as inherently imbalanced datasets. One of the domains that fits this description is the host-based intrusion detection domain. In this work, ADFA-LD dataset is chosen as the dataset of interest containing system calls of small foot-print next generation attacks. The data is first converted into images, and then a Cycle-GAN is used to create images of anomalous data from images of normal data. The generated data is combined with the original dataset and is used to train a model to detect anomalies. By doing so, it is shown that the classification results are improved, with the AUC rising from 0.55 to 0.71, and the anomaly detection rate rising from 17.07% to 80.49%. The results are also compared to SMOTE, showing the potential presented by generative adversarial networks in anomaly generation.
ECG Arrhythmia Classification Using Transfer Learning from 2-Dimensional Deep CNN Features
Dec 11, 2018


Abstract:Due to the recent advances in the area of deep learning, it has been demonstrated that a deep neural network, trained on a huge amount of data, can recognize cardiac arrhythmias better than cardiologists. Moreover, traditionally feature extraction was considered an integral part of ECG pattern recognition; however, recent findings have shown that deep neural networks can carry out the task of feature extraction directly from the data itself. In order to use deep neural networks for their accuracy and feature extraction, high volume of training data is required, which in the case of independent studies is not pragmatic. To arise to this challenge, in this work, the identification and classification of four ECG patterns are studied from a transfer learning perspective, transferring knowledge learned from the image classification domain to the ECG signal classification domain. It is demonstrated that feature maps learned in a deep neural network trained on great amounts of generic input images can be used as general descriptors for the ECG signal spectrograms and result in features that enable classification of arrhythmias. Overall, an accuracy of 97.23 percent is achieved in classifying near 7000 instances by ten-fold cross validation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge