Wentan Liu
A high-accuracy multi-model mixing retrosynthetic method
Sep 06, 2024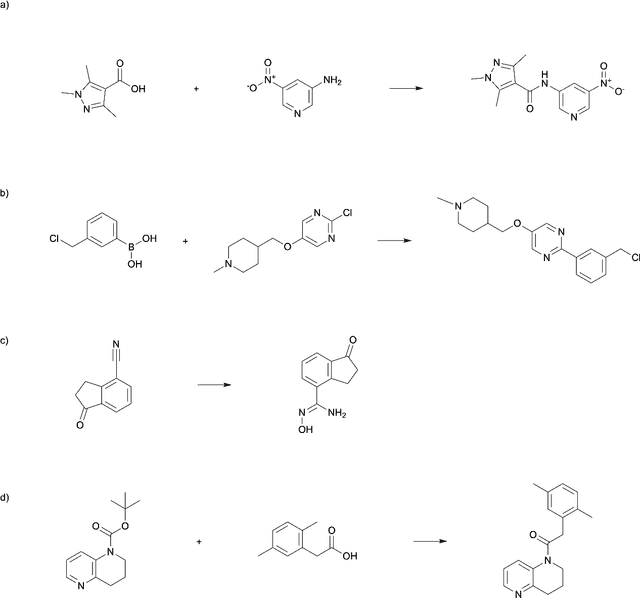
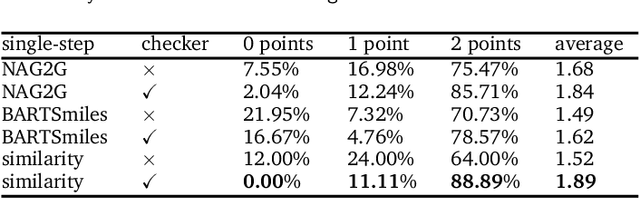
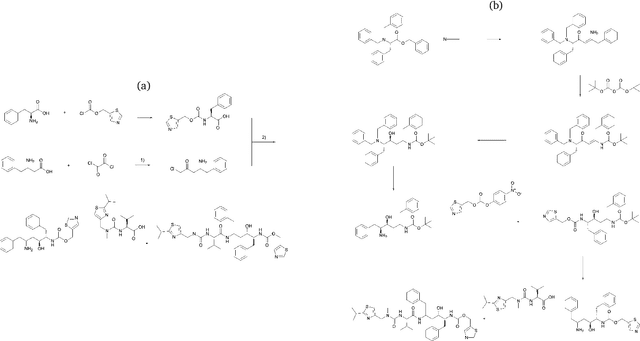
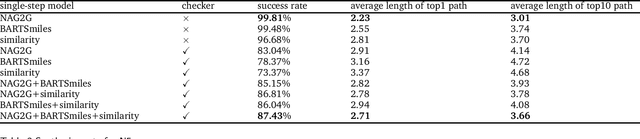
Abstract:The field of computer-aided synthesis planning (CASP) has seen rapid advancements in recent years, achieving significant progress across various algorithmic benchmarks. However, chemists often encounter numerous infeasible reactions when using CASP in practice. This article delves into common errors associated with CASP and introduces a product prediction model aimed at enhancing the accuracy of single-step models. While the product prediction model reduces the number of single-step reactions, it integrates multiple single-step models to maintain the overall reaction count and increase reaction diversity. Based on manual analysis and large-scale testing, the product prediction model, combined with the multi-model ensemble approach, has been proven to offer higher feasibility and greater diversity.
Node-Aligned Graph-to-Graph Generation for Retrosynthesis Prediction
Sep 27, 2023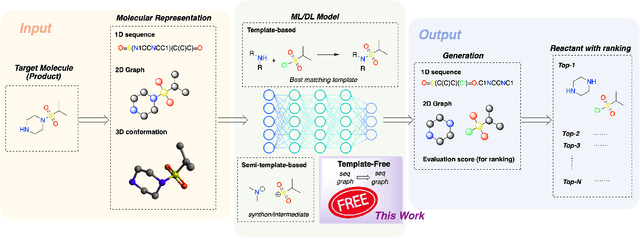

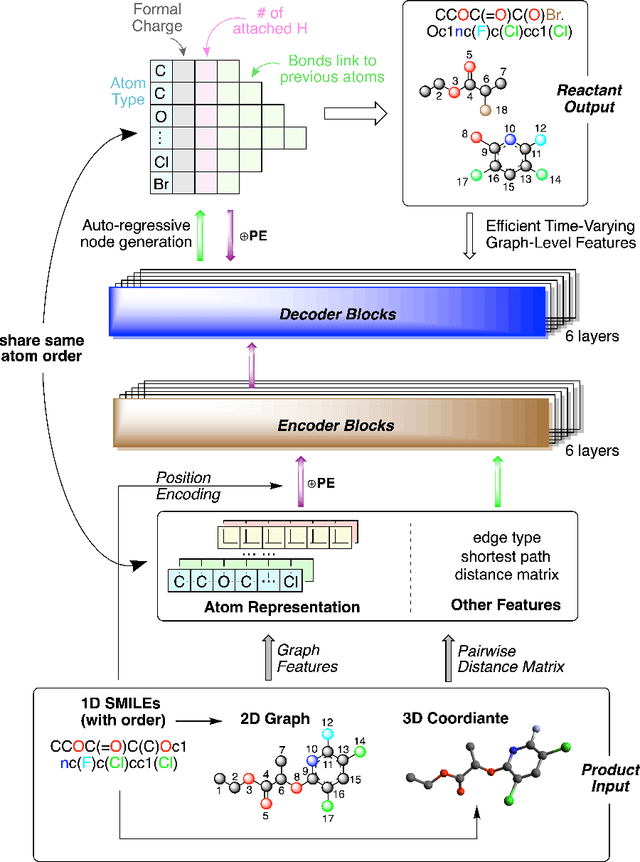

Abstract:Single-step retrosynthesis is a crucial task in organic chemistry and drug design, requiring the identification of required reactants to synthesize a specific compound. with the advent of computer-aided synthesis planning, there is growing interest in using machine-learning techniques to facilitate the process. Existing template-free machine learning-based models typically utilize transformer structures and represent molecules as ID sequences. However, these methods often face challenges in fully leveraging the extensive topological information of the molecule and aligning atoms between the production and reactants, leading to results that are not as competitive as those of semi-template models. Our proposed method, Node-Aligned Graph-to-Graph (NAG2G), also serves as a transformer-based template-free model but utilizes 2D molecular graphs and 3D conformation information. Furthermore, our approach simplifies the incorporation of production-reactant atom mapping alignment by leveraging node alignment to determine a specific order for node generation and generating molecular graphs in an auto-regressive manner node-by-node. This method ensures that the node generation order coincides with the node order in the input graph, overcoming the difficulty of determining a specific node generation order in an auto-regressive manner. Our extensive benchmarking results demonstrate that the proposed NAG2G can outperform the previous state-of-the-art baselines in various metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge