Wendi Ding
Tilt-Ropter: A Novel Hybrid Aerial and Terrestrial Vehicle with Tilt Rotors and Passive Wheels
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:In this work, we present Tilt-Ropter, a novel hybrid aerial-terrestrial vehicle (HATV) that combines tilt rotors with passive wheels to achieve energy-efficient multi-mode locomotion. Unlike existing under-actuated HATVs, the fully actuated design of Tilt-Ropter enables decoupled force and torque control, greatly enhancing its mobility and environmental adaptability. A nonlinear model predictive controller (NMPC) is developed to track reference trajectories and handle contact constraints across locomotion modes, while a dedicated control allocation module exploits actuation redundancy to achieve energy-efficient control of actuators. Additionally, to enhance robustness during ground contact, we introduce an external wrench estimation algorithm that estimates environmental interaction forces and torques in real time. The system is validated through both simulation and real-world experiments, including seamless air-ground transitions and trajectory tracking. Results show low tracking errors in both modes and highlight a 92.8% reduction in power consumption during ground locomotion, demonstrating the system's potential for long-duration missions across large-scale and energy-constrained environments.
UDE-based Dynamic Motion Force Control of Mobile Manipulators
Mar 30, 2024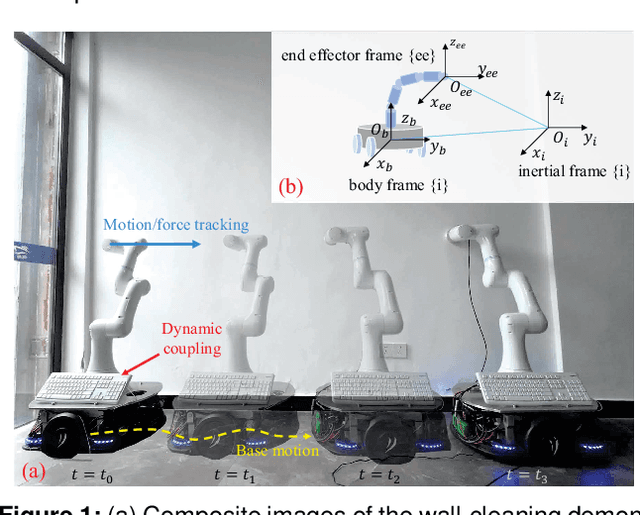
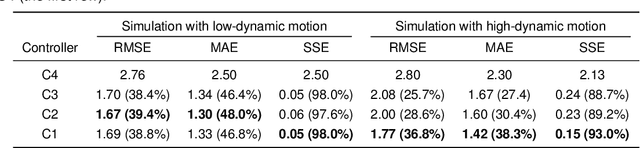
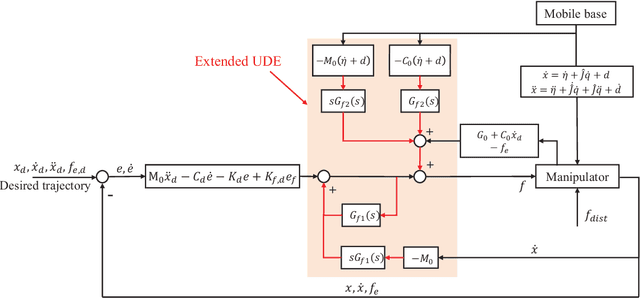
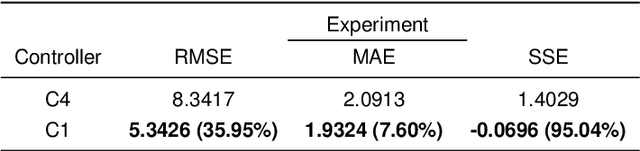
Abstract:Mobile manipulators are known for their superior mobility over manipulators on fixed bases, offering promising applications in smart industry and housekeeping scenarios. However, the dynamic coupling nature between the mobile base and the manipulator presents challenges for the physical interactive tasks of the mobile manipulator. Current methods suffer from complex modeling processes and poor transferability. To address this, this article presents a novel dynamic model of the manipulator on the mobile base that requires only the manipulator dynamics and the kinematic information of the mobile base. In addition, embedding the dynamic model, an uncertainty and disturbance estimator-based (UDE-based) dynamic motion/force control scheme is proposed for the mobile manipulator, which compensates for the dynamic coupling and other unmodeled uncertainties. Passivity and stability analyses justify the proposed control law. Simulation and experimental results on our mobile manipulator platform demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of our proposed methodology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge