Wen Shao
Classification-Reconstruction Learning for Open-Set Recognition
Dec 17, 2018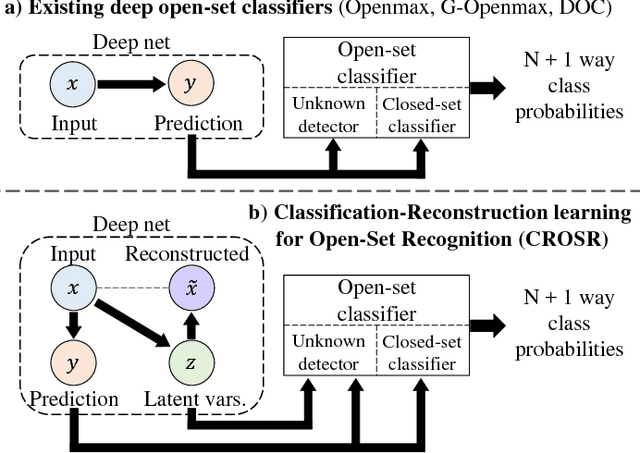
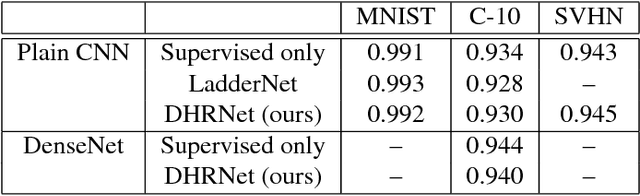
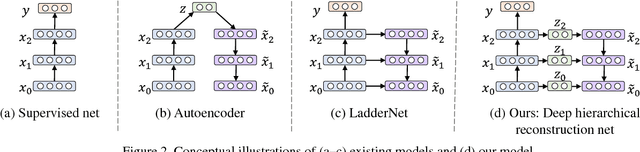
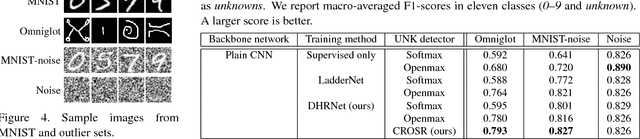
Abstract:Open-set classification is a problem of handling `unknown' classes that are not contained in the training dataset, whereas traditional classifiers assume that only known classes appear in the test environment. Existing open-set classifiers rely on deep networks trained in a supervised manner on known classes in the training set; this causes specialization of learned representations to known classes and makes it hard to distinguish unknowns from knowns. In contrast, we train networks for joint classification and reconstruction of input data. This enhances the learned representation so as to preserve information useful for separating unknowns from knowns, as well as to discriminate classes of knowns. Our novel Classification-Reconstruction learning for Open-Set Recognition (CROSR) utilizes latent representations for reconstruction and enables robust unknown detection without harming the known-class classification accuracy. Extensive experiments reveal that the proposed method outperforms existing deep open-set classifiers in multiple standard datasets and is robust to diverse outliers.
Adaptive Context Tree Weighting
Jan 10, 2012

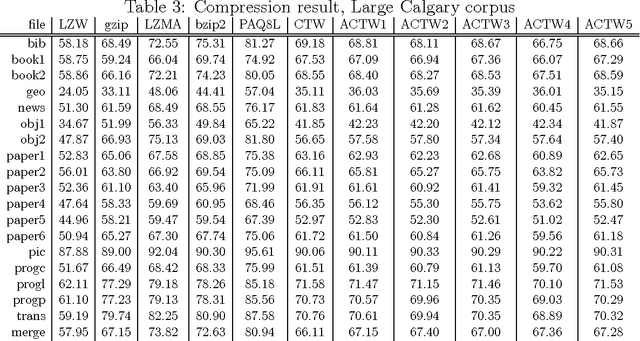
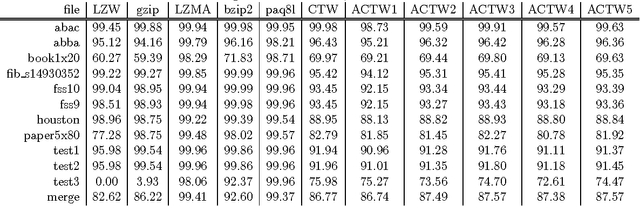
Abstract:We describe an adaptive context tree weighting (ACTW) algorithm, as an extension to the standard context tree weighting (CTW) algorithm. Unlike the standard CTW algorithm, which weights all observations equally regardless of the depth, ACTW gives increasing weight to more recent observations, aiming to improve performance in cases where the input sequence is from a non-stationary distribution. Data compression results show ACTW variants improving over CTW on merged files from standard compression benchmark tests while never being significantly worse on any individual file.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge