Wee Ser
Remote Monitoring of Patient Respiration with Mask Attachment -- A Pragmatic Solution for Medical Facilities
Mar 16, 2021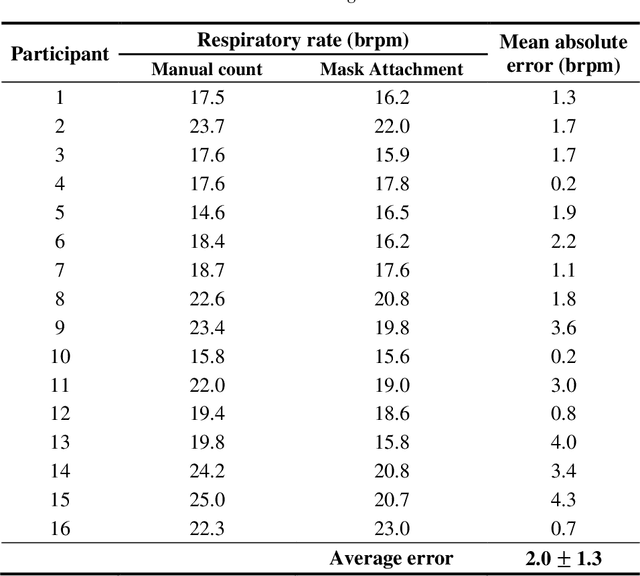
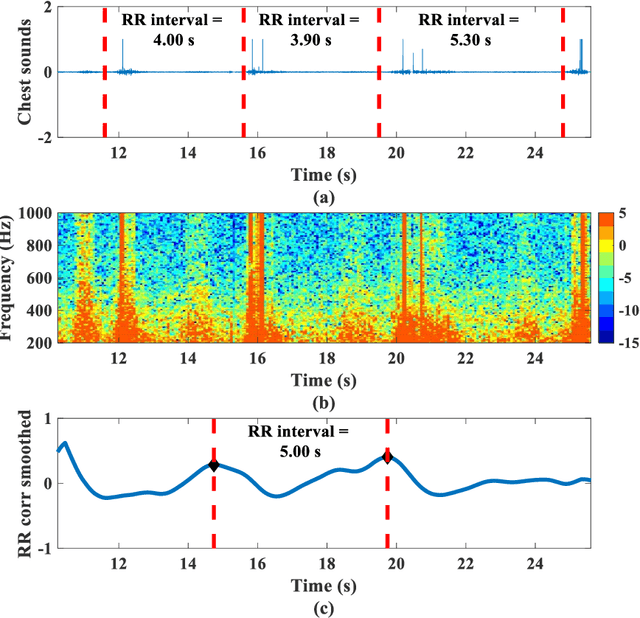
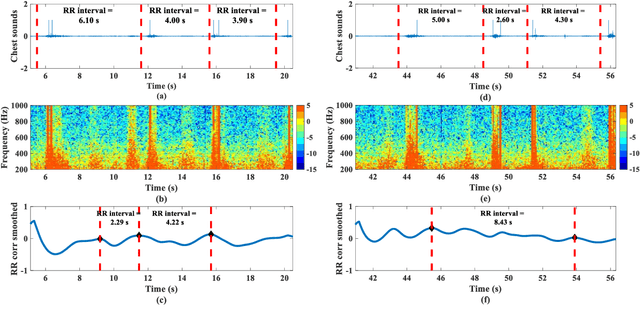

Abstract:Remote monitoring of vital signs in infectious patients minimizes the risks of viral transmissions to healthcare professionals. Evidence indicates that donning face masks reduces the risk of viral transmissions and is now the norm in medical facilities. We propose attaching an acoustic-sensing device onto face masks to assist medical facilities in monitoring patients' respiration remotely. Usability and functionality studies of the modified face mask were evaluated on 16 healthy participants, who were blindfolded throughout the data collection. Around half of the participants noticed the difference between the modified and unmodified masks but they also reported there was no discomfort in using the modified mask. Respiratory rates of the participants were evaluated for one minute and the mean error of respiratory rate was found to be 2.0 +/- 1.3 breath per minute. As all participants were healthy, the wheeze detection algorithm was assessed by playing 176 wheezes and 176 normal breaths through a foam mannequin. The recordings were played at three different times to account for varying environmental noise. The overall accuracy of the wheeze detection algorithm was 91.9%. The current findings support and suggest the use of the mask attachment in medical facilities.
Constrained Maximum Correntropy Adaptive Filtering
Dec 14, 2016



Abstract:Constrained adaptive filtering algorithms inculding constrained least mean square (CLMS), constrained affine projection (CAP) and constrained recursive least squares (CRLS) have been extensively studied in many applications. Most existing constrained adaptive filtering algorithms are developed under mean square error (MSE) criterion, which is an ideal optimality criterion under Gaussian noises. This assumption however fails to model the behavior of non-Gaussian noises found in practice. Motivated by the robustness and simplicity of maximum correntropy criterion (MCC) in non-Gaussian impulsive noises, this paper proposes a new adaptive filtering algorithm called constrained maximum correntropy criterion (CMCC). Specifically, CMCC incorporates a linear constraint into a MCC filter to solve a constrained optimization problem explicitly. The proposed adaptive filtering algorithm is easy to implement and has low computational complexity, and in terms of convergence accuracy (say lower mean square deviation) and stability, can significantly outperform those MSE based constrained adaptive algorithms in presence of heavy-tailed impulsive noises. Additionally, the mean square convergence behaviors are studied under energy conservation relation, and a sufficient condition to ensure the mean square convergence and the steady-state mean square deviation (MSD) of the proposed algorithm are obtained. Simulation results confirm the theoretical predictions under both Gaussian and non- Gaussian noises, and demonstrate the excellent performance of the novel algorithm by comparing it with other conventional methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge