Remote Monitoring of Patient Respiration with Mask Attachment -- A Pragmatic Solution for Medical Facilities
Paper and Code
Mar 16, 2021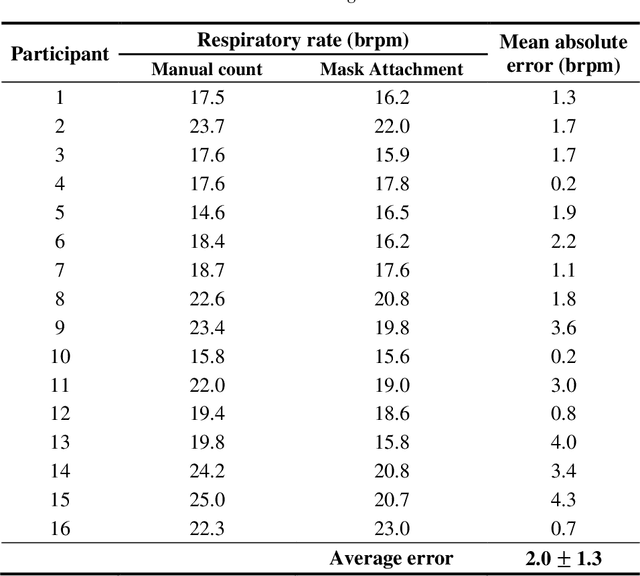
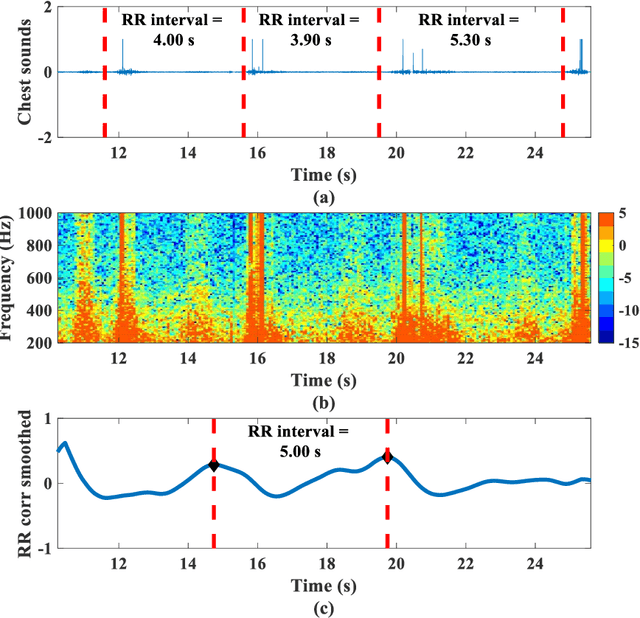
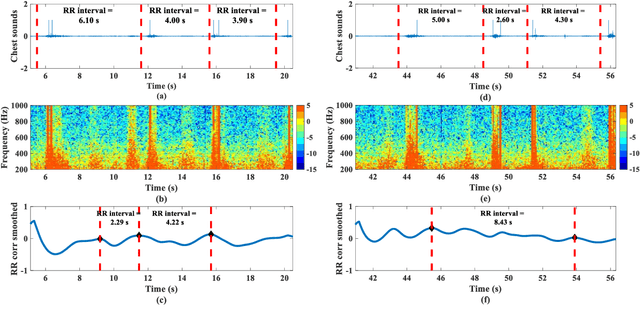

Remote monitoring of vital signs in infectious patients minimizes the risks of viral transmissions to healthcare professionals. Evidence indicates that donning face masks reduces the risk of viral transmissions and is now the norm in medical facilities. We propose attaching an acoustic-sensing device onto face masks to assist medical facilities in monitoring patients' respiration remotely. Usability and functionality studies of the modified face mask were evaluated on 16 healthy participants, who were blindfolded throughout the data collection. Around half of the participants noticed the difference between the modified and unmodified masks but they also reported there was no discomfort in using the modified mask. Respiratory rates of the participants were evaluated for one minute and the mean error of respiratory rate was found to be 2.0 +/- 1.3 breath per minute. As all participants were healthy, the wheeze detection algorithm was assessed by playing 176 wheezes and 176 normal breaths through a foam mannequin. The recordings were played at three different times to account for varying environmental noise. The overall accuracy of the wheeze detection algorithm was 91.9%. The current findings support and suggest the use of the mask attachment in medical facilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge