Vinith Kugathasan
Analyzing the Impact of Accent on English Speech: Acoustic and Articulatory Perspectives
May 21, 2025Abstract:Advancements in AI-driven speech-based applications have transformed diverse industries ranging from healthcare to customer service. However, the increasing prevalence of non-native accented speech in global interactions poses significant challenges for speech-processing systems, which are often trained on datasets dominated by native speech. This study investigates accented English speech through articulatory and acoustic analysis, identifying simpler coordination patterns and higher average pitch than native speech. Using eigenspectra and Vocal Tract Variable-based coordination features, we establish an efficient method for quantifying accent strength without relying on resource-intensive phonetic transcriptions. Our findings provide a new avenue for research on the impacts of accents on speech intelligibility and offer insights for developing inclusive, robust speech processing systems that accommodate diverse linguistic communities.
Multiclass Alignment of Confidence and Certainty for Network Calibration
Sep 06, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have made great strides in pushing the state-of-the-art in several challenging domains. Recent studies reveal that they are prone to making overconfident predictions. This greatly reduces the overall trust in model predictions, especially in safety-critical applications. Early work in improving model calibration employs post-processing techniques which rely on limited parameters and require a hold-out set. Some recent train-time calibration methods, which involve all model parameters, can outperform the postprocessing methods. To this end, we propose a new train-time calibration method, which features a simple, plug-and-play auxiliary loss known as multi-class alignment of predictive mean confidence and predictive certainty (MACC). It is based on the observation that a model miscalibration is directly related to its predictive certainty, so a higher gap between the mean confidence and certainty amounts to a poor calibration both for in-distribution and out-of-distribution predictions. Armed with this insight, our proposed loss explicitly encourages a confident (or underconfident) model to also provide a low (or high) spread in the presoftmax distribution. Extensive experiments on ten challenging datasets, covering in-domain, out-domain, non-visual recognition and medical image classification scenarios, show that our method achieves state-of-the-art calibration performance for both in-domain and out-domain predictions. Our code and models will be publicly released.
Towards Interpretable Sleep Stage Classification Using Cross-Modal Transformers
Aug 15, 2022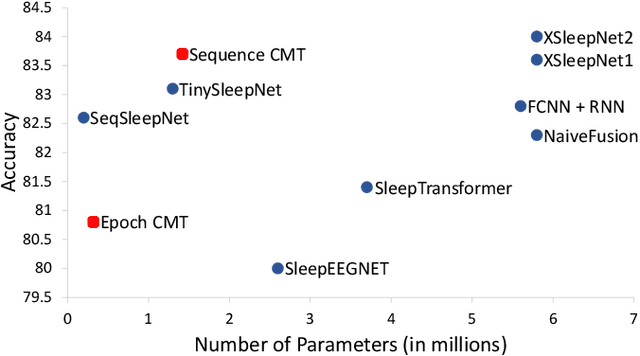
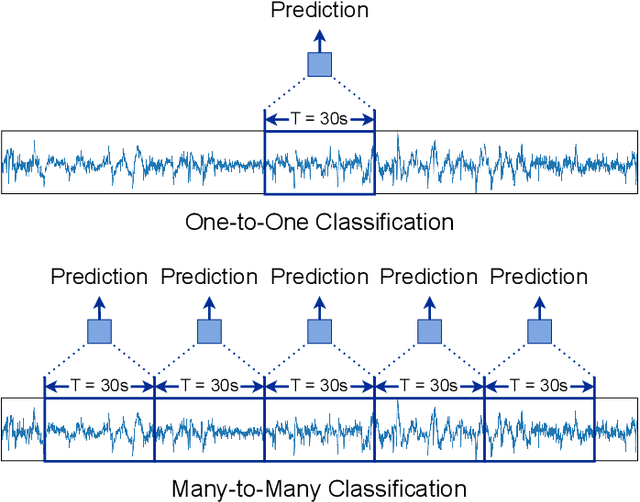
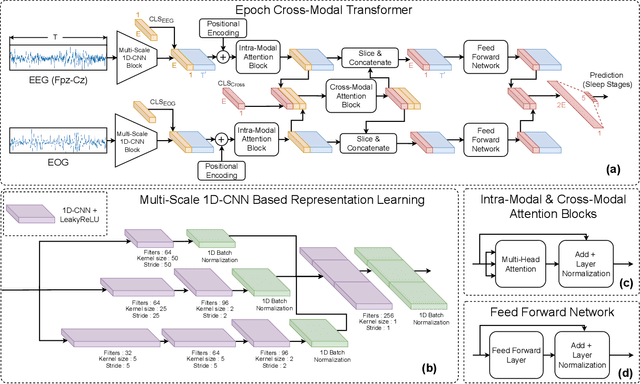
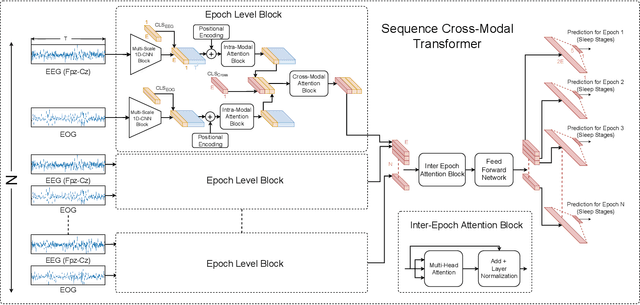
Abstract:Accurate sleep stage classification is significant for sleep health assessment. In recent years, several deep learning and machine learning based sleep staging algorithms have been developed and they have achieved performance on par with human annotation. Despite improved performance, a limitation of most deep-learning based algorithms is their Black-box behavior, which which have limited their use in clinical settings. Here, we propose Cross-Modal Transformers, which is a transformer-based method for sleep stage classification. Our models achieve both competitive performance with the state-of-the-art approaches and eliminates the Black-box behavior of deep-learning models by utilizing the interpretability aspect of the attention modules. The proposed cross-modal transformers consist of a novel cross-modal transformer encoder architecture along with a multi-scale 1-dimensional convolutional neural network for automatic representation learning. Our sleep stage classifier based on this design was able to achieve sleep stage classification performance on par with or better than the state-of-the-art approaches, along with interpretability, a fourfold reduction in the number of parameters and a reduced training time compared to the current state-of-the-art. Our code is available at https://github.com/Jathurshan0330/Cross-Modal-Transformer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge