Victor Ye Dong
Semi-Offline Reinforcement Learning for Optimized Text Generation
Jun 16, 2023



Abstract:In reinforcement learning (RL), there are two major settings for interacting with the environment: online and offline. Online methods explore the environment at significant time cost, and offline methods efficiently obtain reward signals by sacrificing exploration capability. We propose semi-offline RL, a novel paradigm that smoothly transits from offline to online settings, balances exploration capability and training cost, and provides a theoretical foundation for comparing different RL settings. Based on the semi-offline formulation, we present the RL setting that is optimal in terms of optimization cost, asymptotic error, and overfitting error bound. Extensive experiments show that our semi-offline approach is efficient and yields comparable or often better performance compared with state-of-the-art methods.
FAST: Improving Controllability for Text Generation with Feedback Aware Self-Training
Oct 06, 2022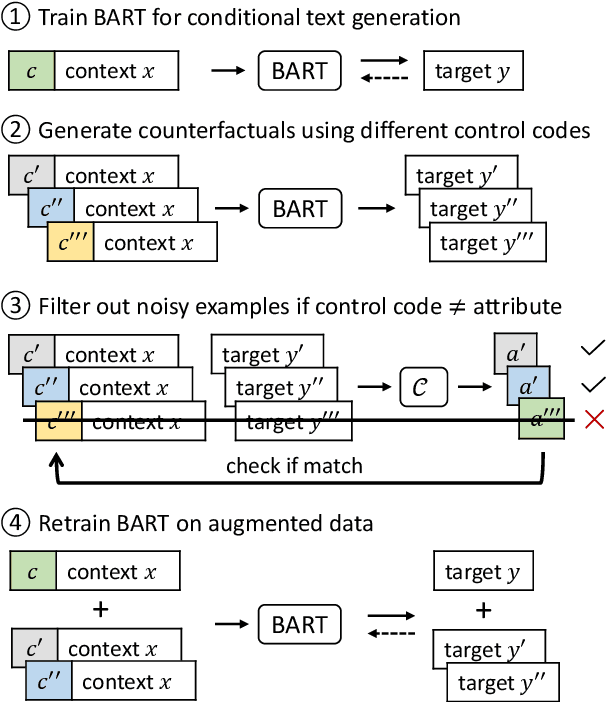
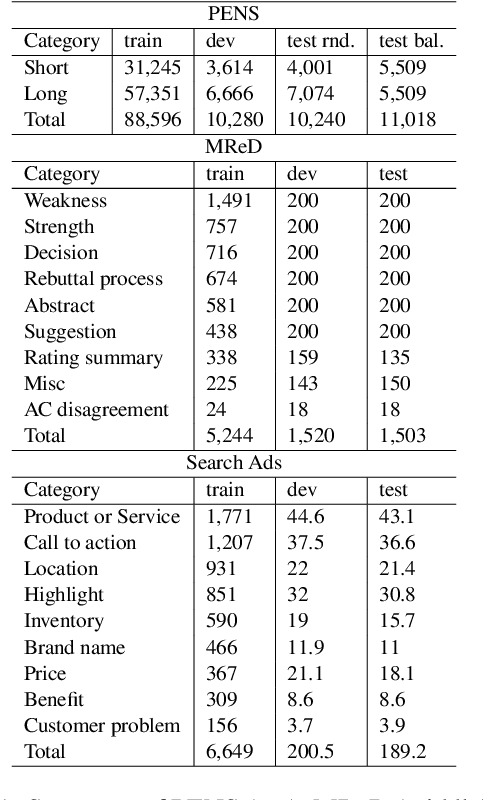
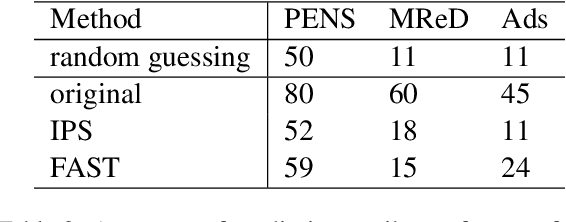

Abstract:Controllable text generation systems often leverage control codes to direct various properties of the output like style and length. Inspired by recent work on causal inference for NLP, this paper reveals a previously overlooked flaw in these control code-based conditional text generation algorithms. Spurious correlations in the training data can lead models to incorrectly rely on parts of the input other than the control code for attribute selection, significantly undermining downstream generation quality and controllability. We demonstrate the severity of this issue with a series of case studies and then propose two simple techniques to reduce these correlations in training sets. The first technique is based on resampling the data according to an example's propensity towards each linguistic attribute (IPS). The second produces multiple counterfactual versions of each example and then uses an additional feedback mechanism to remove noisy examples (feedback aware self-training, FAST). We evaluate on 3 tasks -- news headline, meta review, and search ads generation -- and demonstrate that FAST can significantly improve the controllability and language quality of generated outputs when compared to state-of-the-art controllable text generation approaches.
DeepGen: Diverse Search Ad Generation and Real-Time Customization
Aug 06, 2022


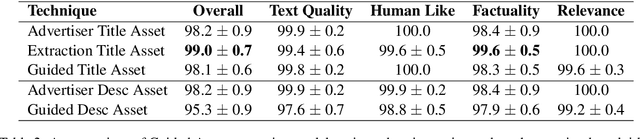
Abstract:We present DeepGen, a system deployed at web scale for automatically creating sponsored search advertisements (ads) for BingAds customers. We leverage state-of-the-art natural language generation (NLG) models to generate fluent ads from advertiser's web pages in an abstractive fashion and solve practical issues such as factuality and inference speed. In addition, our system creates a customized ad in real-time in response to the user's search query, therefore highlighting different aspects of the same product based on what the user is looking for. To achieve this, our system generates a diverse choice of smaller pieces of the ad ahead of time and, at query time, selects the most relevant ones to be stitched into a complete ad. We improve generation diversity by training a controllable NLG model to generate multiple ads for the same web page highlighting different selling points. Our system design further improves diversity horizontally by first running an ensemble of generation models trained with different objectives and then using a diversity sampling algorithm to pick a diverse subset of generation results for online selection. Experimental results show the effectiveness of our proposed system design. Our system is currently deployed in production, serving ${\sim}4\%$ of global ads served in Bing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge