Valdir Grassi Jr
Uniform Loss vs. Specialized Optimization: A Comparative Analysis in Multi-Task Learning
May 15, 2025Abstract:Specialized Multi-Task Optimizers (SMTOs) balance task learning in Multi-Task Learning by addressing issues like conflicting gradients and differing gradient norms, which hinder equal-weighted task training. However, recent critiques suggest that equally weighted tasks can achieve competitive results compared to SMTOs, arguing that previous SMTO results were influenced by poor hyperparameter optimization and lack of regularization. In this work, we evaluate these claims through an extensive empirical evaluation of SMTOs, including some of the latest methods, on more complex multi-task problems to clarify this behavior. Our findings indicate that SMTOs perform well compared to uniform loss and that fixed weights can achieve competitive performance compared to SMTOs. Furthermore, we demonstrate why uniform loss perform similarly to SMTOs in some instances. The code will be made publicly available.
Semantic SuperPoint: A Deep Semantic Descriptor
Nov 02, 2022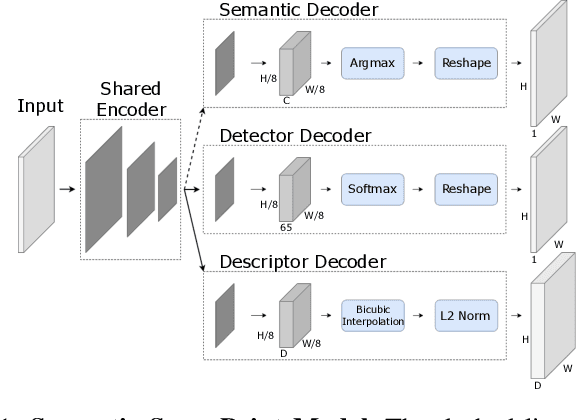
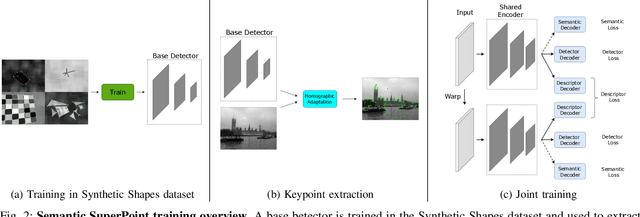
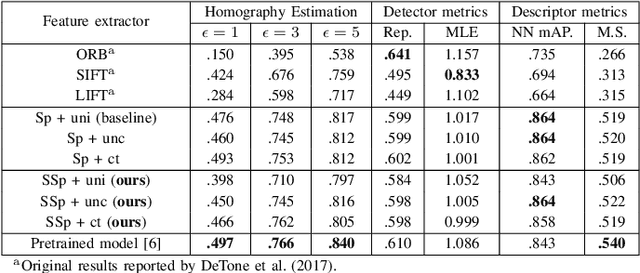
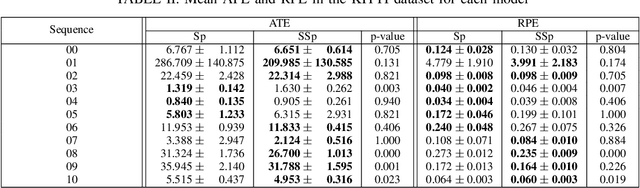
Abstract:Several SLAM methods benefit from the use of semantic information. Most integrate photometric methods with high-level semantics such as object detection and semantic segmentation. We propose that adding a semantic segmentation decoder in a shared encoder architecture would help the descriptor decoder learn semantic information, improving the feature extractor. This would be a more robust approach than only using high-level semantic information since it would be intrinsically learned in the descriptor and would not depend on the final quality of the semantic prediction. To add this information, we take advantage of multi-task learning methods to improve accuracy and balance the performance of each task. The proposed models are evaluated according to detection and matching metrics on the HPatches dataset. The results show that the Semantic SuperPoint model performs better than the baseline one.
Leveraging convergence behavior to balance conflicting tasks in multi-task learning
Apr 14, 2022
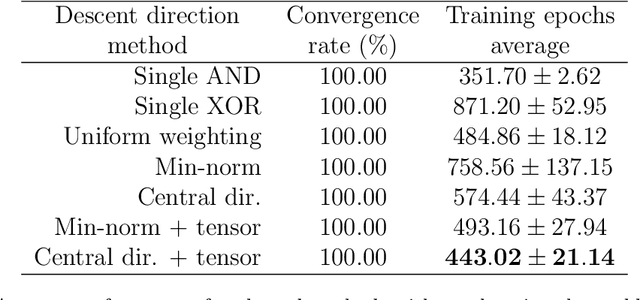
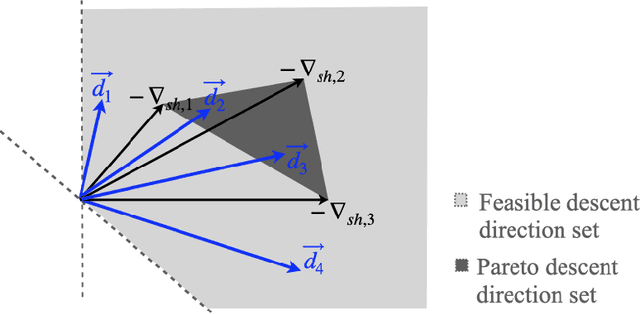

Abstract:Multi-Task Learning is a learning paradigm that uses correlated tasks to improve performance generalization. A common way to learn multiple tasks is through the hard parameter sharing approach, in which a single architecture is used to share the same subset of parameters, creating an inductive bias between them during the training process. Due to its simplicity, potential to improve generalization, and reduce computational cost, it has gained the attention of the scientific and industrial communities. However, tasks often conflict with each other, which makes it challenging to define how the gradients of multiple tasks should be combined to allow simultaneous learning. To address this problem, we use the idea of multi-objective optimization to propose a method that takes into account temporal behaviour of the gradients to create a dynamic bias that adjust the importance of each task during the backpropagation. The result of this method is to give more attention to the tasks that are diverging or that are not being benefited during the last iterations, allowing to ensure that the simultaneous learning is heading to the performance maximization of all tasks. As a result, we empirically show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-art approaches on learning conflicting tasks. Unlike the adopted baselines, our method ensures that all tasks reach good generalization performances.
On Deep Learning Techniques to Boost Monocular Depth Estimation for Autonomous Navigation
Oct 13, 2020



Abstract:Inferring the depth of images is a fundamental inverse problem within the field of Computer Vision since depth information is obtained through 2D images, which can be generated from infinite possibilities of observed real scenes. Benefiting from the progress of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to explore structural features and spatial image information, Single Image Depth Estimation (SIDE) is often highlighted in scopes of scientific and technological innovation, as this concept provides advantages related to its low implementation cost and robustness to environmental conditions. In the context of autonomous vehicles, state-of-the-art CNNs optimize the SIDE task by producing high-quality depth maps, which are essential during the autonomous navigation process in different locations. However, such networks are usually supervised by sparse and noisy depth data, from Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) laser scans, and are carried out at high computational cost, requiring high-performance Graphic Processing Units (GPUs). Therefore, we propose a new lightweight and fast supervised CNN architecture combined with novel feature extraction models which are designed for real-world autonomous navigation. We also introduce an efficient surface normals module, jointly with a simple geometric 2.5D loss function, to solve SIDE problems. We also innovate by incorporating multiple Deep Learning techniques, such as the use of densification algorithms and additional semantic, surface normals and depth information to train our framework. The method introduced in this work focuses on robotic applications in indoor and outdoor environments and its results are evaluated on the competitive and publicly available NYU Depth V2 and KITTI Depth datasets.
Sparse-to-Continuous: Enhancing Monocular Depth Estimation using Occupancy Maps
Sep 24, 2018



Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of single image depth estimation (SIDE), focusing on improving the accuracy of deep neural network predictions. In a supervised learning scenario, the quality of predictions is intrinsically related to the training labels, which guide the optimization process. For indoor scenes, structured-light-based depth sensors (e.g. Kinect) are able to provide dense, albeit short-range, depth maps. On the other hand, for outdoor scenes, LiDARs are still considered the standard sensor, which comparatively provide much sparser measurements, especially in areas further away. Rather than modifying the neural network structure to deal with sparse depth maps, this paper introduces a novel technique for the densification of depth maps based on the Hilbert Maps framework. A continuous occupancy map is produced based on 3D points from LiDAR scans, and the resulting reconstructed surface is projected into a 2D depth map with arbitrary resolution. Experiments conducted with various subsets of the KITTI dataset show the improvement produced by the proposed Sparse-to-Continuous technique, without the introduction of extra information into the training methodology.
Learning to Race through Coordinate Descent Bayesian Optimisation
Feb 17, 2018



Abstract:In the automation of many kinds of processes, the observable outcome can often be described as the combined effect of an entire sequence of actions, or controls, applied throughout its execution. In these cases, strategies to optimise control policies for individual stages of the process might not be applicable, and instead the whole policy might have to be optimised at once. On the other hand, the cost to evaluate the policy's performance might also be high, being desirable that a solution can be found with as few interactions as possible with the real system. We consider the problem of optimising control policies to allow a robot to complete a given race track within a minimum amount of time. We assume that the robot has no prior information about the track or its own dynamical model, just an initial valid driving example. Localisation is only applied to monitor the robot and to provide an indication of its position along the track's centre axis. We propose a method for finding a policy that minimises the time per lap while keeping the vehicle on the track using a Bayesian optimisation (BO) approach over a reproducing kernel Hilbert space. We apply an algorithm to search more efficiently over high-dimensional policy-parameter spaces with BO, by iterating over each dimension individually, in a sequential coordinate descent-like scheme. Experiments demonstrate the performance of the algorithm against other methods in a simulated car racing environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge