Vaclav Petricek
Evolutionary Contrastive Distillation for Language Model Alignment
Oct 10, 2024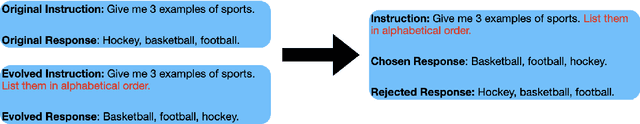
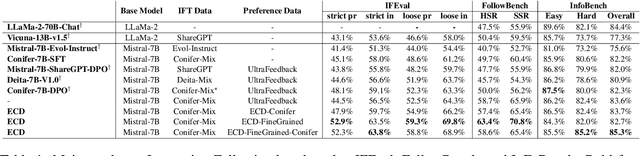
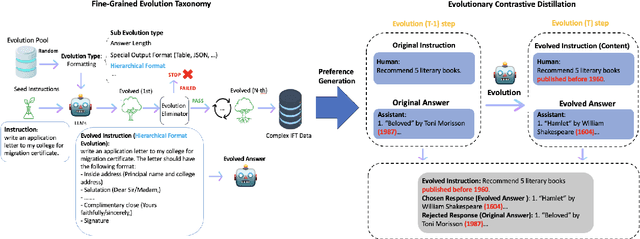
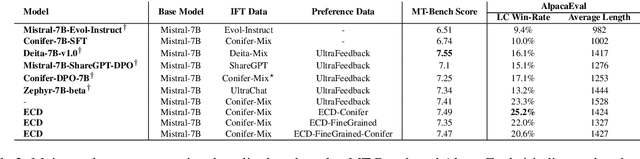
Abstract:The ability of large language models (LLMs) to execute complex instructions is essential for their real-world applications. However, several recent studies indicate that LLMs struggle with challenging instructions. In this paper, we propose Evolutionary Contrastive Distillation (ECD), a novel method for generating high-quality synthetic preference data designed to enhance the complex instruction-following capability of language models. ECD generates data that specifically illustrates the difference between a response that successfully follows a set of complex instructions and a response that is high-quality, but nevertheless makes some subtle mistakes. This is done by prompting LLMs to progressively evolve simple instructions to more complex instructions. When the complexity of an instruction is increased, the original successful response to the original instruction becomes a "hard negative" response for the new instruction, mostly meeting requirements of the new instruction, but barely missing one or two. By pairing a good response with such a hard negative response, and employing contrastive learning algorithms such as DPO, we improve language models' ability to follow complex instructions. Empirically, we observe that our method yields a 7B model that exceeds the complex instruction-following performance of current SOTA 7B models and is competitive even with open-source 70B models.
Efficient Online Bootstrapping for Large Scale Learning
Dec 18, 2013



Abstract:Bootstrapping is a useful technique for estimating the uncertainty of a predictor, for example, confidence intervals for prediction. It is typically used on small to moderate sized datasets, due to its high computation cost. This work describes a highly scalable online bootstrapping strategy, implemented inside Vowpal Wabbit, that is several times faster than traditional strategies. Our experiments indicate that, in addition to providing a black box-like method for estimating uncertainty, our implementation of online bootstrapping may also help to train models with better prediction performance due to model averaging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge