Uwe Kühnapfel
Predicting the power grid frequency of European islands
Sep 27, 2022
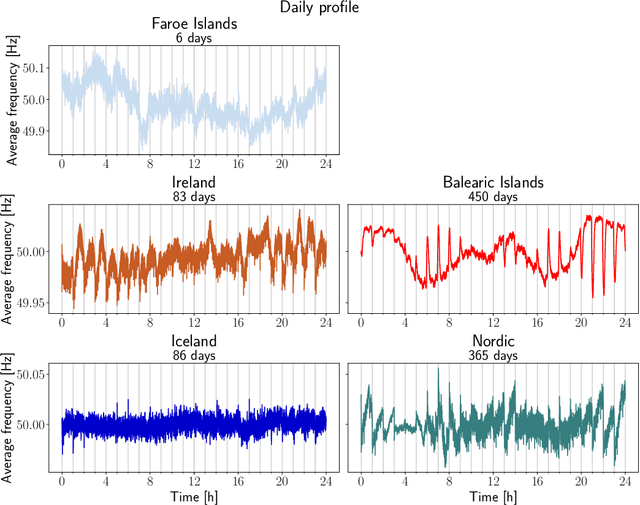

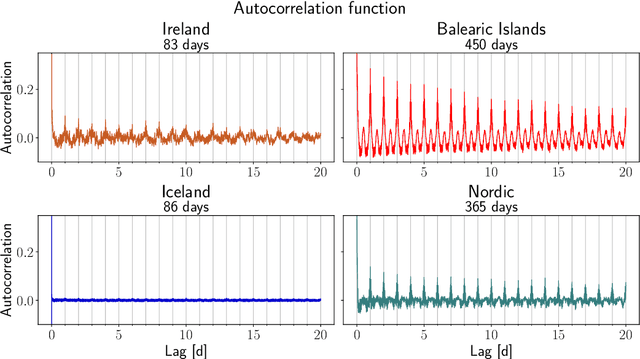
Abstract:Modelling, forecasting and overall understanding of the dynamics of the power grid and its frequency is essential for the safe operation of existing and future power grids. Much previous research was focused on large continental areas, while small systems, such as islands are less well-studied. These natural island systems are ideal testing environments for microgrid proposals and artificially islanded grid operation. In the present paper, we utilize measurements of the power grid frequency obtained in European islands: the Faroe Islands, Ireland, the Balearic Islands and Iceland and investigate how their frequency can be predicted, compared to the Nordic power system, acting as a reference. The Balearic islands are found to be particularly deterministic and easy to predict in contrast to hard-to-predict Iceland. Furthermore, we show that typically 2-4 weeks of data are needed to improve prediction performance beyond simple benchmarks.
Data-Driven Copy-Paste Imputation for Energy Time Series
Jan 05, 2021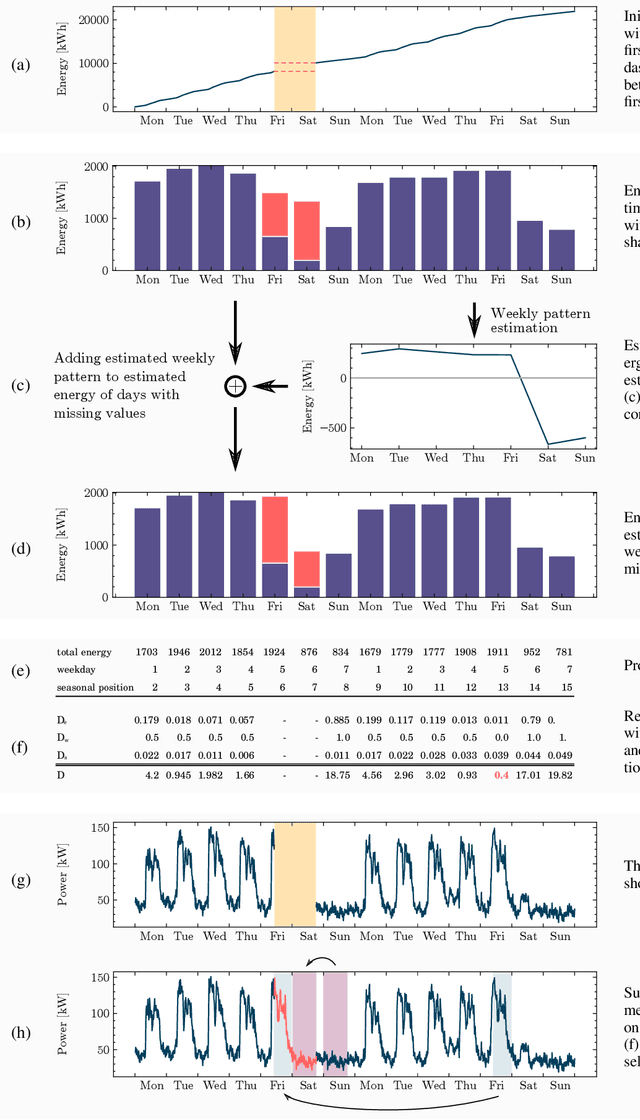
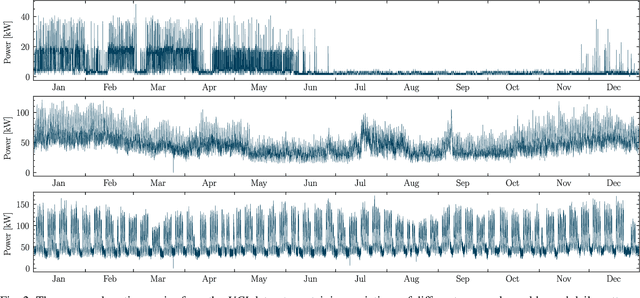
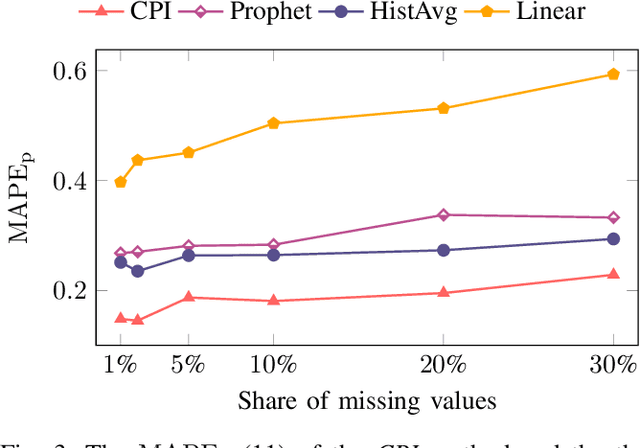
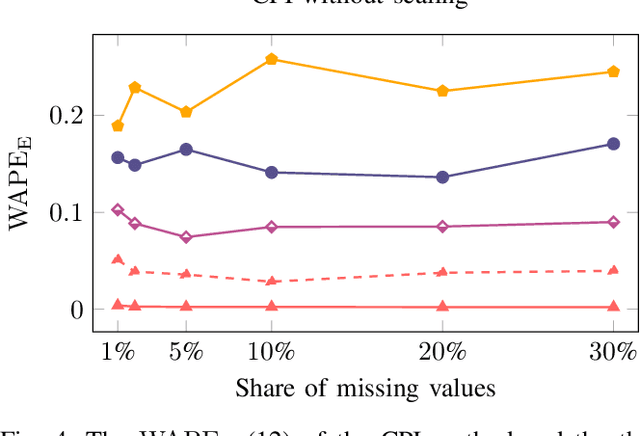
Abstract:A cornerstone of the worldwide transition to smart grids are smart meters. Smart meters typically collect and provide energy time series that are vital for various applications, such as grid simulations, fault-detection, load forecasting, load analysis, and load management. Unfortunately, these time series are often characterized by missing values that must be handled before the data can be used. A common approach to handle missing values in time series is imputation. However, existing imputation methods are designed for power time series and do not take into account the total energy of gaps, resulting in jumps or constant shifts when imputing energy time series. In order to overcome these issues, the present paper introduces the new Copy-Paste Imputation (CPI) method for energy time series. The CPI method copies data blocks with similar properties and pastes them into gaps of the time series while preserving the total energy of each gap. The new method is evaluated on a real-world dataset that contains six shares of artificially inserted missing values between 1 and 30%. It outperforms by far the three benchmark imputation methods selected for comparison. The comparison furthermore shows that the CPI method uses matching patterns and preserves the total energy of each gap while requiring only a moderate run-time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge