Tzu-Heng Lin
A Survey of Large Language Model Empowered Agents for Recommendation and Search: Towards Next-Generation Information Retrieval
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Information technology has profoundly altered the way humans interact with information. The vast amount of content created, shared, and disseminated online has made it increasingly difficult to access relevant information. Over the past two decades, search and recommendation systems (collectively referred to as information retrieval systems) have evolved significantly to address these challenges. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated capabilities that surpass human performance in various language-related tasks and exhibit general understanding, reasoning, and decision-making abilities. This paper explores the transformative potential of large language model agents in enhancing search and recommendation systems. We discuss the motivations and roles of LLM agents, and establish a classification framework to elaborate on the existing research. We highlight the immense potential of LLM agents in addressing current challenges in search and recommendation, providing insights into future research directions. This paper is the first to systematically review and classify the research on LLM agents in these domains, offering a novel perspective on leveraging this advanced AI technology for information retrieval. To help understand the existing works, we list the existing papers on agent-based simulation with large language models at this link: https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/LLM-Agent-for-Recommendation-and-Search.
Session-aware Item-combination Recommendation with Transformer Network
Nov 13, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we detailedly describe our solution for the IEEE BigData Cup 2021: RL-based RecSys (Track 1: Item Combination Prediction). We first conduct an exploratory data analysis on the dataset and then utilize the findings to design our framework. Specifically, we use a two-headed transformer-based network to predict user feedback and unlocked sessions, along with the proposed session-aware reweighted loss, multi-tasking with click behavior prediction, and randomness-in-session augmentation. In the final private leaderboard on Kaggle, our method ranked 2nd with a categorization accuracy of 0.39224.
Aggregation and Finetuning for Clothes Landmark Detection
May 01, 2020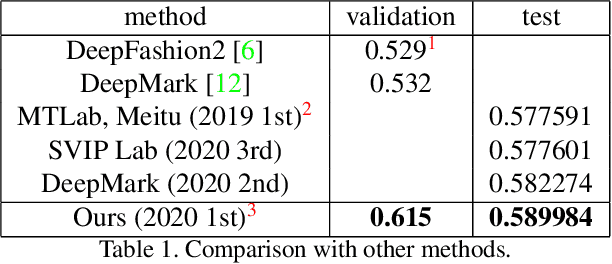
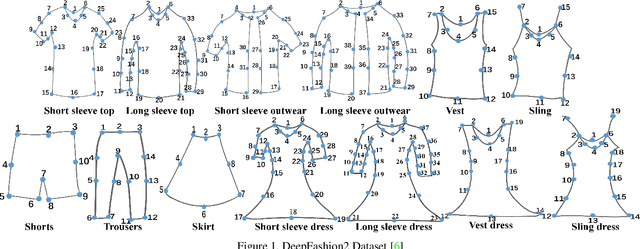
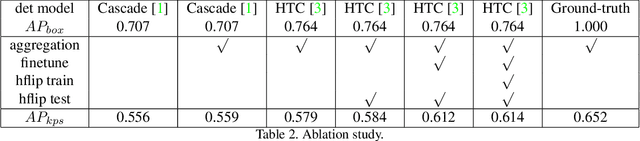
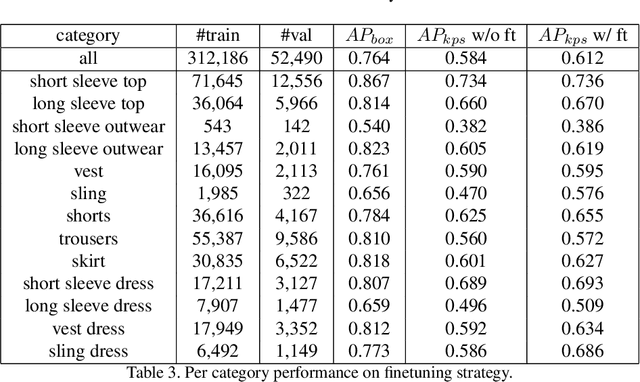
Abstract:Landmark detection for clothes is a fundamental problem for many applications. In this paper, a new training scheme for clothes landmark detection: $\textit{Aggregation and Finetuning}$, is proposed. We investigate the homogeneity among landmarks of different categories of clothes, and utilize it to design the procedure of training. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms current state-of-the-art methods by a large margin. Our method also won the 1st place in the DeepFashion2 Challenge 2020 - Clothes Landmark Estimation Track with an AP of 0.590 on the test set, and 0.615 on the validation set. Code will be publicly available at https://github.com/lzhbrian/deepfashion2-kps-agg-finetune .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge