Tushar Goswamy
DELFI: Deep Mixture Models for Long-term Air Quality Forecasting in the Delhi National Capital Region
Oct 28, 2022
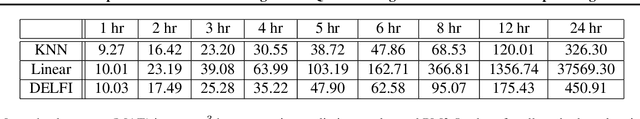
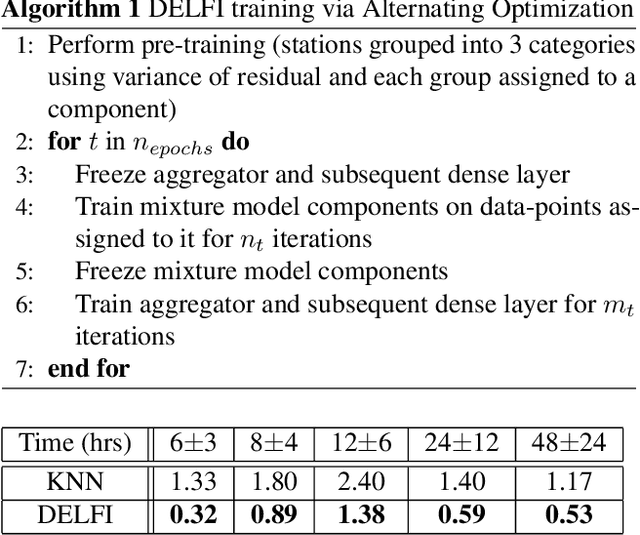

Abstract:The identification and control of human factors in climate change is a rapidly growing concern and robust, real-time air-quality monitoring and forecasting plays a critical role in allowing effective policy formulation and implementation. This paper presents DELFI, a novel deep learning-based mixture model to make effective long-term predictions of Particulate Matter (PM) 2.5 concentrations. A key novelty in DELFI is its multi-scale approach to the forecasting problem. The observation that point predictions are more suitable in the short-term and probabilistic predictions in the long-term allows accurate predictions to be made as much as 24 hours in advance. DELFI incorporates meteorological data as well as pollutant-based features to ensure a robust model that is divided into two parts: (i) a stack of three Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks that perform differential modelling of the same window of past data, and (ii) a fully-connected layer enabling attention to each of the components. Experimental evaluation based on deployment of 13 stations in the Delhi National Capital Region (Delhi-NCR) in India establishes that DELFI offers far superior predictions especially in the long-term as compared to even non-parametric baselines. The Delhi-NCR recorded the 3rd highest PM levels amongst 39 mega-cities across the world during 2011-2015 and DELFI's performance establishes it as a potential tool for effective long-term forecasting of PM levels to enable public health management and environment protection.
Adapting a Language Model for Controlled Affective Text Generation
Nov 08, 2020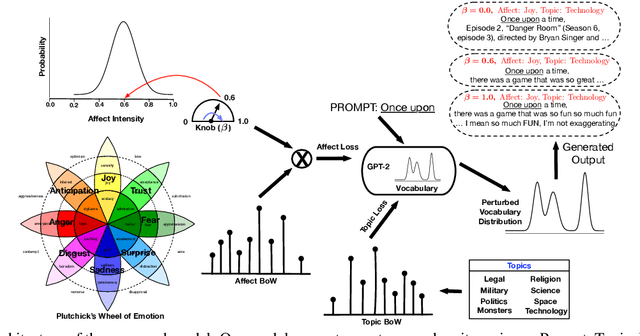
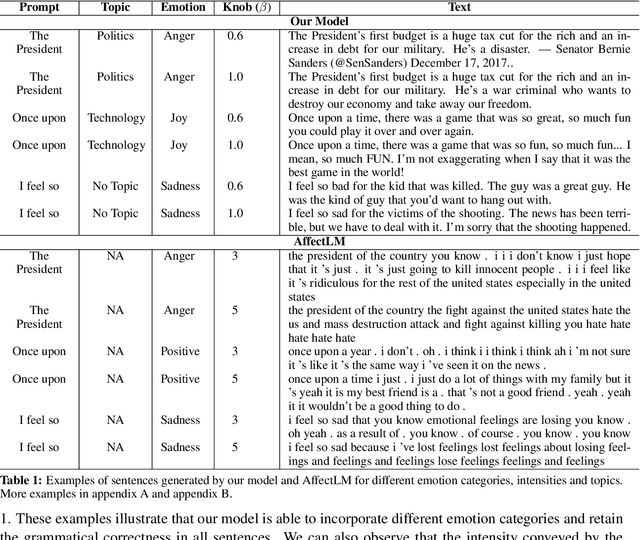
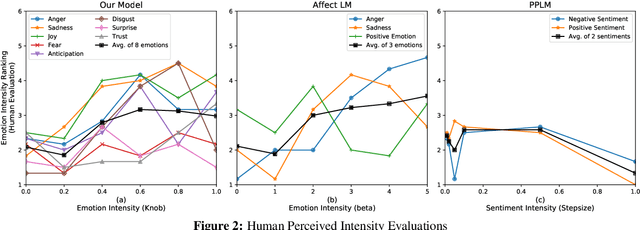
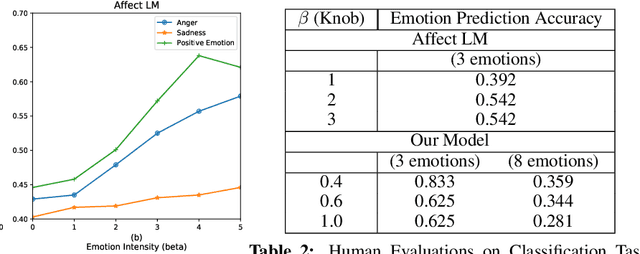
Abstract:Human use language not just to convey information but also to express their inner feelings and mental states. In this work, we adapt the state-of-the-art language generation models to generate affective (emotional) text. We posit a model capable of generating affect-driven and topic-focused sentences without losing grammatical correctness as the affect intensity increases. We propose to incorporate emotion as prior for the probabilistic state-of-the-art text generation model such as GPT-2. The model gives a user the flexibility to control the category and intensity of emotion as well as the topic of the generated text. Previous attempts at modelling fine-grained emotions fall out on grammatical correctness at extreme intensities, but our model is resilient to this and delivers robust results at all intensities. We conduct automated evaluations and human studies to test the performance of our model and provide a detailed comparison of the results with other models. In all evaluations, our model outperforms existing affective text generation models.
AI-based Monitoring and Response System for Hospital Preparedness towards COVID-19 in Southeast Asia
Jul 30, 2020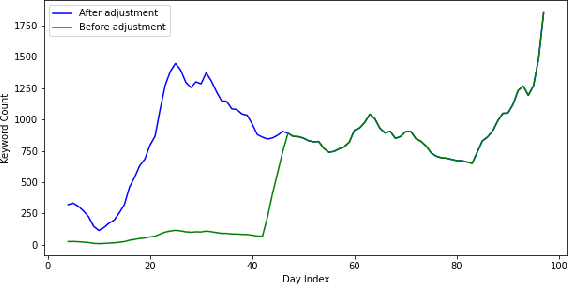
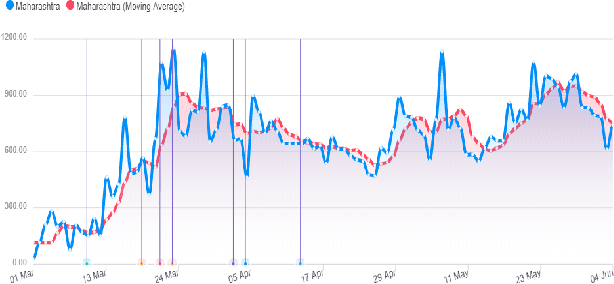
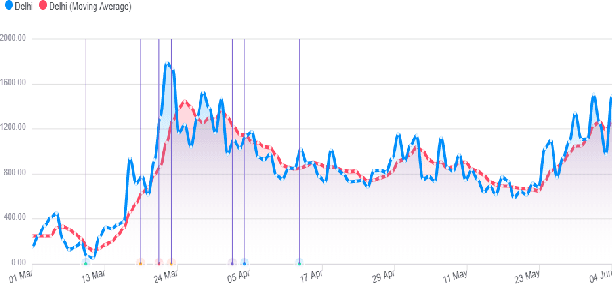
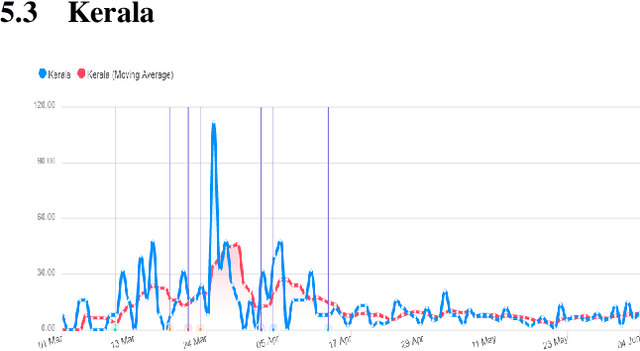
Abstract:This research paper proposes a COVID-19 monitoring and response system to identify the surge in the volume of patients at hospitals and shortage of critical equipment like ventilators in South-east Asian countries, to understand the burden on health facilities. This can help authorities in these regions with resource planning measures to redirect resources to the regions identified by the model. Due to the lack of publicly available data on the influx of patients in hospitals, or the shortage of equipment, ICU units or hospital beds that regions in these countries might be facing, we leverage Twitter data for gleaning this information. The approach has yielded accurate results for states in India, and we are working on validating the model for the remaining countries so that it can serve as a reliable tool for authorities to monitor the burden on hospitals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge