Tuomo Sipola
Red Teaming with Artificial Intelligence-Driven Cyberattacks: A Scoping Review
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:The progress of artificial intelligence (AI) has made sophisticated methods available for cyberattacks and red team activities. These AI attacks can automate the process of penetrating a target or collecting sensitive data. The new methods can also accelerate the execution of the attacks. This review article examines the use of AI technologies in cybersecurity attacks. It also tries to describe typical targets for such attacks. We employed a scoping review methodology to analyze articles and identify AI methods, targets, and models that red teams can utilize to simulate cybercrime. From the 470 records screened, 11 were included in the review. Various cyberattack methods were identified, targeting sensitive data, systems, social media profiles, passwords, and URLs. The application of AI in cybercrime to develop versatile attack models presents an increasing threat. Furthermore, AI-based techniques in red team use can provide new ways to address these issues.
Machine Learning Applications of Quantum Computing: A Review
Jun 19, 2024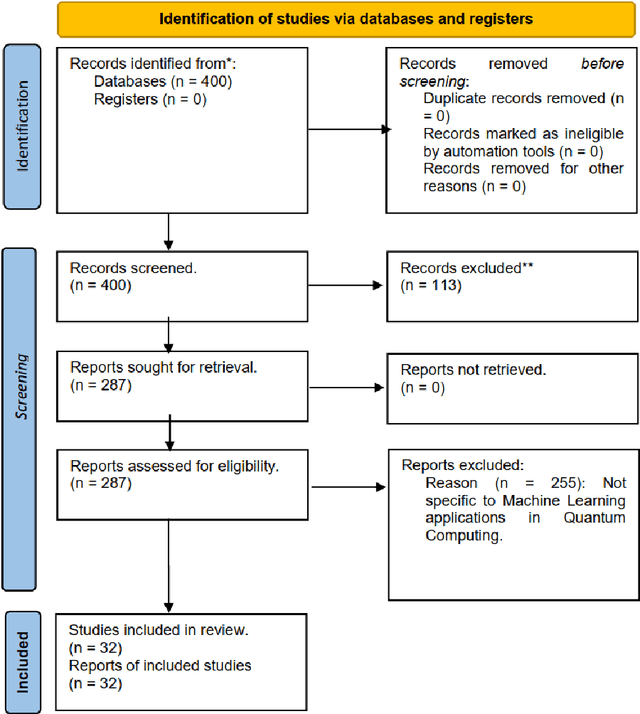
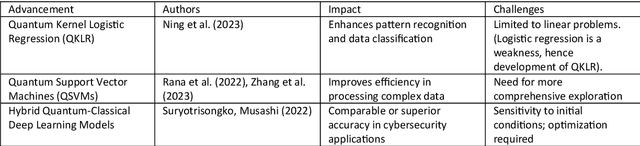
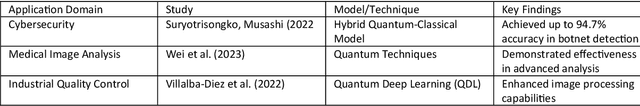

Abstract:At the intersection of quantum computing and machine learning, this review paper explores the transformative impact these technologies are having on the capabilities of data processing and analysis, far surpassing the bounds of traditional computational methods. Drawing upon an in-depth analysis of 32 seminal papers, this review delves into the interplay between quantum computing and machine learning, focusing on transcending the limitations of classical computing in advanced data processing and applications. This review emphasizes the potential of quantum-enhanced methods in enhancing cybersecurity, a critical sector that stands to benefit significantly from these advancements. The literature review, primarily leveraging Science Direct as an academic database, delves into the transformative effects of quantum technologies on machine learning, drawing insights from a diverse collection of studies and scholarly articles. While the focus is primarily on the growing significance of quantum computing in cybersecurity, the review also acknowledges the promising implications for other sectors as the field matures. Our systematic approach categorizes sources based on quantum machine learning algorithms, applications, challenges, and potential future developments, uncovering that quantum computing is increasingly being implemented in practical machine learning scenarios. The review highlights advancements in quantum-enhanced machine learning algorithms and their potential applications in sectors such as cybersecurity, emphasizing the need for industry-specific solutions while considering ethical and security concerns. By presenting an overview of the current state and projecting future directions, the paper sets a foundation for ongoing research and strategic advancement in quantum machine learning.
Latest Trends in Artificial Intelligence Technology: A Scoping Review
May 23, 2023Abstract:Artificial intelligence is more ubiquitous in multiple domains. Smartphones, social media platforms, search engines, and autonomous vehicles are just a few examples of applications that utilize artificial intelligence technologies to enhance their performance. This study carries out a scoping review of the current state-of-the-art artificial intelligence technologies following the PRISMA framework. The goal was to find the most advanced technologies used in different domains of artificial intelligence technology research. Three recognized journals were used from artificial intelligence and machine learning domain: Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, Journal of Machine Learning Research, and Machine Learning, and articles published in 2022 were observed. Certain qualifications were laid for the technological solutions: the technology must be tested against comparable solutions, commonly approved or otherwise well justified datasets must be used while applying, and results must show improvements against comparable solutions. One of the most important parts of the technology development appeared to be how to process and exploit the data gathered from multiple sources. The data can be highly unstructured and the technological solution should be able to utilize the data with minimum manual work from humans. The results of this review indicate that creating labeled datasets is very laborious, and solutions exploiting unsupervised or semi-supervised learning technologies are more and more researched. The learning algorithms should be able to be updated efficiently, and predictions should be interpretable. Using artificial intelligence technologies in real-world applications, safety and explainable predictions are mandatory to consider before mass adoption can occur.
Improved Difference Images for Change Detection Classifiers in SAR Imagery Using Deep Learning
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:Satellite-based Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images can be used as a source of remote sensed imagery regardless of cloud cover and day-night cycle. However, the speckle noise and varying image acquisition conditions pose a challenge for change detection classifiers. This paper proposes a new method of improving SAR image processing to produce higher quality difference images for the classification algorithms. The method is built on a neural network-based mapping transformation function that produces artificial SAR images from a location in the requested acquisition conditions. The inputs for the model are: previous SAR images from the location, imaging angle information from the SAR images, digital elevation model, and weather conditions. The method was tested with data from a location in North-East Finland by using Sentinel-1 SAR images from European Space Agency, weather data from Finnish Meteorological Institute, and a digital elevation model from National Land Survey of Finland. In order to verify the method, changes to the SAR images were simulated, and the performance of the proposed method was measured using experimentation where it gave substantial improvements to performance when compared to a more conventional method of creating difference images.
Chromatic and spatial analysis of one-pixel attacks against an image classifier
Jun 07, 2021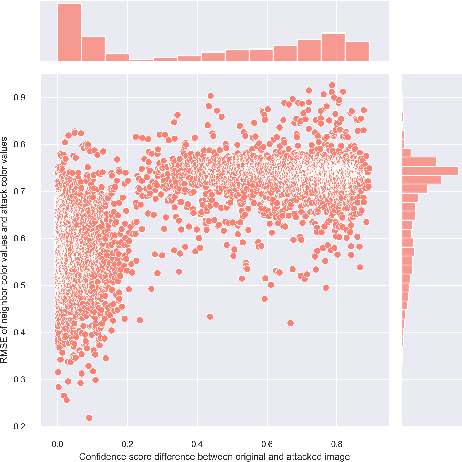
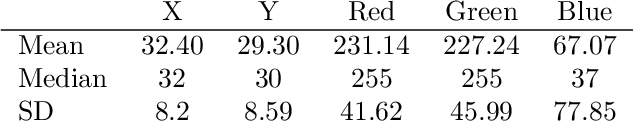
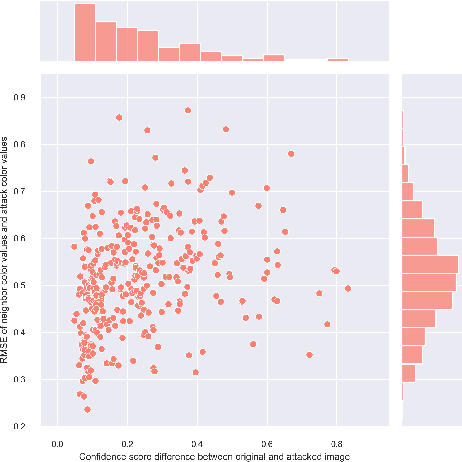
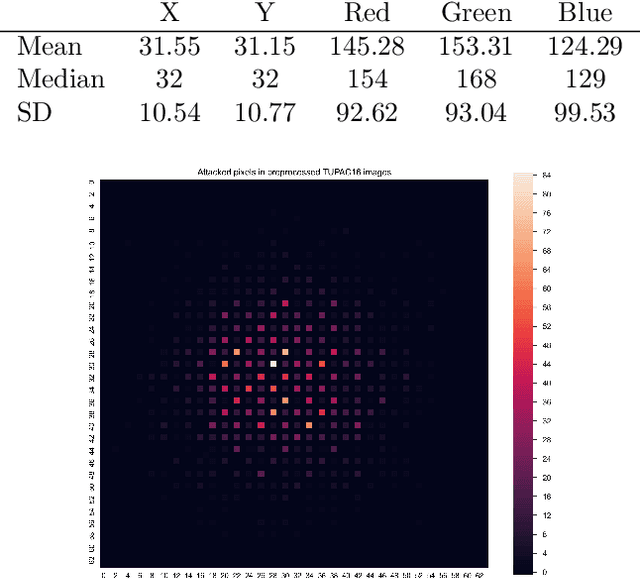
Abstract:One-pixel attack is a curious way of deceiving neural network classifier by changing only one pixel in the input image. The full potential and boundaries of this attack method are not yet fully understood. In this research, the successful and unsuccessful attacks are studied in more detail to illustrate the working mechanisms of a one-pixel attack created using differential evolution. The data comes from our earlier studies where we applied the attack against medical imaging. We used a real breast cancer tissue dataset and a real classifier as the attack target. This research presents ways to analyze chromatic and spatial distributions of one-pixel attacks. In addition, we present one-pixel attack confidence maps to illustrate the behavior of the target classifier. We show that the more effective attacks change the color of the pixel more, and that the successful attacks are situated at the center of the images. This kind of analysis is not only useful for understanding the behavior of the attack but also the qualities of the classifying neural network.
One-Pixel Attack Deceives Automatic Detection of Breast Cancer
Dec 16, 2020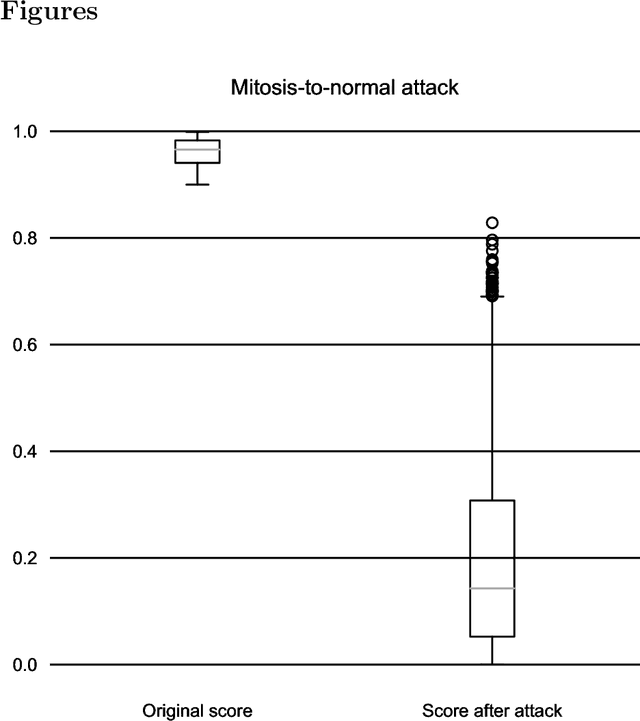
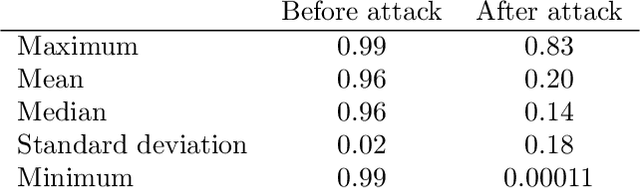
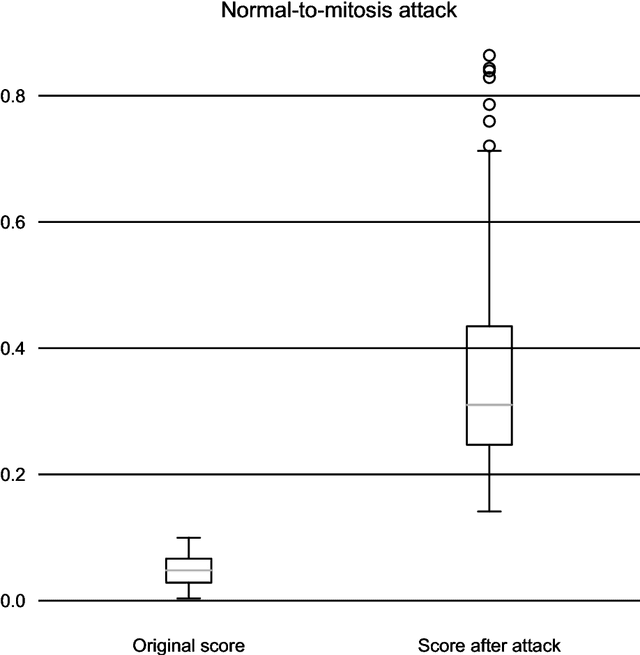
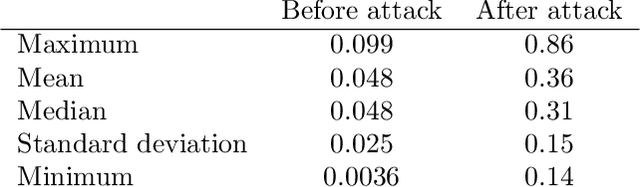
Abstract:In this article we demonstrate that a state-of-the-art machine learning model predicting whether a whole slide image contains mitosis can be fooled by changing just a single pixel in the input image. Computer vision and machine learning can be used to automate various tasks in cancer diagnostic and detection. If an attacker can manipulate the automated processing, the results can be devastating and in the worst case lead to wrong diagnostic and treatments. In this research one-pixel attack is demonstrated in a real-life scenario with a real tumor dataset. The results indicate that a minor one-pixel modification of a whole slide image under analysis can affect the diagnosis. The attack poses a threat from the cyber security perspective: the one-pixel method can be used as an attack vector by a motivated attacker.
Anomaly Detection Framework Using Rule Extraction for Efficient Intrusion Detection
Oct 28, 2014



Abstract:Huge datasets in cyber security, such as network traffic logs, can be analyzed using machine learning and data mining methods. However, the amount of collected data is increasing, which makes analysis more difficult. Many machine learning methods have not been designed for big datasets, and consequently are slow and difficult to understand. We address the issue of efficient network traffic classification by creating an intrusion detection framework that applies dimensionality reduction and conjunctive rule extraction. The system can perform unsupervised anomaly detection and use this information to create conjunctive rules that classify huge amounts of traffic in real time. We test the implemented system with the widely used KDD Cup 99 dataset and real-world network logs to confirm that the performance is satisfactory. This system is transparent and does not work like a black box, making it intuitive for domain experts, such as network administrators.
Diffusion map for clustering fMRI spatial maps extracted by independent component analysis
Sep 27, 2013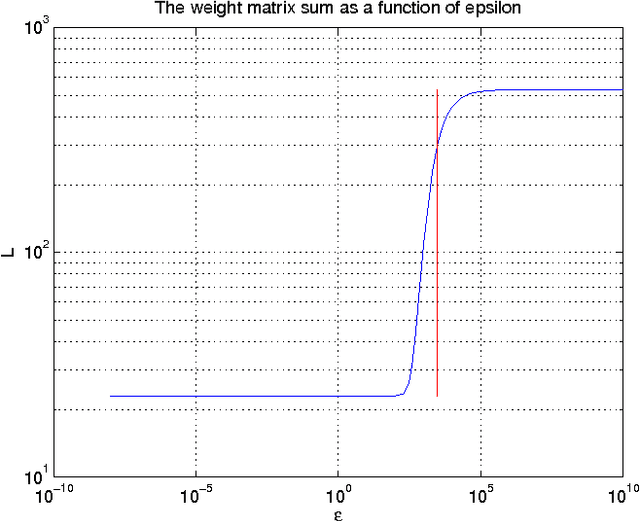

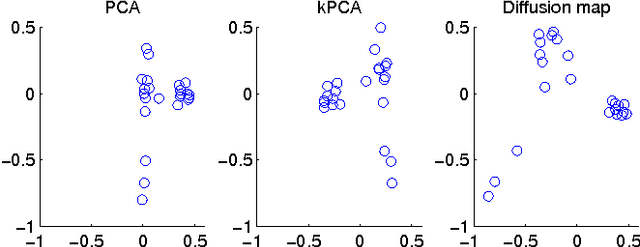

Abstract:Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) produces data about activity inside the brain, from which spatial maps can be extracted by independent component analysis (ICA). In datasets, there are n spatial maps that contain p voxels. The number of voxels is very high compared to the number of analyzed spatial maps. Clustering of the spatial maps is usually based on correlation matrices. This usually works well, although such a similarity matrix inherently can explain only a certain amount of the total variance contained in the high-dimensional data where n is relatively small but p is large. For high-dimensional space, it is reasonable to perform dimensionality reduction before clustering. In this research, we used the recently developed diffusion map for dimensionality reduction in conjunction with spectral clustering. This research revealed that the diffusion map based clustering worked as well as the more traditional methods, and produced more compact clusters when needed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge