Tuan-Anh D. Nguyen
Towards Safer Operations: An Expert-involved Dataset of High-Pressure Gas Incidents for Preventing Future Failures
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces a new IncidentAI dataset for safety prevention. Different from prior corpora that usually contain a single task, our dataset comprises three tasks: named entity recognition, cause-effect extraction, and information retrieval. The dataset is annotated by domain experts who have at least six years of practical experience as high-pressure gas conservation managers. We validate the contribution of the dataset in the scenario of safety prevention. Preliminary results on the three tasks show that NLP techniques are beneficial for analyzing incident reports to prevent future failures. The dataset facilitates future research in NLP and incident management communities. The access to the dataset is also provided (the IncidentAI dataset is available at: https://github.com/Cinnamon/incident-ai-dataset).
Jointly Learning Span Extraction and Sequence Labeling for Information Extraction from Business Documents
May 26, 2022
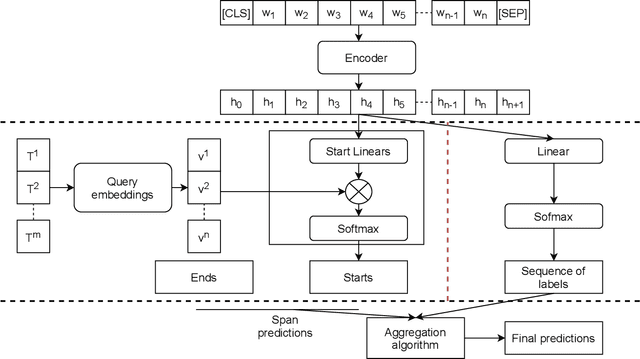
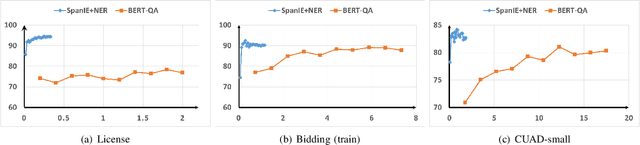
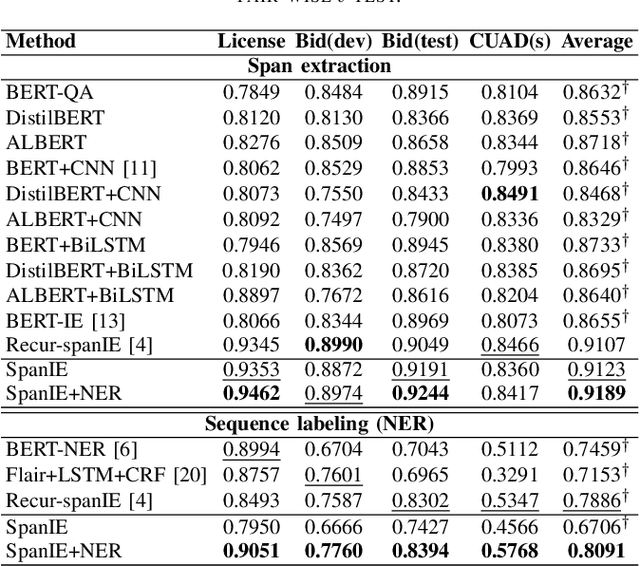
Abstract:This paper introduces a new information extraction model for business documents. Different from prior studies which only base on span extraction or sequence labeling, the model takes into account advantage of both span extraction and sequence labeling. The combination allows the model to deal with long documents with sparse information (the small amount of extracted information). The model is trained end-to-end to jointly optimize the two tasks in a unified manner. Experimental results on four business datasets in English and Japanese show that the model achieves promising results and is significantly faster than the normal span-based extraction method. The code is also available.
A Span Extraction Approach for Information Extraction on Visually-Rich Documents
Jun 02, 2021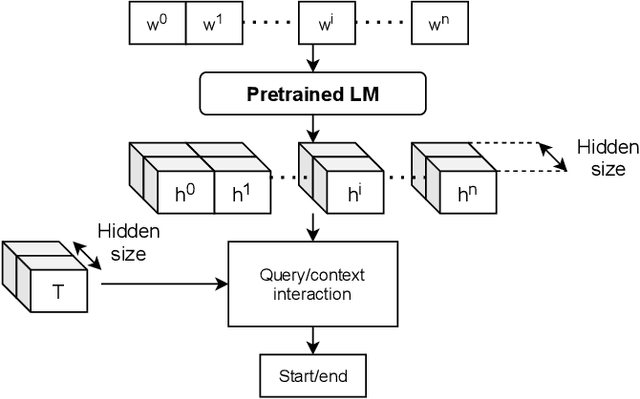
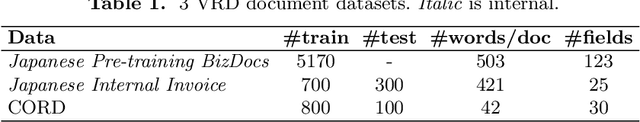
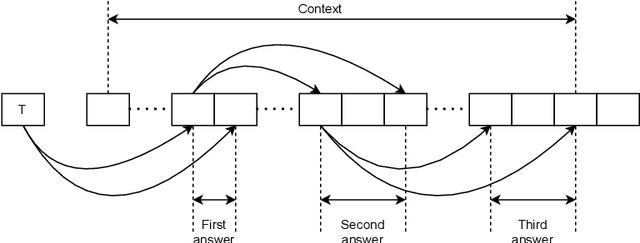
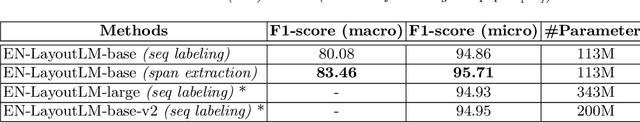
Abstract:Information extraction (IE) from visually-rich documents (VRDs) has achieved SOTA performance recently thanks to the adaptation of Transformer-based language models, which demonstrates great potential of pre-training methods. In this paper, we present a new approach to improve the capability of language model pre-training on VRDs. Firstly, we introduce a new IE model that is query-based and employs the span extraction formulation instead of the commonly used sequence labelling approach. Secondly, to further extend the span extraction formulation, we propose a new training task which focuses on modelling the relationships between semantic entities within a document. This task enables the spans to be extracted recursively and can be used as both a pre-training objective as well as an IE downstream task. Evaluation on various datasets of popular business documents (invoices, receipts) shows that our proposed method can improve the performance of existing models significantly, while providing a mechanism to accumulate model knowledge from multiple downstream IE tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge