Tixian Wang
Neural Models and Algorithms for Sensorimotor Control of an Octopus Arm
Feb 02, 2024



Abstract:In this article, a biophysically realistic model of a soft octopus arm with internal musculature is presented. The modeling is motivated by experimental observations of sensorimotor control where an arm localizes and reaches a target. Major contributions of this article are: (i) development of models to capture the mechanical properties of arm musculature, the electrical properties of the arm peripheral nervous system (PNS), and the coupling of PNS with muscular contractions; (ii) modeling the arm sensory system, including chemosensing and proprioception; and (iii) algorithms for sensorimotor control, which include a novel feedback neural motor control law for mimicking target-oriented arm reaching motions, and a novel consensus algorithm for solving sensing problems such as locating a food source from local chemical sensory information (exogenous) and arm deformation information (endogenous). Several analytical results, including rest-state characterization and stability properties of the proposed sensing and motor control algorithms, are provided. Numerical simulations demonstrate the efficacy of our approach. Qualitative comparisons against observed arm rest shapes and target-oriented reaching motions are also reported.
Modeling the Neuromuscular Control System of an Octopus Arm
Nov 12, 2022



Abstract:The octopus arm is a neuromechanical system that involves a complex interplay between peripheral nervous system (PNS) and arm musculature. This makes the arm capable of carrying out rich maneuvers. In this paper, we build a model for the PNS and integrate it with a muscular soft octopus arm. The proposed neuromuscular architecture is used to qualitatively reproduce several biophysical observations in real octopuses, including curled rest shapes and target-directed arm reaching motions. Two control laws are proposed for target-oriented arm motions, and their performance is compared against a benchmark. Several analytical results, including rest-state characterization and stability properties of the proposed control laws, are provided.
A Sensory Feedback Control Law for Octopus Arm Movements
Apr 01, 2022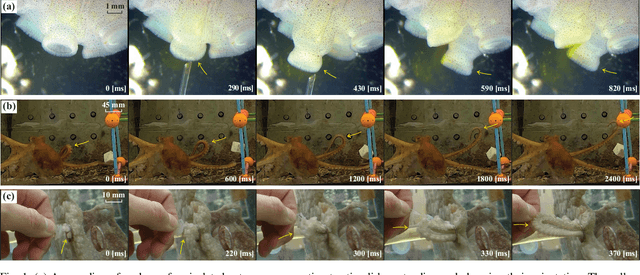
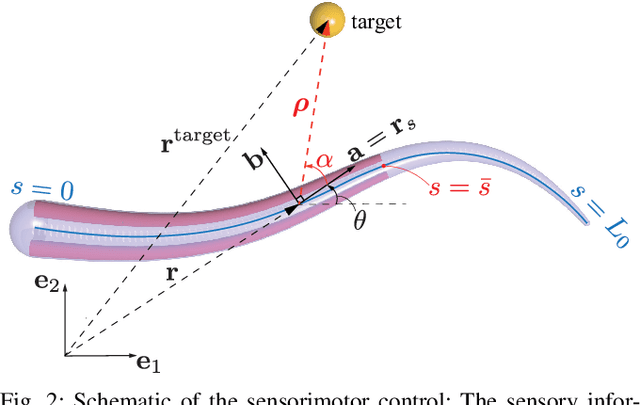
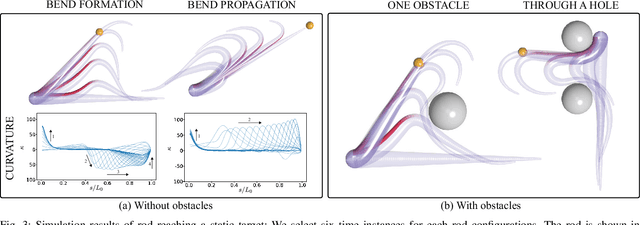
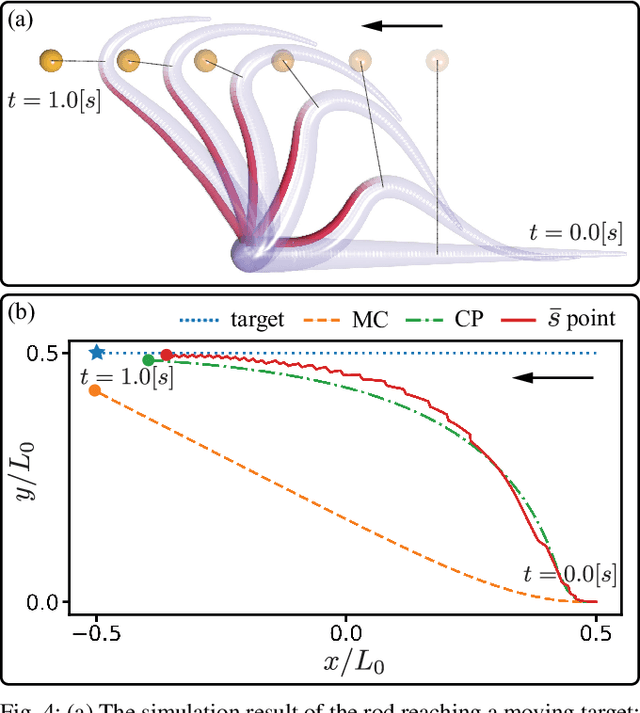
Abstract:The main contribution of this paper is a novel sensory feedback control law for an octopus arm. The control law is inspired by, and helps integrate, several observations made by biologists. The proposed control law is distinct from prior work which has mainly focused on open-loop control strategies. Several analytical results are described including characterization of the equilibrium and its stability analysis. Numerical simulations demonstrate life-like motion of the soft octopus arm, qualitatively matching behavioral experiments. Quantitative comparison with bend propagation experiments helps provide the first explanation of such canonical motion using a sensory feedback control law. Several remarks are included that help draw parallels with natural pursuit strategies such as motion camouflage or classical pursuit.
Optimal Control of a Soft CyberOctopus Arm
Oct 02, 2020
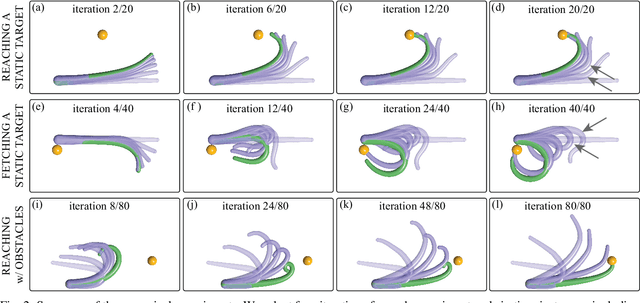
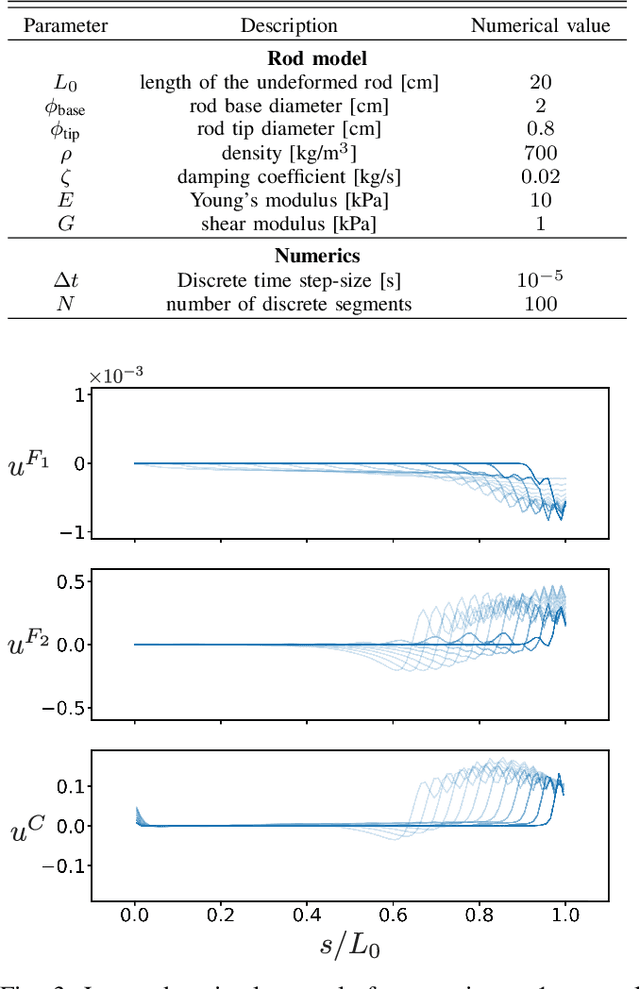
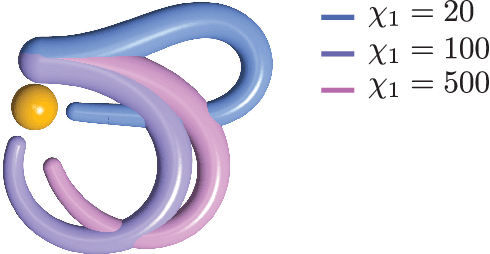
Abstract:In this paper, we use the optimal control methodology to control a flexible, elastic Cosserat rod. An inspiration comes from stereotypical movement patterns in octopus arms, which are observed in a variety of manipulation tasks, such as reaching or fetching. To help uncover the mechanisms underlying these observed behaviors, we outline an optimal control-based framework. A single octopus arm is modeled as a Hamiltonian control system, where the continuum mechanics of the arm is captured by the Cosserat rod theory, and internal, distributed muscle forces and couples are considered as controls. First order necessary optimality conditions are derived for an optimal control problem formulated for this infinite dimensional system. Solutions to this problem are obtained numerically by an iterative forward-backward algorithm. The state and adjoint equations are solved in a dynamic simulation environment, setting the stage for studying a broader class of optimal control problems. Trajectories that minimize control effort are demonstrated and qualitatively compared with observed behaviors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge