A Sensory Feedback Control Law for Octopus Arm Movements
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2022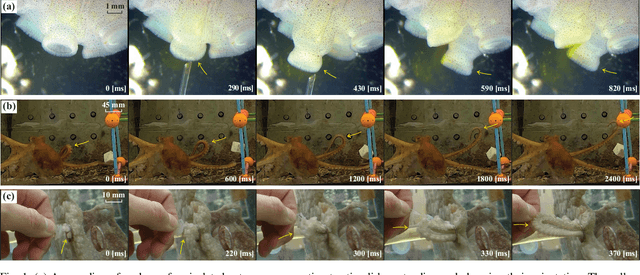
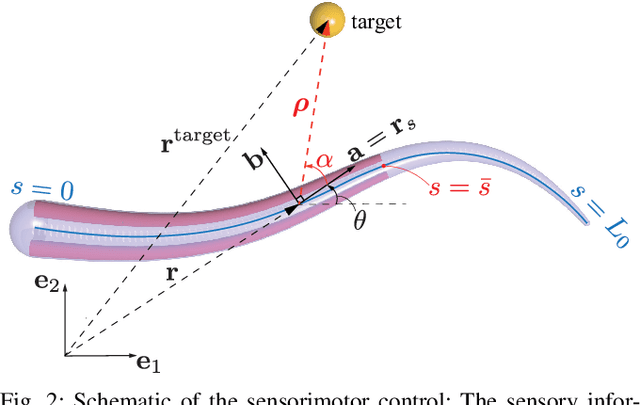
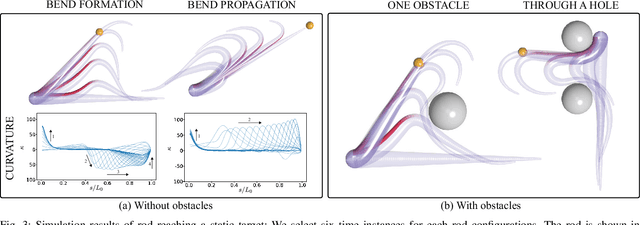
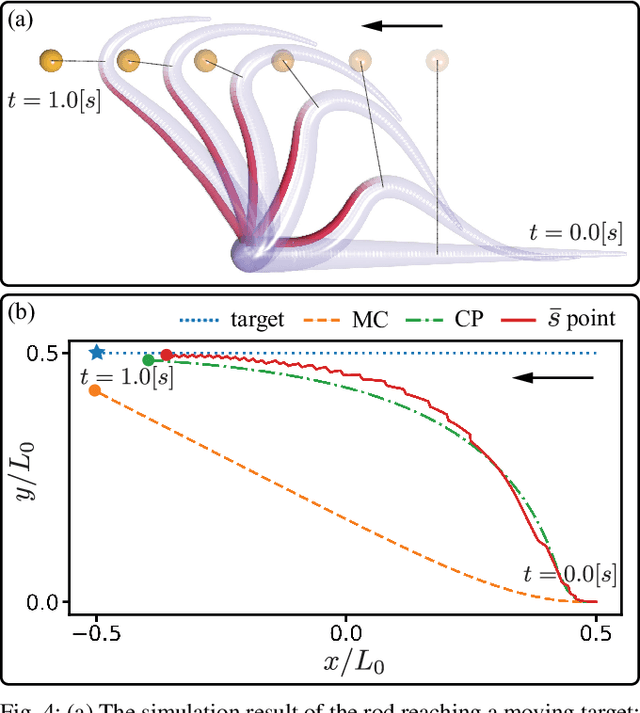
The main contribution of this paper is a novel sensory feedback control law for an octopus arm. The control law is inspired by, and helps integrate, several observations made by biologists. The proposed control law is distinct from prior work which has mainly focused on open-loop control strategies. Several analytical results are described including characterization of the equilibrium and its stability analysis. Numerical simulations demonstrate life-like motion of the soft octopus arm, qualitatively matching behavioral experiments. Quantitative comparison with bend propagation experiments helps provide the first explanation of such canonical motion using a sensory feedback control law. Several remarks are included that help draw parallels with natural pursuit strategies such as motion camouflage or classical pursuit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge