Ting Wei Li
A Metadata-Driven Approach to Understand Graph Neural Networks
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved remarkable success in various applications, but their performance can be sensitive to specific data properties of the graph datasets they operate on. Current literature on understanding the limitations of GNNs has primarily employed a $\textit{model-driven}$ approach that leverage heuristics and domain knowledge from network science or graph theory to model the GNN behaviors, which is time-consuming and highly subjective. In this work, we propose a $\textit{metadata-driven}$ approach to analyze the sensitivity of GNNs to graph data properties, motivated by the increasing availability of graph learning benchmarks. We perform a multivariate sparse regression analysis on the metadata derived from benchmarking GNN performance across diverse datasets, yielding a set of salient data properties. To validate the effectiveness of our data-driven approach, we focus on one identified data property, the degree distribution, and investigate how this property influences GNN performance through theoretical analysis and controlled experiments. Our theoretical findings reveal that datasets with more balanced degree distribution exhibit better linear separability of node representations, thus leading to better GNN performance. We also conduct controlled experiments using synthetic datasets with varying degree distributions, and the results align well with our theoretical findings. Collectively, both the theoretical analysis and controlled experiments verify that the proposed metadata-driven approach is effective in identifying critical data properties for GNNs.
Graph Learning Indexer: A Contributor-Friendly and Metadata-Rich Platform for Graph Learning Benchmarks
Dec 08, 2022
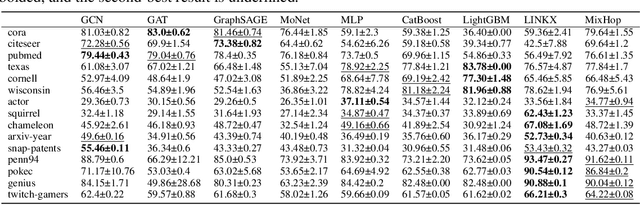

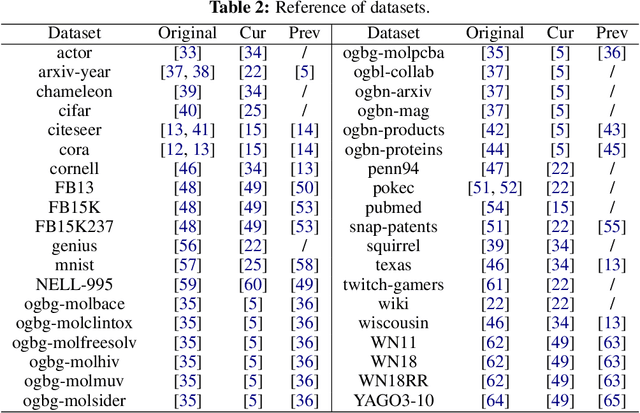
Abstract:Establishing open and general benchmarks has been a critical driving force behind the success of modern machine learning techniques. As machine learning is being applied to broader domains and tasks, there is a need to establish richer and more diverse benchmarks to better reflect the reality of the application scenarios. Graph learning is an emerging field of machine learning that urgently needs more and better benchmarks. To accommodate the need, we introduce Graph Learning Indexer (GLI), a benchmark curation platform for graph learning. In comparison to existing graph learning benchmark libraries, GLI highlights two novel design objectives. First, GLI is designed to incentivize \emph{dataset contributors}. In particular, we incorporate various measures to minimize the effort of contributing and maintaining a dataset, increase the usability of the contributed dataset, as well as encourage attributions to different contributors of the dataset. Second, GLI is designed to curate a knowledge base, instead of a plain collection, of benchmark datasets. We use multiple sources of meta information to augment the benchmark datasets with \emph{rich characteristics}, so that they can be easily selected and used in downstream research or development. The source code of GLI is available at \url{https://github.com/Graph-Learning-Benchmarks/gli}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge