Tim Brüdigam
Online Constraint Tightening in Stochastic Model Predictive Control: A Regression Approach
Oct 04, 2023Abstract:Solving chance-constrained stochastic optimal control problems is a significant challenge in control. This is because no analytical solutions exist for up to a handful of special cases. A common and computationally efficient approach for tackling chance-constrained stochastic optimal control problems consists of reformulating the chance constraints as hard constraints with a constraint-tightening parameter. However, in such approaches, the choice of constraint-tightening parameter remains challenging, and guarantees can mostly be obtained assuming that the process noise distribution is known a priori. Moreover, the chance constraints are often not tightly satisfied, leading to unnecessarily high costs. This work proposes a data-driven approach for learning the constraint-tightening parameters online during control. To this end, we reformulate the choice of constraint-tightening parameter for the closed-loop as a binary regression problem. We then leverage a highly expressive \gls{gp} model for binary regression to approximate the smallest constraint-tightening parameters that satisfy the chance constraints. By tuning the algorithm parameters appropriately, we show that the resulting constraint-tightening parameters satisfy the chance constraints up to an arbitrarily small margin with high probability. Our approach yields constraint-tightening parameters that tightly satisfy the chance constraints in numerical experiments, resulting in a lower average cost than three other state-of-the-art approaches.
Gaussian Process-based Stochastic Model Predictive Control for Overtaking in Autonomous Racing
May 25, 2021

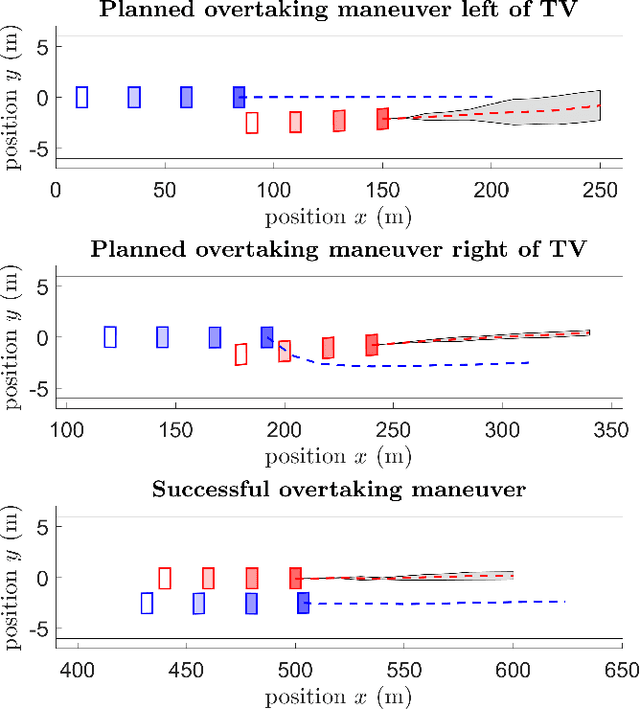
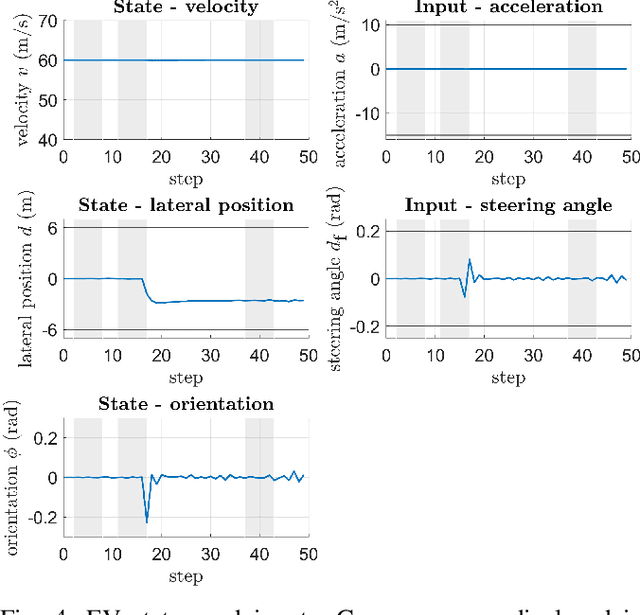
Abstract:A fundamental aspect of racing is overtaking other race cars. Whereas previous research on autonomous racing has majorly focused on lap-time optimization, here, we propose a method to plan overtaking maneuvers in autonomous racing. A Gaussian process is used to learn the behavior of the leading vehicle. Based on the outputs of the Gaussian process, a stochastic Model Predictive Control algorithm plans optimistic trajectories, such that the controlled autonomous race car is able to overtake the leading vehicle. The proposed method is tested in a simple simulation scenario.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge