Tianxiang Pan
Semantic Hierarchical Prompt Tuning for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:As the scale of vision models continues to grow, Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT) has emerged as a parameter-efficient transfer learning technique, noted for its superior performance compared to full fine-tuning. However, indiscriminately applying prompts to every layer without considering their inherent correlations, can cause significant disturbances, leading to suboptimal transferability. Additionally, VPT disrupts the original self-attention structure, affecting the aggregation of visual features, and lacks a mechanism for explicitly mining discriminative visual features, which are crucial for classification. To address these issues, we propose a Semantic Hierarchical Prompt (SHIP) fine-tuning strategy. We adaptively construct semantic hierarchies and use semantic-independent and semantic-shared prompts to learn hierarchical representations. We also integrate attribute prompts and a prompt matching loss to enhance feature discrimination and employ decoupled attention for robustness and reduced inference costs. SHIP significantly improves performance, achieving a 4.9% gain in accuracy over VPT with a ViT-B/16 backbone on VTAB-1k tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/haoweiz23/SHIP.
Low-Confidence Samples Mining for Semi-supervised Object Detection
Jun 28, 2023Abstract:Reliable pseudo-labels from unlabeled data play a key role in semi-supervised object detection (SSOD). However, the state-of-the-art SSOD methods all rely on pseudo-labels with high confidence, which ignore valuable pseudo-labels with lower confidence. Additionally, the insufficient excavation for unlabeled data results in an excessively low recall rate thus hurting the network training. In this paper, we propose a novel Low-confidence Samples Mining (LSM) method to utilize low-confidence pseudo-labels efficiently. Specifically, we develop an additional pseudo information mining (PIM) branch on account of low-resolution feature maps to extract reliable large-area instances, the IoUs of which are higher than small-area ones. Owing to the complementary predictions between PIM and the main branch, we further design self-distillation (SD) to compensate for both in a mutually-learning manner. Meanwhile, the extensibility of the above approaches enables our LSM to apply to Faster-RCNN and Deformable-DETR respectively. On the MS-COCO benchmark, our method achieves 3.54% mAP improvement over state-of-the-art methods under 5% labeling ratios.
Semi-Supervised Object Detection with Adaptive Class-Rebalancing Self-Training
Jul 11, 2021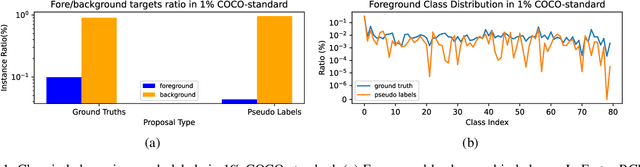
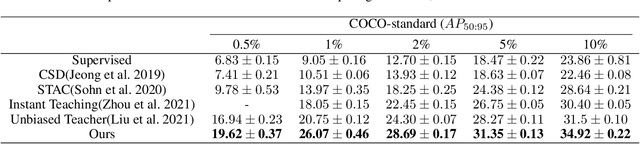
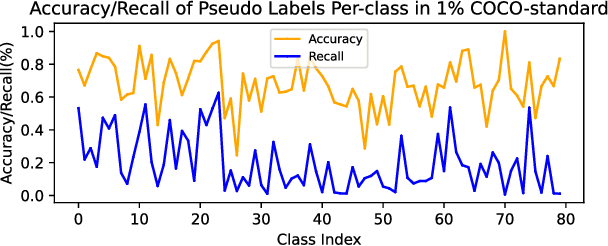
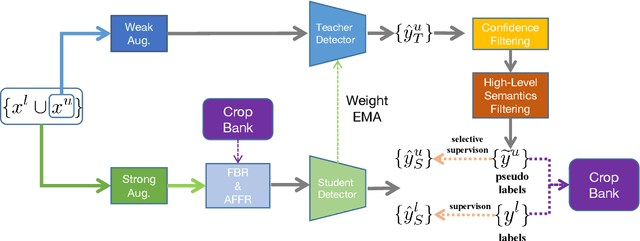
Abstract:This study delves into semi-supervised object detection (SSOD) to improve detector performance with additional unlabeled data. State-of-the-art SSOD performance has been achieved recently by self-training, in which training supervision consists of ground truths and pseudo-labels. In current studies, we observe that class imbalance in SSOD severely impedes the effectiveness of self-training. To address the class imbalance, we propose adaptive class-rebalancing self-training (ACRST) with a novel memory module called CropBank. ACRST adaptively rebalances the training data with foreground instances extracted from the CropBank, thereby alleviating the class imbalance. Owing to the high complexity of detection tasks, we observe that both self-training and data-rebalancing suffer from noisy pseudo-labels in SSOD. Therefore, we propose a novel two-stage filtering algorithm to generate accurate pseudo-labels. Our method achieves satisfactory improvements on MS-COCO and VOC benchmarks. When using only 1\% labeled data in MS-COCO, our method achieves 17.02 mAP improvement over supervised baselines, and 5.32 mAP improvement compared with state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge