Tianbo Liu
A survey of machine learning-based physics event generation
Jun 01, 2021
Abstract:Event generators in high-energy nuclear and particle physics play an important role in facilitating studies of particle reactions. We survey the state-of-the-art of machine learning (ML) efforts at building physics event generators. We review ML generative models used in ML-based event generators and their specific challenges, and discuss various approaches of incorporating physics into the ML model designs to overcome these challenges. Finally, we explore some open questions related to super-resolution, fidelity, and extrapolation for physics event generation based on ML technology.
Simulation of electron-proton scattering events by a Feature-Augmented and Transformed Generative Adversarial Network (FAT-GAN)
Jan 29, 2020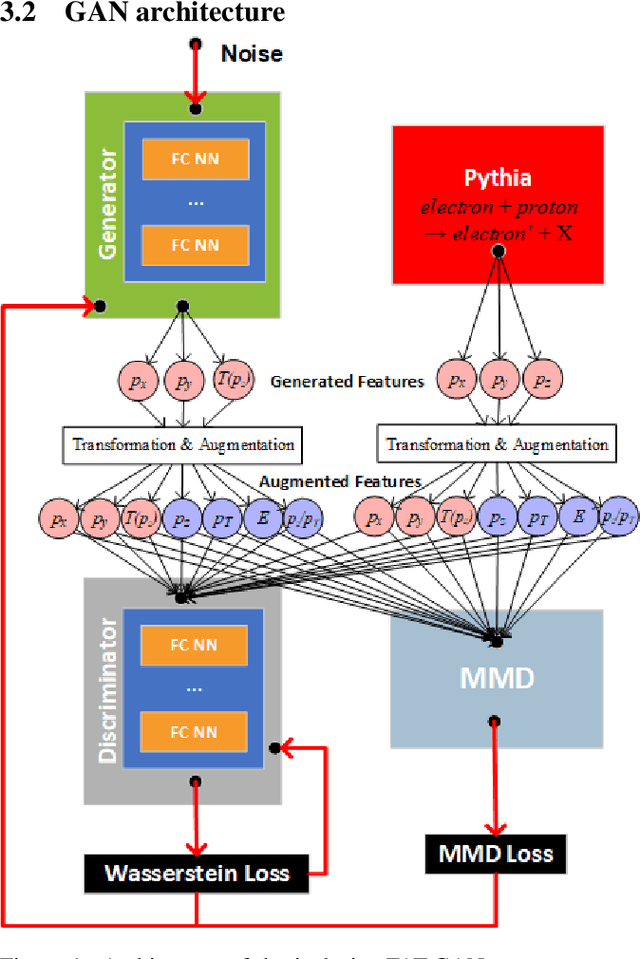
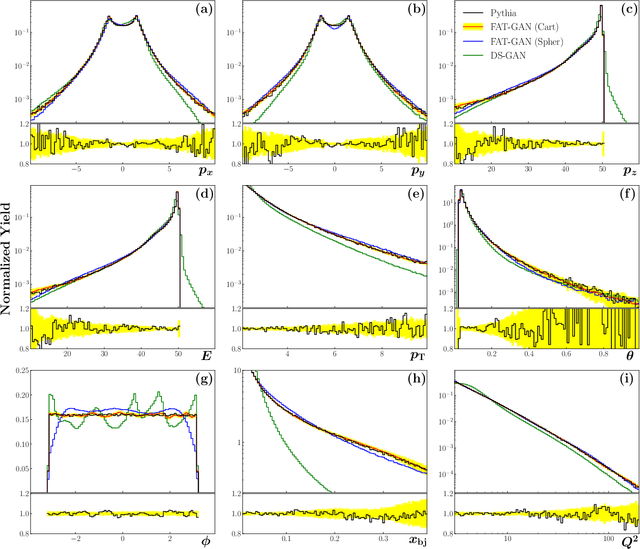
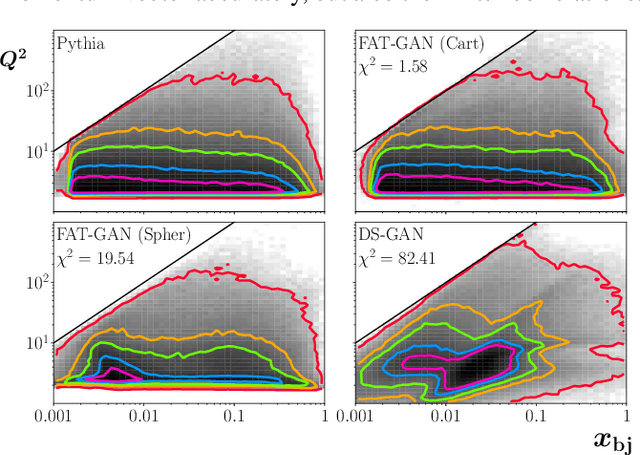
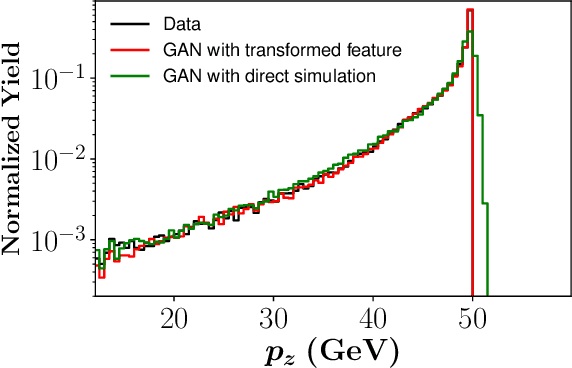
Abstract:We apply generative adversarial network (GAN) technology to build an event generator that simulates particle production in electron-proton scattering that is free of theoretical assumptions about underlying particle dynamics. The difficulty of efficiently training a GAN event simulator lies in learning the complicated patterns of the distributions of the particles physical properties. We develop a GAN that selects a set of transformed features from particle momenta that can be generated easily by the generator, and uses these to produce a set of augmented features that improve the sensitivity of the discriminator. The new Feature-Augmented and Transformed GAN (FAT-GAN) is able to faithfully reproduce the distribution of final state electron momenta in inclusive electron scattering, without the need for input derived from domain-based theoretical assumptions. The developed technology can play a significant role in boosting the science of the Jefferson Lab 12 GeV program and the future Electron-Ion Collider.
Learning Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Control for Autonomous Target Following
Sep 24, 2017



Abstract:While deep reinforcement learning (RL) methods have achieved unprecedented successes in a range of challenging problems, their applicability has been mainly limited to simulation or game domains due to the high sample complexity of the trial-and-error learning process. However, real-world robotic applications often need a data-efficient learning process with safety-critical constraints. In this paper, we consider the challenging problem of learning unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) control for tracking a moving target. To acquire a strategy that combines perception and control, we represent the policy by a convolutional neural network. We develop a hierarchical approach that combines a model-free policy gradient method with a conventional feedback proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller to enable stable learning without catastrophic failure. The neural network is trained by a combination of supervised learning from raw images and reinforcement learning from games of self-play. We show that the proposed approach can learn a target following policy in a simulator efficiently and the learned behavior can be successfully transferred to the DJI quadrotor platform for real-world UAV control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge