Thomas März
Fast Trajectory-Independent Model-Based Reconstruction Algorithm for Multi-Dimensional Magnetic Particle Imaging
May 28, 2025Abstract:Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) is a promising tomographic technique for visualizing the spatio-temporal distribution of superparamagnetic nanoparticles, with applications ranging from cancer detection to real-time cardiovascular monitoring. Traditional MPI reconstruction relies on either time-consuming calibration (measured system matrix) or model-based simulation of the forward operator. Recent developments have shown the applicability of Chebyshev polynomials to multi-dimensional Lissajous Field-Free Point (FFP) scans. This method is bound to the particular choice of sinusoidal scanning trajectories. In this paper, we present the first reconstruction on real 2D MPI data with a trajectory-independent model-based MPI reconstruction algorithm. We further develop the zero-shot Plug-and-Play (PnP) algorithm of the authors -- with automatic noise level estimation -- to address the present deconvolution problem, leveraging a state-of-the-art denoiser trained on natural images without retraining on MPI-specific data. We evaluate our method on the publicly available 2D FFP MPI dataset ``MPIdata: Equilibrium Model with Anisotropy", featuring scans of six phantoms acquired using a Bruker preclinical scanner. Moreover, we show reconstruction performed on custom data on a 2D scanner with additional high-frequency excitation field and partial data. Our results demonstrate strong reconstruction capabilities across different scanning scenarios -- setting a precedent for general-purpose, flexible model-based MPI reconstruction.
Remote Sensing Imagery for Flood Detection: Exploration of Augmentation Strategies
Apr 28, 2025
Abstract:Floods cause serious problems around the world. Responding quickly and effectively requires accurate and timely information about the affected areas. The effective use of Remote Sensing images for accurate flood detection requires specific detection methods. Typically, Deep Neural Networks are employed, which are trained on specific datasets. For the purpose of river flood detection in RGB imagery, we use the BlessemFlood21 dataset. We here explore the use of different augmentation strategies, ranging from basic approaches to more complex techniques, including optical distortion. By identifying effective strategies, we aim to refine the training process of state-of-the-art Deep Learning segmentation networks.
BlessemFlood21: Advancing Flood Analysis with a High-Resolution Georeferenced Dataset for Humanitarian Aid Support
Jul 06, 2024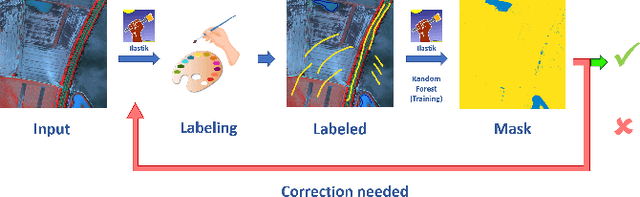
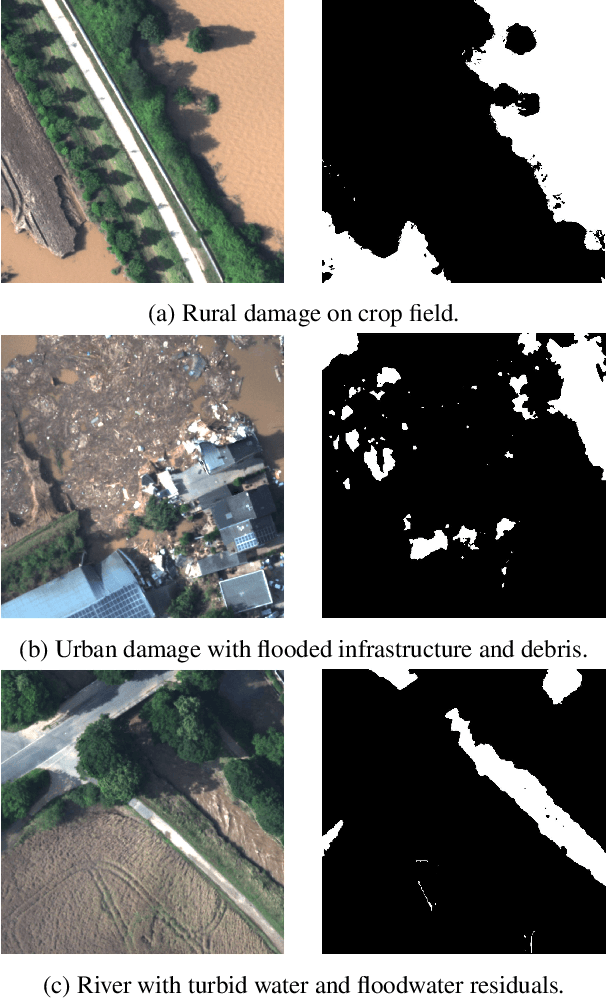
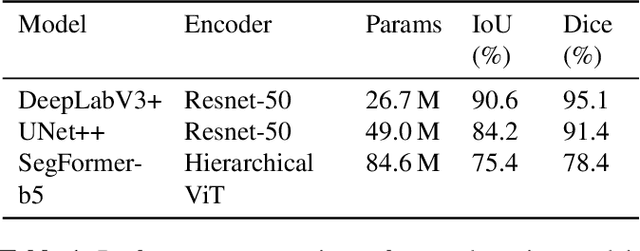


Abstract:Floods are an increasingly common global threat, causing emergencies and severe damage to infrastructure. During crises, organisations such as the World Food Programme use remotely sensed imagery, typically obtained through drones, for rapid situational analysis to plan life-saving actions. Computer Vision tools are needed to support task force experts on-site in the evaluation of the imagery to improve their efficiency and to allocate resources strategically. We introduce the BlessemFlood21 dataset to stimulate research on efficient flood detection tools. The imagery was acquired during the 2021 Erftstadt-Blessem flooding event and consists of high-resolution and georeferenced RGB-NIR images. In the resulting RGB dataset, the images are supplemented with detailed water masks, obtained via a semi-supervised human-in-the-loop technique, where in particular the NIR information is leveraged to classify pixels as either water or non-water. We evaluate our dataset by training and testing established Deep Learning models for semantic segmentation. With BlessemFlood21 we provide labeled high-resolution RGB data and a baseline for further development of algorithmic solutions tailored to flood detection in RGB imagery.
Low-Dose CT Image Reconstruction by Fine-Tuning a UNet Pretrained for Gaussian Denoising for the Downstream Task of Image Enhancement
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Computed Tomography (CT) is a widely used medical imaging modality, and as it is based on ionizing radiation, it is desirable to minimize the radiation dose. However, a reduced radiation dose comes with reduced image quality, and reconstruction from low-dose CT (LDCT) data is still a challenging task which is subject to research. According to the LoDoPaB-CT benchmark, a benchmark for LDCT reconstruction, many state-of-the-art methods use pipelines involving UNet-type architectures. Specifically the top ranking method, ItNet, employs a three-stage process involving filtered backprojection (FBP), a UNet trained on CT data, and an iterative refinement step. In this paper, we propose a less complex two-stage method. The first stage also employs FBP, while the novelty lies in the training strategy for the second stage, characterized as the CT image enhancement stage. The crucial point of our approach is that the neural network is pretrained on a distinctly different pretraining task with non-CT data, namely Gaussian noise removal on a variety of natural grayscale images (photographs). We then fine-tune this network for the downstream task of CT image enhancement using pairs of LDCT images and corresponding normal-dose CT images (NDCT). Despite being notably simpler than the state-of-the-art, as the pretraining did not depend on domain-specific CT data and no further iterative refinement step was necessary, the proposed two-stage method achieves competitive results. The proposed method achieves a shared top ranking in the LoDoPaB-CT challenge and a first position with respect to the SSIM metric.
An $\ell^1$-Plug-and-Play Approach for Magnetic Particle Imaging Using a Zero Shot Denoiser with Validation on the 3D Open MPI Dataset
Dec 30, 2023Abstract:Magnetic particle imaging (MPI) is an emerging medical imaging modality which has gained increasing interest in recent years. Among the benefits of MPI are its high temporal resolution, and that the technique does not expose the specimen to any kind of ionizing radiation. It is based on the non-linear response of magnetic nanoparticles to an applied magnetic field. From the electric signal measured in receive coils, the particle concentration has to be reconstructed. Due to the ill-posedness of the reconstruction problem, various regularization methods have been proposed for reconstruction ranging from early stopping methods, via classical Tikhonov regularization and iterative methods to modern machine learning approaches. In this work, we contribute to the latter class: we propose a plug-and-play approach based on a generic zero-shot denoiser with an $\ell^1$-prior. Moreover, we develop parameter selection strategies. Finally, we quantitatively and qualitatively evaluate the proposed algorithmic scheme on the 3D Open MPI data set with different levels of preprocessing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge