Thomas Boulay
Enhanced Parking Perception by Multi-Task Fisheye Cross-view Transformers
Aug 22, 2024Abstract:Current parking area perception algorithms primarily focus on detecting vacant slots within a limited range, relying on error-prone homographic projection for both labeling and inference. However, recent advancements in Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) require interaction with end-users through comprehensive and intelligent Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs). These interfaces should present a complete perception of the parking area going from distinguishing vacant slots' entry lines to the orientation of other parked vehicles. This paper introduces Multi-Task Fisheye Cross View Transformers (MT F-CVT), which leverages features from a four-camera fisheye Surround-view Camera System (SVCS) with multihead attentions to create a detailed Bird-Eye View (BEV) grid feature map. Features are processed by both a segmentation decoder and a Polygon-Yolo based object detection decoder for parking slots and vehicles. Trained on data labeled using LiDAR, MT F-CVT positions objects within a 25m x 25m real open-road scenes with an average error of only 20 cm. Our larger model achieves an F-1 score of 0.89. Moreover the smaller model operates at 16 fps on an Nvidia Jetson Orin embedded board, with similar detection results to the larger one. MT F-CVT demonstrates robust generalization capability across different vehicles and camera rig configurations. A demo video from an unseen vehicle and camera rig is available at: https://streamable.com/jjw54x.
Holistic Parking Slot Detection with Polygon-Shaped Representations
Oct 17, 2023
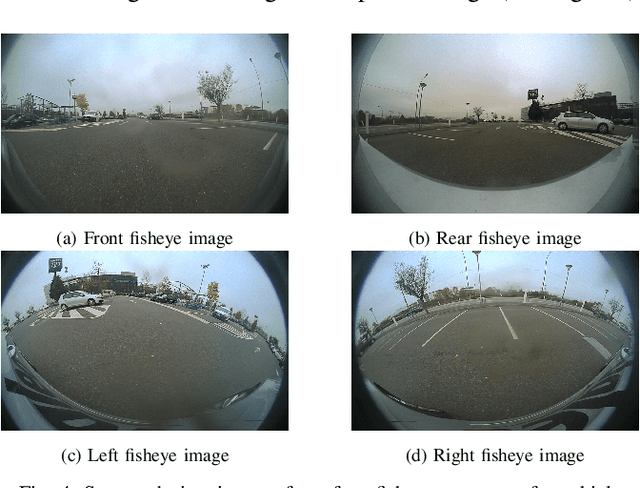
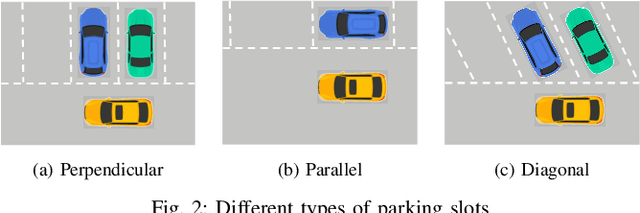
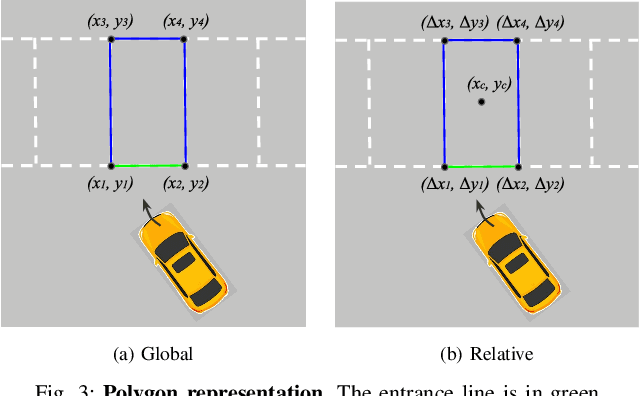

Abstract:Current parking slot detection in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) primarily relies on ultrasonic sensors. This method has several limitations such as the need to scan the entire parking slot before detecting it, the incapacity of detecting multiple slots in a row, and the difficulty of classifying them. Due to the complex visual environment, vehicles are equipped with surround view camera systems to detect vacant parking slots. Previous research works in this field mostly use image-domain models to solve the problem. These two-stage approaches separate the 2D detection and 3D pose estimation steps using camera calibration. In this paper, we propose one-step Holistic Parking Slot Network (HPS-Net), a tailor-made adaptation of the You Only Look Once (YOLO)v4 algorithm. This camera-based approach directly outputs the four vertex coordinates of the parking slot in topview domain, instead of a bounding box in raw camera images. Several visible points and shapes can be proposed from different angles. A novel regression loss function named polygon-corner Generalized Intersection over Union (GIoU) for polygon vertex position optimization is also proposed to manage the slot orientation and to distinguish the entrance line. Experiments show that HPS-Net can detect various vacant parking slots with a F1-score of 0.92 on our internal Valeo Parking Slots Dataset (VPSD) and 0.99 on the public dataset PS2.0. It provides a satisfying generalization and robustness in various parking scenarios, such as indoor (F1: 0.86) or paved ground (F1: 0.91). Moreover, it achieves a real-time detection speed of 17 FPS on Nvidia Drive AGX Xavier. A demo video can be found at https://streamable.com/75j7sj.
Multi-Task Network Pruning and Embedded Optimization for Real-time Deployment in ADAS
Jan 19, 2021
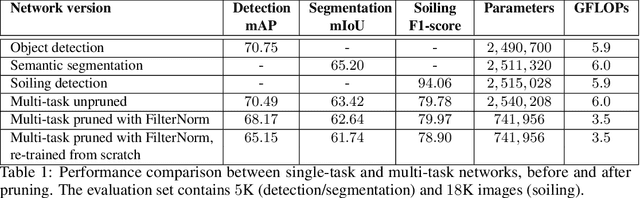
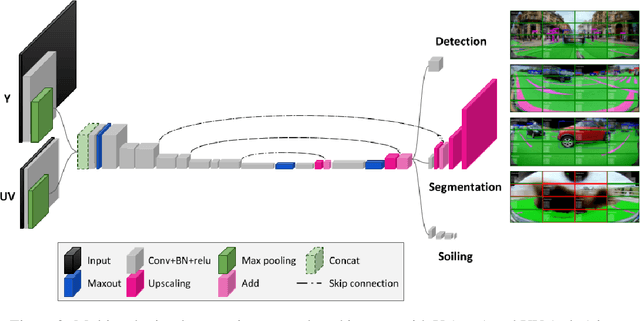
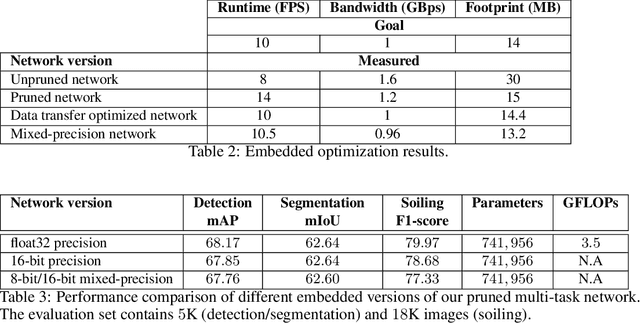
Abstract:Camera-based Deep Learning algorithms are increasingly needed for perception in Automated Driving systems. However, constraints from the automotive industry challenge the deployment of CNNs by imposing embedded systems with limited computational resources. In this paper, we propose an approach to embed a multi-task CNN network under such conditions on a commercial prototype platform, i.e. a low power System on Chip (SoC) processing four surround-view fisheye cameras at 10 FPS. The first focus is on designing an efficient and compact multi-task network architecture. Secondly, a pruning method is applied to compress the CNN, helping to reduce the runtime and memory usage by a factor of 2 without lowering the performances significantly. Finally, several embedded optimization techniques such as mixed-quantization format usage and efficient data transfers between different memory areas are proposed to ensure real-time execution and avoid bandwidth bottlenecks. The approach is evaluated on the hardware platform, considering embedded detection performances, runtime and memory bandwidth. Unlike most works from the literature that focus on classification task, we aim here to study the effect of pruning and quantization on a compact multi-task network with object detection, semantic segmentation and soiling detection tasks.
YUVMultiNet: Real-time YUV multi-task CNN for autonomous driving
Apr 11, 2019
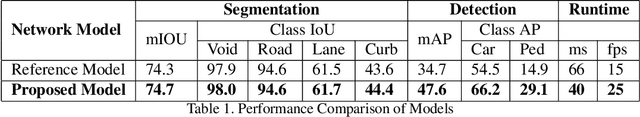
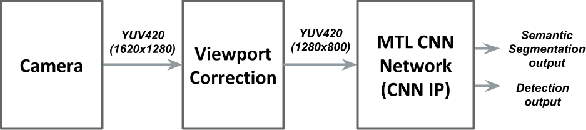
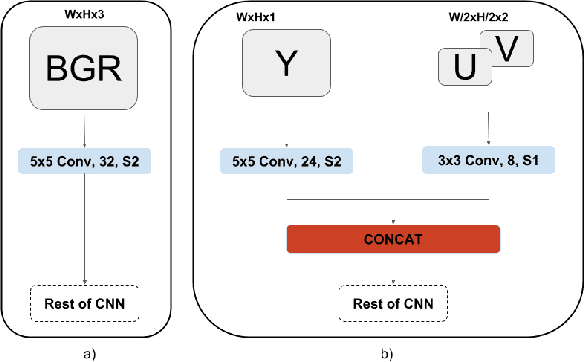
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a multi-task convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture optimized for a low power automotive grade SoC. We introduce a network based on a unified architecture where the encoder is shared among the two tasks namely detection and segmentation. The pro-posed network runs at 25FPS for 1280x800 resolution. We briefly discuss the methods used to optimize the network architecture such as using native YUV image directly, optimization of layers & feature maps and applying quantization. We also focus on memory bandwidth in our design as convolutions are data intensives and most SOCs are bandwidth bottlenecked. We then demonstrate the efficiency of our proposed network for a dedicated CNN accelerators presenting the key performance indicators (KPI) for the detection and segmentation tasks obtained from the hardware execution and the corresponding run-time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge