Thibault de Surrel
A probabilistic view on Riemannian machine learning models for SPD matrices
May 05, 2025Abstract:The goal of this paper is to show how different machine learning tools on the Riemannian manifold $\mathcal{P}_d$ of Symmetric Positive Definite (SPD) matrices can be united under a probabilistic framework. For this, we will need several Gaussian distributions defined on $\mathcal{P}_d$. We will show how popular classifiers on $\mathcal{P}_d$ can be reinterpreted as Bayes Classifiers using these Gaussian distributions. These distributions will also be used for outlier detection and dimension reduction. By showing that those distributions are pervasive in the tools used on $\mathcal{P}_d$, we allow for other machine learning tools to be extended to $\mathcal{P}_d$.
Wrapped Gaussian on the manifold of Symmetric Positive Definite Matrices
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Circular and non-flat data distributions are prevalent across diverse domains of data science, yet their specific geometric structures often remain underutilized in machine learning frameworks. A principled approach to accounting for the underlying geometry of such data is pivotal, particularly when extending statistical models, like the pervasive Gaussian distribution. In this work, we tackle those issue by focusing on the manifold of symmetric positive definite matrices, a key focus in information geometry. We introduced a non-isotropic wrapped Gaussian by leveraging the exponential map, we derive theoretical properties of this distribution and propose a maximum likelihood framework for parameter estimation. Furthermore, we reinterpret established classifiers on SPD through a probabilistic lens and introduce new classifiers based on the wrapped Gaussian model. Experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the robustness and flexibility of this geometry-aware distribution, underscoring its potential to advance manifold-based data analysis. This work lays the groundwork for extending classical machine learning and statistical methods to more complex and structured data.
RipsNet: a general architecture for fast and robust estimation of the persistent homology of point clouds
Feb 04, 2022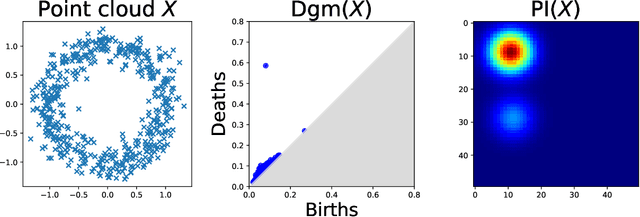
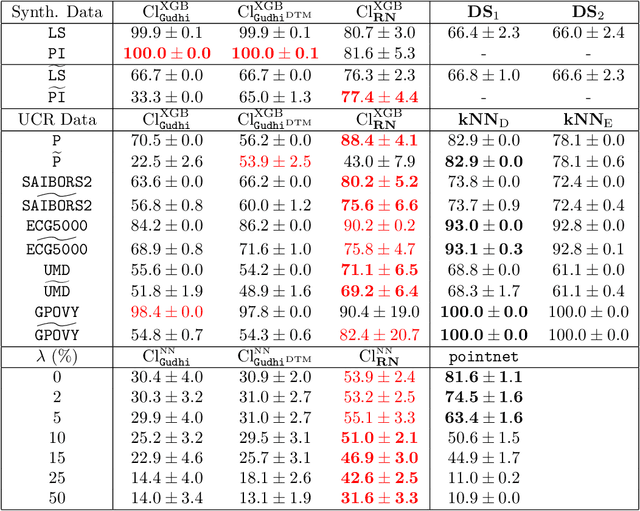

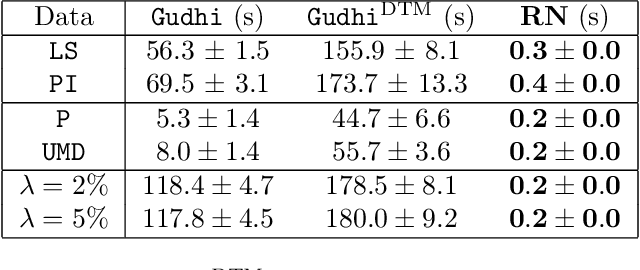
Abstract:The use of topological descriptors in modern machine learning applications, such as Persistence Diagrams (PDs) arising from Topological Data Analysis (TDA), has shown great potential in various domains. However, their practical use in applications is often hindered by two major limitations: the computational complexity required to compute such descriptors exactly, and their sensitivity to even low-level proportions of outliers. In this work, we propose to bypass these two burdens in a data-driven setting by entrusting the estimation of (vectorization of) PDs built on top of point clouds to a neural network architecture that we call RipsNet. Once trained on a given data set, RipsNet can estimate topological descriptors on test data very efficiently with generalization capacity. Furthermore, we prove that RipsNet is robust to input perturbations in terms of the 1-Wasserstein distance, a major improvement over the standard computation of PDs that only enjoys Hausdorff stability, yielding RipsNet to substantially outperform exactly-computed PDs in noisy settings. We showcase the use of RipsNet on both synthetic and real-world data. Our open-source implementation is publicly available at https://github.com/hensel-f/ripsnet and will be included in the Gudhi library.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge