Theodore Kim
Robust automated calcification meshing for biomechanical cardiac digital twins
Mar 08, 2024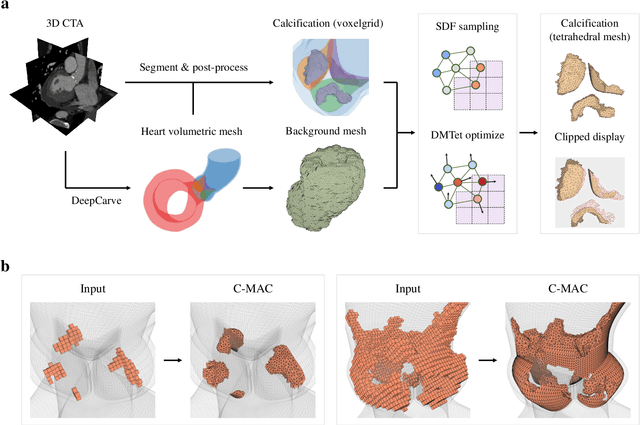
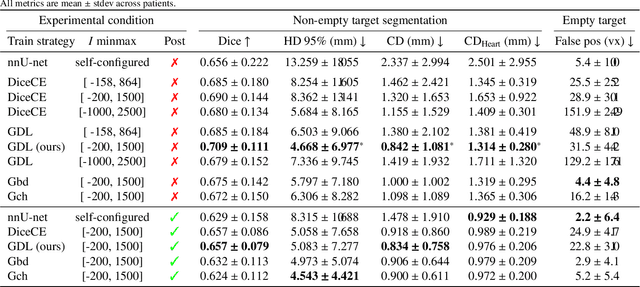
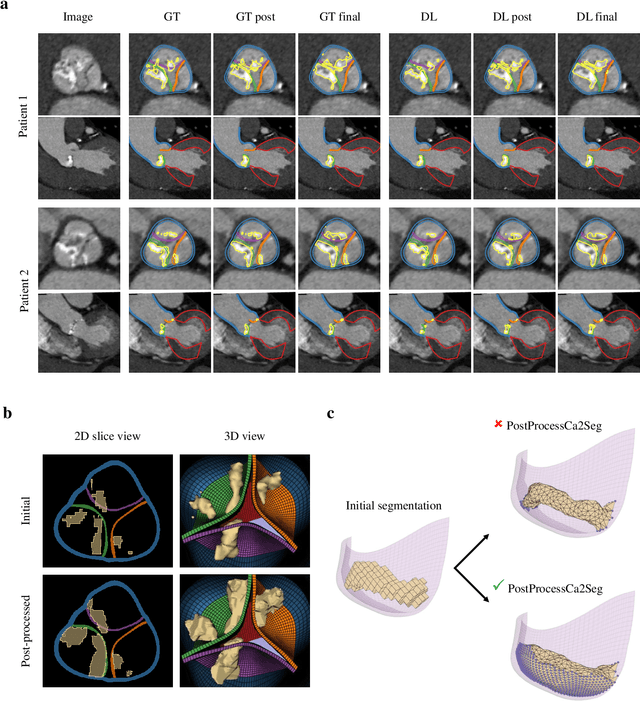
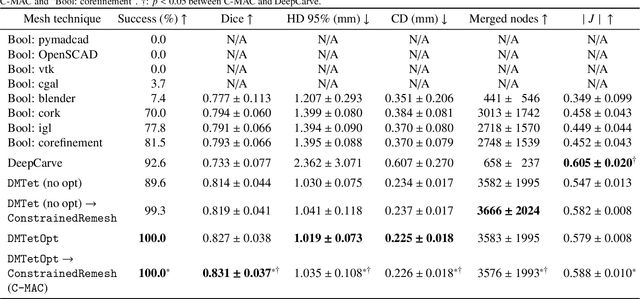
Abstract:Calcification has significant influence over cardiovascular diseases and interventions. Detailed characterization of calcification is thus desired for predictive modeling, but calcified heart meshes for physics-driven simulations are still often reconstructed using manual operations. This poses a major bottleneck for large-scale adoption of computational simulations for research or clinical use. To address this, we propose an end-to-end automated meshing algorithm that enables robust incorporation of patient-specific calcification onto a given heart mesh. The algorithm provides a substantial speed-up from several hours of manual meshing to $\sim$1 minute of automated computation, and it solves an important problem that cannot be addressed with recent template registration-based heart meshing techniques. We validated our final calcified heart meshes with extensive simulations, demonstrating our ability to accurately model patient-specific aortic stenosis and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. Our method may serve as an important tool for accelerating the development and usage of physics-driven simulations for cardiac digital twins.
Deep Fluids: A Generative Network for Parameterized Fluid Simulations
Jun 06, 2018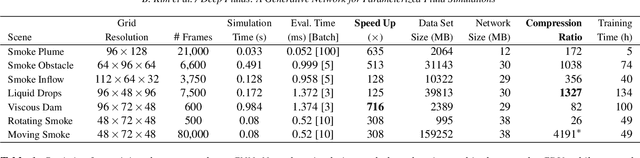

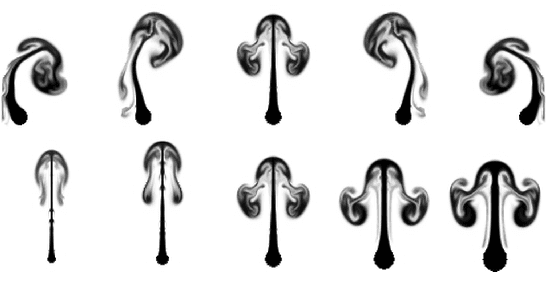
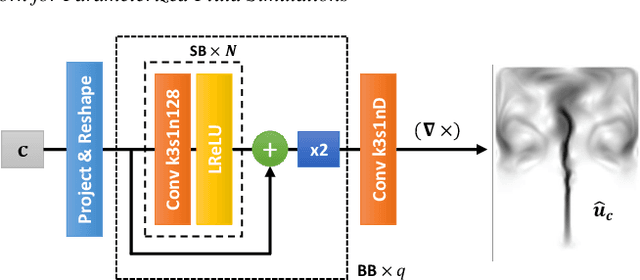
Abstract:This paper presents a novel generative model to synthesize fluid simulations from a set of reduced parameters. A convolutional neural network is trained on a collection of discrete, parameterizable fluid simulation velocity fields. Due to the capability of deep learning architectures to learn representative features of the data, our generative model is able to accurately approximate the training data set, while providing plausible interpolated in-betweens. The proposed generative model is optimized for fluids by a novel loss function that guarantees divergence-free velocity fields at all times. In addition, we demonstrate that we can handle complex parameterizations in reduced spaces, and advance simulations in time by integrating in the latent space with a second network. Our method models a wide variety of fluid behaviors, thus enabling applications such as fast construction of simulations, interpolation of fluids with different parameters, time re-sampling, latent space simulations, and compression of fluid simulation data. Reconstructed velocity fields are generated up to 700x faster than traditional CPU solvers, while achieving compression rates of over 1300x.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge