Tengrong Su
Competitive Wakeup Scheme for Distributed Devices
May 19, 2020



Abstract:Wakeup is the primary function in voice interaction which is the mainstream scheme in man-machine interaction (HMI) applications for smart home. All devices will response if the same wake-up word is used for all devices. This will bring chaos and reduce user quality of experience (QoE). The only way to solve this problem is to make all the devices in the same wireless local area network (WLAN) competing to wake-up based on the same scoring rule. The one closest to the user would be selected for response. To this end, a competitive wakeup scheme is proposed in this paper with elaborately designed calibration method for receiving energy of microphones. Moreover, the user orientation is assisted to determine the optimal device. Experiments reveal the feasibility and validity of this scheme.
A Lite Microphone Array Beamforming Scheme with Maximum Signal-to-Noise Ratio Filter
May 19, 2020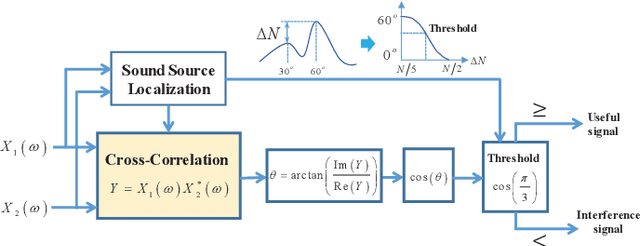
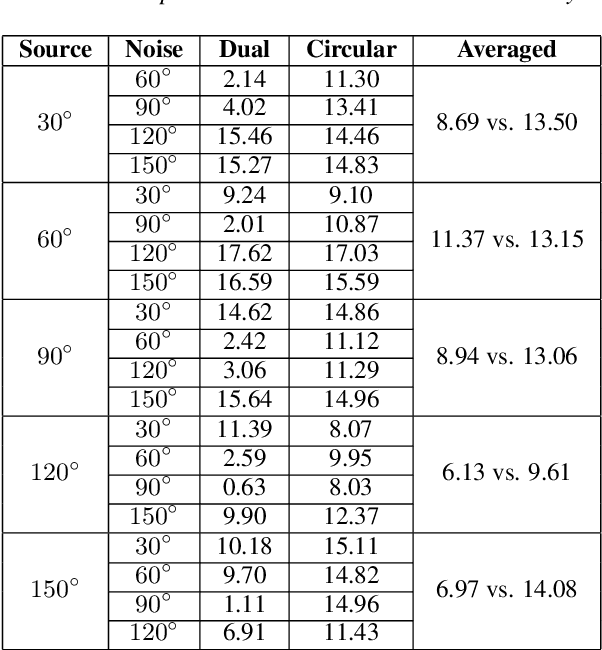
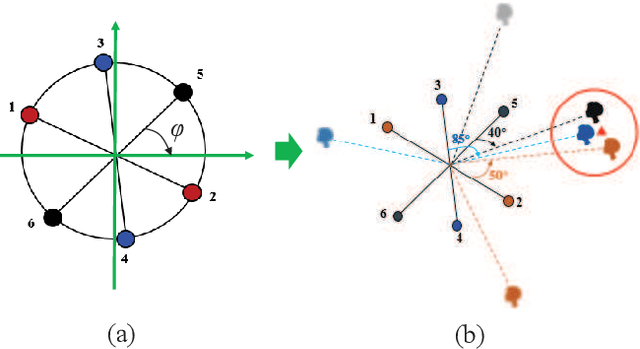
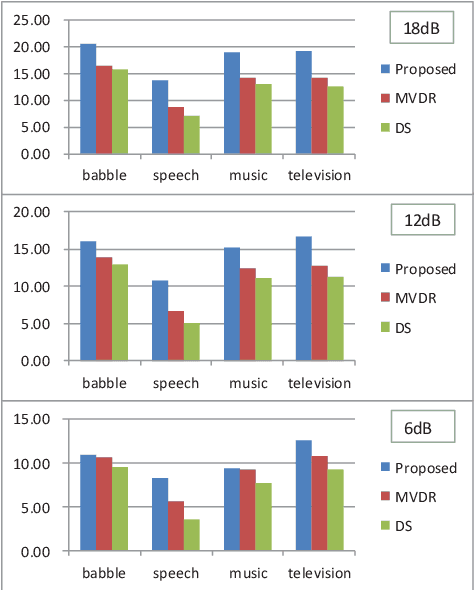
Abstract:Since space-domain information can be utilized, microphone array beamforming is often used to enhance the quality of the speech by suppressing directional disturbance. However, with the increasing number of microphone, the complexity would be increased. In this paper, a concise beamforming scheme using Maximum Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) filter is proposed to reduce the beamforming complexity. The maximum SNR filter is implemented by using the estimated direction-of-arrival (DOA) of the speech source localization (SSL) and the solving method of independent vector analysis (IVA). Our experiments show that when compared with other widely-used algorithms, the proposed algorithm obtain higher gain of signal-to-interference and noise ratio (SINR).
Acoustic Echo Cancellation by Combining Adaptive Digital Filter and Recurrent Neural Network
May 19, 2020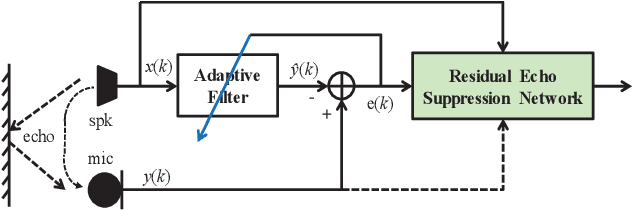
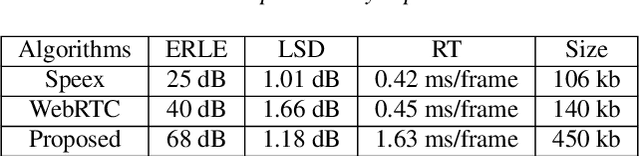
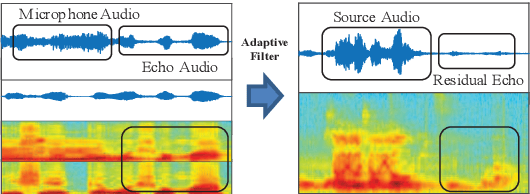
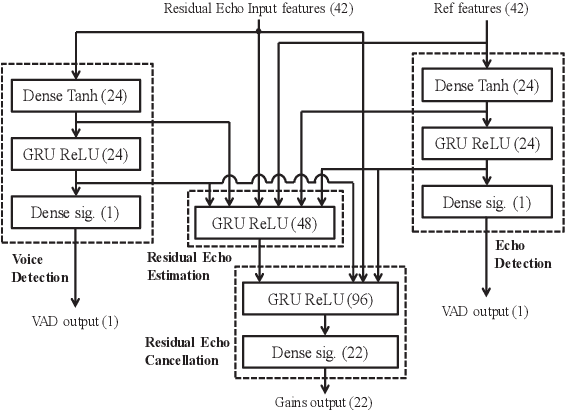
Abstract:Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) plays a key role in voice interaction. Due to the explicit mathematical principle and intelligent nature to accommodate conditions, adaptive filters with different types of implementations are always used for AEC, giving considerable performance. However, there would be some kinds of residual echo in the results, including linear residue introduced by mismatching between estimation and the reality and non-linear residue mostly caused by non-linear components on the audio devices. The linear residue can be reduced with elaborate structure and methods, leaving the non-linear residue intractable for suppression. Though, some non-linear processing methods have already be raised, they are complicated and inefficient for suppression, and would bring damage to the speech audio. In this paper, a fusion scheme by combining adaptive filter and neural network is proposed for AEC. The echo could be reduced in a large scale by adaptive filtering, resulting in little residual echo. Though it is much smaller than speech audio, it could also be perceived by human ear and would make communication annoy. The neural network is elaborately designed and trained for suppressing such residual echo. Experiments compared with prevailing methods are conducted, validating the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed combination scheme.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge