Temma Choji
ULTRA: Unleash LLMs' Potential for Event Argument Extraction through Hierarchical Modeling and Pair-wise Refinement
Jan 24, 2024


Abstract:Structural extraction of events within discourse is critical since it avails a deeper understanding of communication patterns and behavior trends. Event argument extraction (EAE), at the core of event-centric understanding, is the task of identifying role-specific text spans (i.e., arguments) for a given event. Document-level EAE (DocEAE) focuses on arguments that are scattered across an entire document. In this work, we explore the capabilities of open source Large Language Models (LLMs), i.e., Flan-UL2, for the DocEAE task. To this end, we propose ULTRA, a hierarchical framework that extracts event arguments more cost-effectively -- the method needs as few as 50 annotations and doesn't require hitting costly API endpoints. Further, it alleviates the positional bias issue intrinsic to LLMs. ULTRA first sequentially reads text chunks of a document to generate a candidate argument set, upon which ULTRA learns to drop non-pertinent candidates through self-refinement. We further introduce LEAFER to address the challenge LLMs face in locating the exact boundary of an argument span. ULTRA outperforms strong baselines, which include strong supervised models and ChatGPT, by 9.8% when evaluated by the exact match (EM) metric.
Don't Retrain, Just Rewrite: Countering Adversarial Perturbations by Rewriting Text
May 25, 2023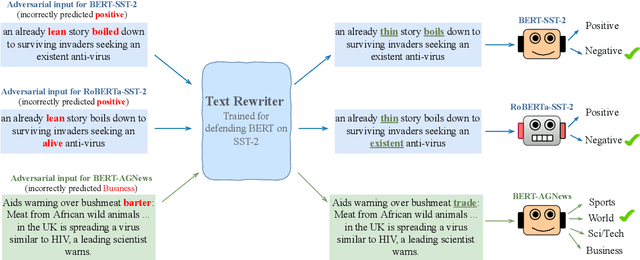
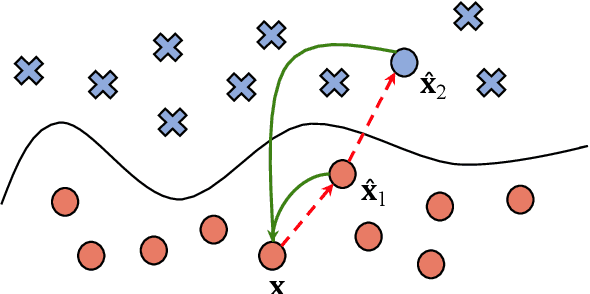
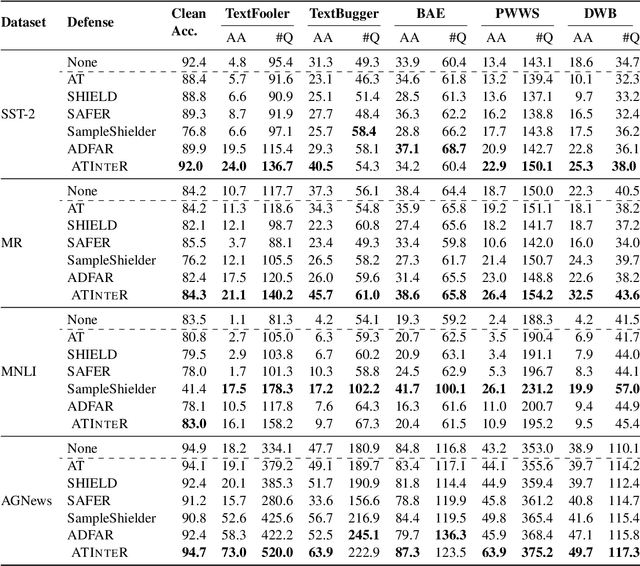
Abstract:Can language models transform inputs to protect text classifiers against adversarial attacks? In this work, we present ATINTER, a model that intercepts and learns to rewrite adversarial inputs to make them non-adversarial for a downstream text classifier. Our experiments on four datasets and five attack mechanisms reveal that ATINTER is effective at providing better adversarial robustness than existing defense approaches, without compromising task accuracy. For example, on sentiment classification using the SST-2 dataset, our method improves the adversarial accuracy over the best existing defense approach by more than 4% with a smaller decrease in task accuracy (0.5% vs 2.5%). Moreover, we show that ATINTER generalizes across multiple downstream tasks and classifiers without having to explicitly retrain it for those settings. Specifically, we find that when ATINTER is trained to remove adversarial perturbations for the sentiment classification task on the SST-2 dataset, it even transfers to a semantically different task of news classification (on AGNews) and improves the adversarial robustness by more than 10%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge