Tatsuya Kobayashi
Full reference point cloud quality assessment using support vector regression
Jun 15, 2024



Abstract:Point clouds are a general format for representing realistic 3D objects in diverse 3D applications. Since point clouds have large data sizes, developing efficient point cloud compression methods is crucial. However, excessive compression leads to various distortions, which deteriorates the point cloud quality perceived by end users. Thus, establishing reliable point cloud quality assessment (PCQA) methods is essential as a benchmark to develop efficient compression methods. This paper presents an accurate full-reference point cloud quality assessment (FR-PCQA) method called full-reference quality assessment using support vector regression (FRSVR) for various types of degradations such as compression distortion, Gaussian noise, and down-sampling. The proposed method demonstrates accurate PCQA by integrating five FR-based metrics covering various types of errors (e.g., considering geometric distortion, color distortion, and point count) using support vector regression (SVR). Moreover, the proposed method achieves a superior trade-off between accuracy and calculation speed because it includes only the calculation of these five simple metrics and SVR, which can perform fast prediction. Experimental results with three types of open datasets show that the proposed method is more accurate than conventional FR-PCQA methods. In addition, the proposed method is faster than state-of-the-art methods that utilize complicated features such as curvature and multi-scale features. Thus, the proposed method provides excellent performance in terms of the accuracy of PCQA and processing speed. Our method is available from https://github.com/STAC-USC/FRSVR-PCQA.
Fast graph-based denoising for point cloud color information
Jan 19, 2024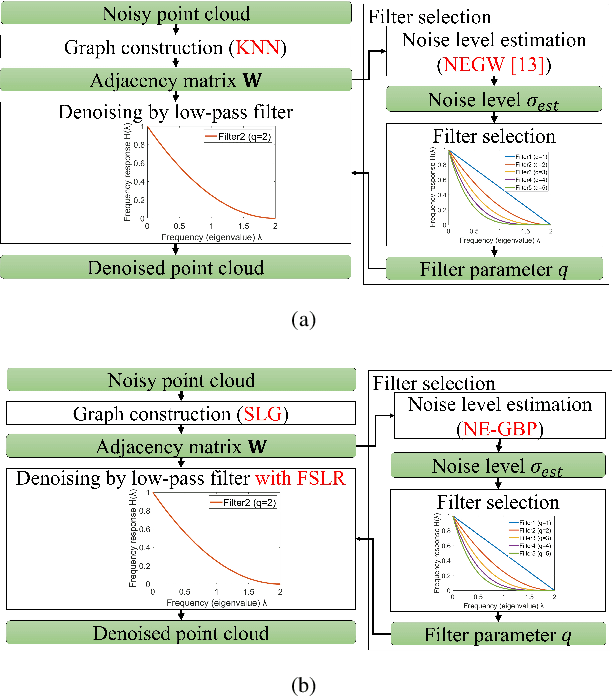
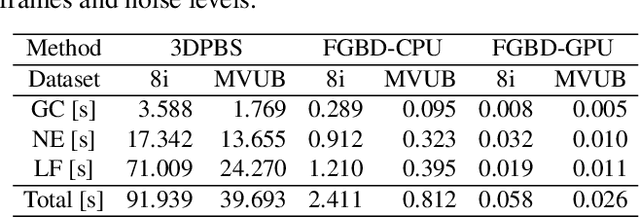
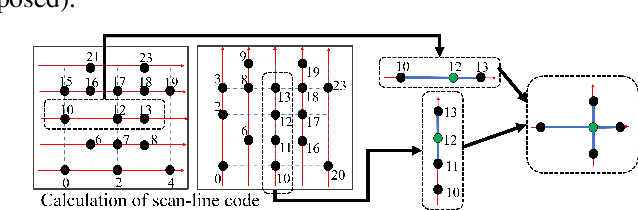
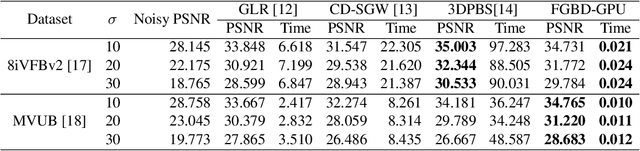
Abstract:Point clouds are utilized in various 3D applications such as cross-reality (XR) and realistic 3D displays. In some applications, e.g., for live streaming using a 3D point cloud, real-time point cloud denoising methods are required to enhance the visual quality. However, conventional high-precision denoising methods cannot be executed in real time for large-scale point clouds owing to the complexity of graph constructions with K nearest neighbors and noise level estimation. This paper proposes a fast graph-based denoising (FGBD) for a large-scale point cloud. First, high-speed graph construction is achieved by scanning a point cloud in various directions and searching adjacent neighborhoods on the scanning lines. Second, we propose a fast noise level estimation method using eigenvalues of the covariance matrix on a graph. Finally, we also propose a new low-cost filter selection method to enhance denoising accuracy to compensate for the degradation caused by the acceleration algorithms. In our experiments, we succeeded in reducing the processing time dramatically while maintaining accuracy relative to conventional denoising methods. Denoising was performed at 30fps, with frames containing approximately 1 million points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge