Tatiana Khanova
SceneCAD: Predicting Object Alignments and Layouts in RGB-D Scans
Mar 27, 2020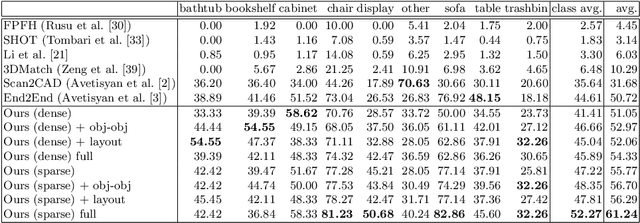
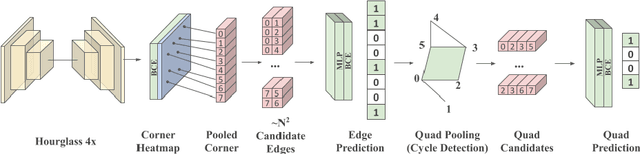
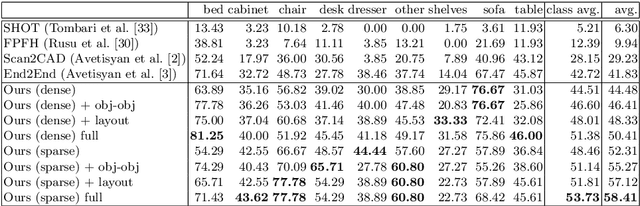
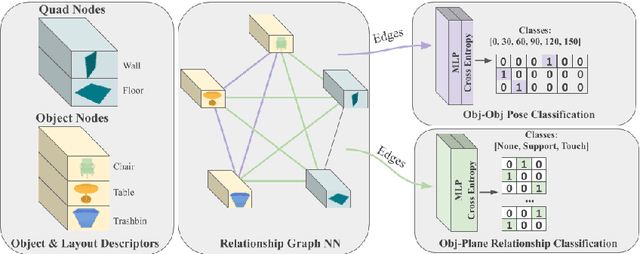
Abstract:We present a novel approach to reconstructing lightweight, CAD-based representations of scanned 3D environments from commodity RGB-D sensors. Our key idea is to jointly optimize for both CAD model alignments as well as layout estimations of the scanned scene, explicitly modeling inter-relationships between objects-to-objects and objects-to-layout. Since object arrangement and scene layout are intrinsically coupled, we show that treating the problem jointly significantly helps to produce globally-consistent representations of a scene. Object CAD models are aligned to the scene by establishing dense correspondences between geometry, and we introduce a hierarchical layout prediction approach to estimate layout planes from corners and edges of the scene.To this end, we propose a message-passing graph neural network to model the inter-relationships between objects and layout, guiding generation of a globally object alignment in a scene. By considering the global scene layout, we achieve significantly improved CAD alignments compared to state-of-the-art methods, improving from 41.83% to 58.41% alignment accuracy on SUNCG and from 50.05% to 61.24% on ScanNet, respectively. The resulting CAD-based representations makes our method well-suited for applications in content creation such as augmented- or virtual reality.
Towards lightweight convolutional neural networks for object detection
Oct 05, 2017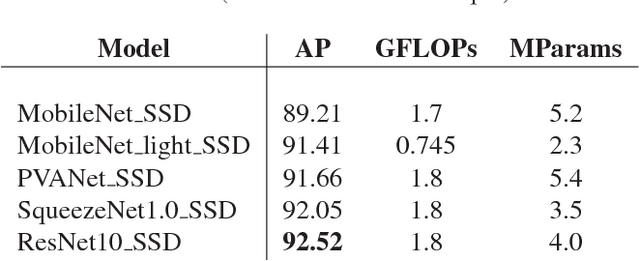



Abstract:We propose model with larger spatial size of feature maps and evaluate it on object detection task. With the goal to choose the best feature extraction network for our model we compare several popular lightweight networks. After that we conduct a set of experiments with channels reduction algorithms in order to accelerate execution. Our vehicle detection models are accurate, fast and therefore suit for embedded visual applications. With only 1.5 GFLOPs our best model gives 93.39 AP on validation subset of challenging DETRAC dataset. The smallest of our models is the first to achieve real-time inference speed on CPU with reasonable accuracy drop to 91.43 AP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge