Tatiana Agback
Towards Ultimate NMR Resolution with Deep Learning
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:In multidimensional NMR spectroscopy, practical resolution is defined as the ability to distinguish and accurately determine signal positions against a background of overlapping peaks, thermal noise, and spectral artifacts. In the pursuit of ultimate resolution, we introduce Peak Probability Presentations ($P^3$)- a statistical spectral representation that assigns a probability to each spectral point, indicating the likelihood of a peak maximum occurring at that location. The mapping between the spectrum and $P^3$ is achieved using MR-Ai, a physics-inspired deep learning neural network architecture, designed to handle multidimensional NMR spectra. Furthermore, we demonstrate that MR-Ai enables coprocessing of multiple spectra, facilitating direct information exchange between datasets. This feature significantly enhances spectral quality, particularly in cases of highly sparse sampling. Performance of MR-Ai and high value of the $P^3$ are demonstrated on the synthetic data and spectra of Tau, MATL1, Calmodulin, and several other proteins.
Resolution enhancement of NMR by decoupling with low-rank Hankel model
Dec 02, 2022

Abstract:Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has become a formidable tool for biochemistry and medicine. Although J-coupling carries essential structural information it may also limit the spectral resolution. Homonuclear decoupling remains a challenging problem. In this work, we introduce a new approach that uses a specific coupling value as prior knowledge, and Hankel property of exponential NMR signal to achieve the broadband heteronuclear decoupling using the low-rank method. Our results on synthetic and realistic HMQC spectra demonstrate that the proposed method not only effectively enhances resolution by decoupling, but also maintains sensitivity and suppresses spectral artefacts. The approach can be combined with the non-uniform sampling, which means that the resolution can be further improved without any extra acquisition time
Accelerated Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy with Deep Learning
May 14, 2019
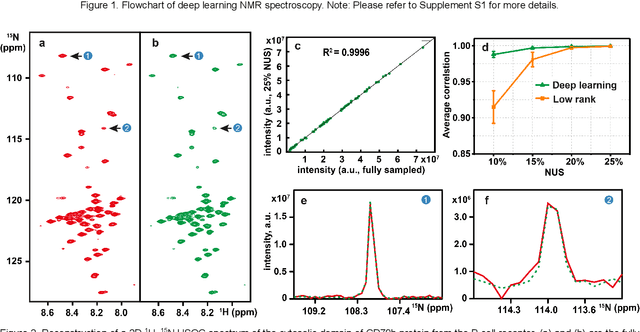
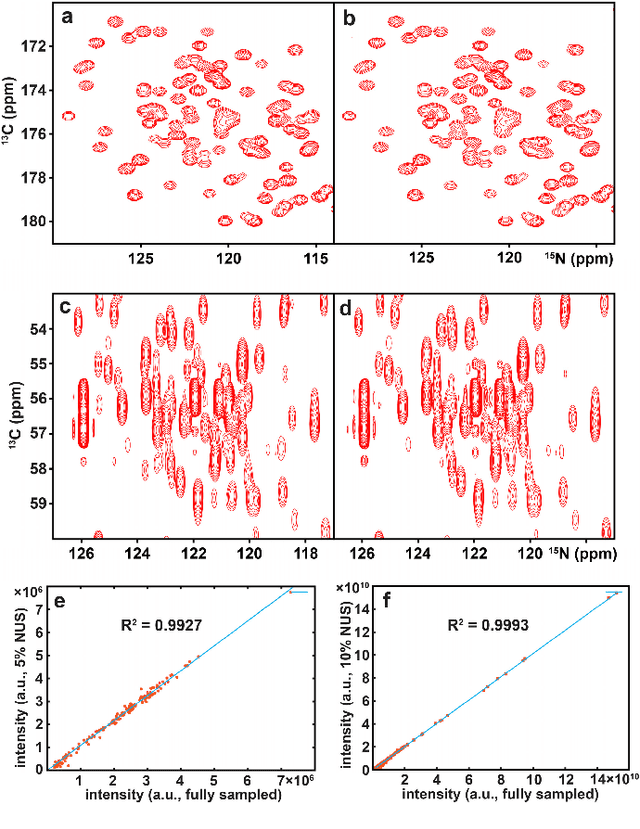

Abstract:Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy serves as an indispensable tool in chemistry and biology but often suffers from long experimental time. We present a proof-of-concept of application of deep learning and neural network for high-quality, reliable, and very fast NMR spectra reconstruction from limited experimental data. We show that the neural network training can be achieved using solely synthetic NMR signal, which lifts the prohibiting demand for a large volume of realistic training data usually required in the deep learning approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge