Tapas Kumar Mishra
Comparative analysis of subword tokenization approaches for Indian languages
May 22, 2025Abstract:Tokenization is the act of breaking down text into smaller parts, or tokens, that are easier for machines to process. This is a key phase in machine translation (MT) models. Subword tokenization enhances this process by breaking down words into smaller subword units, which is especially beneficial in languages with complicated morphology or a vast vocabulary. It is useful in capturing the intricate structure of words in Indian languages (ILs), such as prefixes, suffixes, and other morphological variations. These languages frequently use agglutinative structures, in which words are formed by the combination of multiple morphemes such as suffixes, prefixes, and stems. As a result, a suitable tokenization strategy must be chosen to address these scenarios. This paper examines how different subword tokenization techniques, such as SentencePiece, Byte Pair Encoding (BPE), and WordPiece Tokenization, affect ILs. The effectiveness of these subword tokenization techniques is investigated in statistical, neural, and multilingual neural machine translation models. All models are examined using standard evaluation metrics, such as the Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) score, TER, METEOR, CHRF, RIBES, and COMET. Based on the results, it appears that for the majority of language pairs for the Statistical and Neural MT models, the SentencePiece tokenizer continuously performed better than other tokenizers in terms of BLEU score. However, BPE tokenization outperformed other tokenization techniques in the context of Multilingual Neural Machine Translation model. The results show that, despite using the same tokenizer and dataset for each model, translations from ILs to English surpassed translations from English to ILs.
Novel Human Machine Interface via Robust Hand Gesture Recognition System using Channel Pruned YOLOv5s Model
Jul 02, 2024Abstract:Hand gesture recognition (HGR) is a vital component in enhancing the human-computer interaction experience, particularly in multimedia applications, such as virtual reality, gaming, smart home automation systems, etc. Users can control and navigate through these applications seamlessly by accurately detecting and recognizing gestures. However, in a real-time scenario, the performance of the gesture recognition system is sometimes affected due to the presence of complex background, low-light illumination, occlusion problems, etc. Another issue is building a fast and robust gesture-controlled human-computer interface (HCI) in the real-time scenario. The overall objective of this paper is to develop an efficient hand gesture detection and classification model using a channel-pruned YOLOv5-small model and utilize the model to build a gesture-controlled HCI with a quick response time (in ms) and higher detection speed (in fps). First, the YOLOv5s model is chosen for the gesture detection task. Next, the model is simplified by using a channel-pruned algorithm. After that, the pruned model is further fine-tuned to ensure detection efficiency. We have compared our suggested scheme with other state-of-the-art works, and it is observed that our model has shown superior results in terms of mAP (mean average precision), precision (\%), recall (\%), and F1-score (\%), fast inference time (in ms), and detection speed (in fps). Our proposed method paves the way for deploying a pruned YOLOv5s model for a real-time gesture-command-based HCI to control some applications, such as the VLC media player, Spotify player, etc., using correctly classified gesture commands in real-time scenarios. The average detection speed of our proposed system has reached more than 60 frames per second (fps) in real-time, which meets the perfect requirement in real-time application control.
An approach for mistranslation removal from popular dataset for Indic MT Task
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:The conversion of content from one language to another utilizing a computer system is known as Machine Translation (MT). Various techniques have come up to ensure effective translations that retain the contextual and lexical interpretation of the source language. End-to-end Neural Machine Translation (NMT) is a popular technique and it is now widely used in real-world MT systems. Massive amounts of parallel datasets (sentences in one language alongside translations in another) are required for MT systems. These datasets are crucial for an MT system to learn linguistic structures and patterns of both languages during the training phase. One such dataset is Samanantar, the largest publicly accessible parallel dataset for Indian languages (ILs). Since the corpus has been gathered from various sources, it contains many incorrect translations. Hence, the MT systems built using this dataset cannot perform to their usual potential. In this paper, we propose an algorithm to remove mistranslations from the training corpus and evaluate its performance and efficiency. Two Indic languages (ILs), namely, Hindi (HIN) and Odia (ODI) are chosen for the experiment. A baseline NMT system is built for these two ILs, and the effect of different dataset sizes is also investigated. The quality of the translations in the experiment is evaluated using standard metrics such as BLEU, METEOR, and RIBES. From the results, it is observed that removing the incorrect translation from the dataset makes the translation quality better. It is also noticed that, despite the fact that the ILs-English and English-ILs systems are trained using the same corpus, ILs-English works more effectively across all the evaluation metrics.
Multilingual Neural Machine Translation System for Indic to Indic Languages
Jun 22, 2023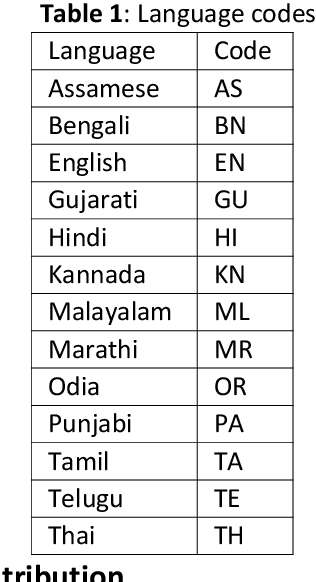
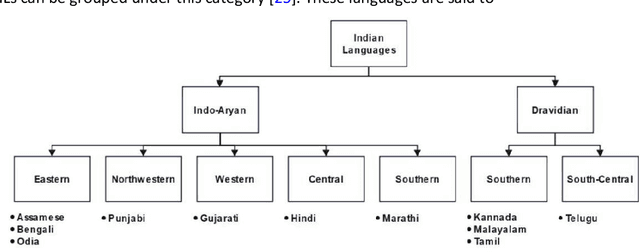
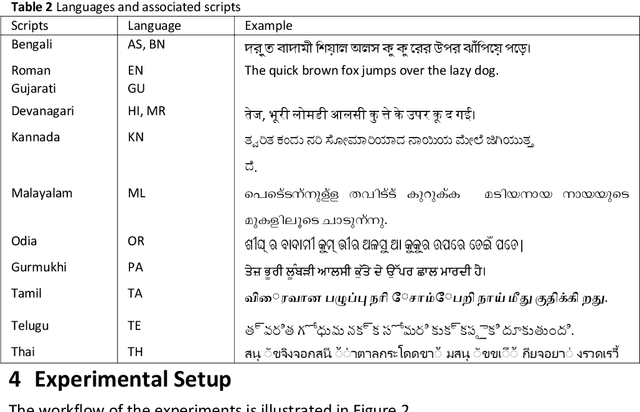
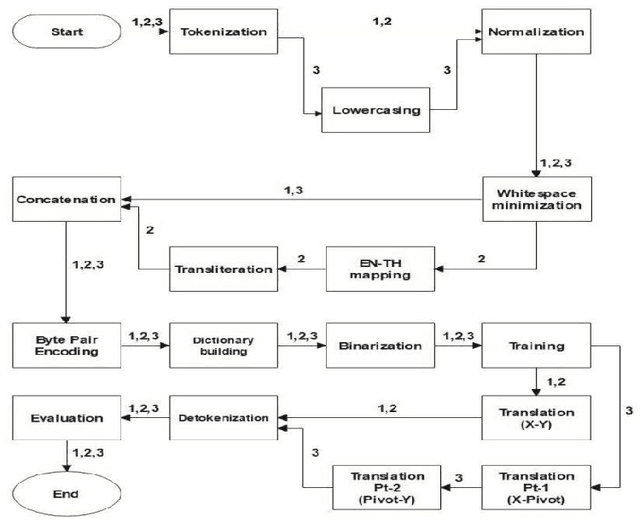
Abstract:This paper gives an Indic-to-Indic (IL-IL) MNMT baseline model for 11 ILs implemented on the Samanantar corpus and analyzed on the Flores-200 corpus. All the models are evaluated using the BLEU score. In addition, the languages are classified under three groups namely East Indo- Aryan (EI), Dravidian (DR), and West Indo-Aryan (WI). The effect of language relatedness on MNMT model efficiency is studied. Owing to the presence of large corpora from English (EN) to ILs, MNMT IL-IL models using EN as a pivot are also built and examined. To achieve this, English- Indic (EN-IL) models are also developed, with and without the usage of related languages. Results reveal that using related languages is beneficial for the WI group only, while it is detrimental for the EI group and shows an inconclusive effect on the DR group, but it is useful for EN-IL models. Thus, related language groups are used to develop pivot MNMT models. Furthermore, the IL corpora are transliterated from the corresponding scripts to a modified ITRANS script, and the best MNMT models from the previous approaches are built on the transliterated corpus. It is observed that the usage of pivot models greatly improves MNMT baselines with AS-TA achieving the minimum BLEU score and PA-HI achieving the maximum score. Among languages, AS, ML, and TA achieve the lowest BLEU score, whereas HI, PA, and GU perform the best. Transliteration also helps the models with few exceptions. The best increment of scores is observed in ML, TA, and BN and the worst average increment is observed in KN, HI, and PA, across all languages. The best model obtained is the PA-HI language pair trained on PAWI transliterated corpus which gives 24.29 BLEU.
Statistical Machine Translation for Indic Languages
Jan 02, 2023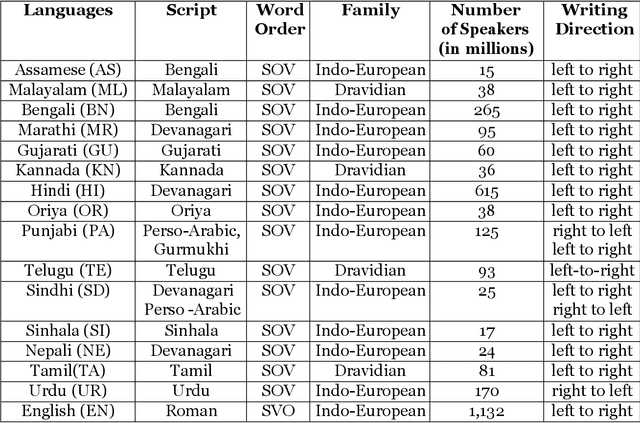
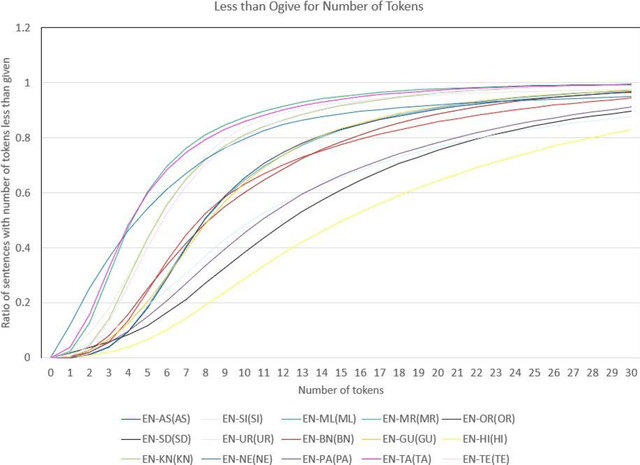
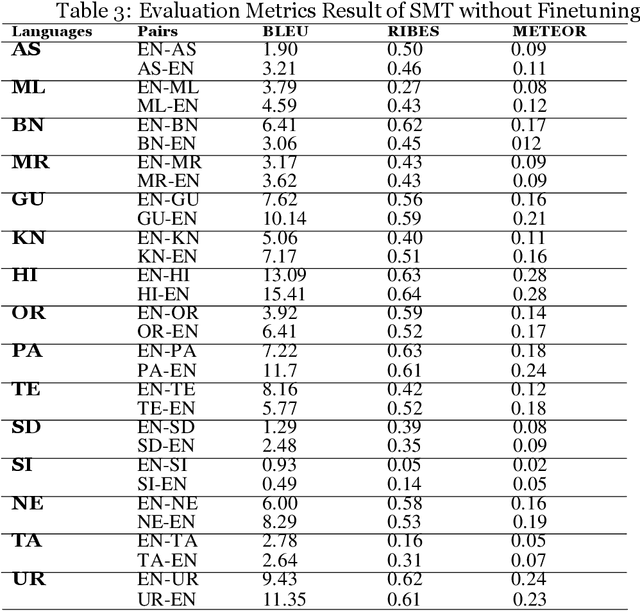
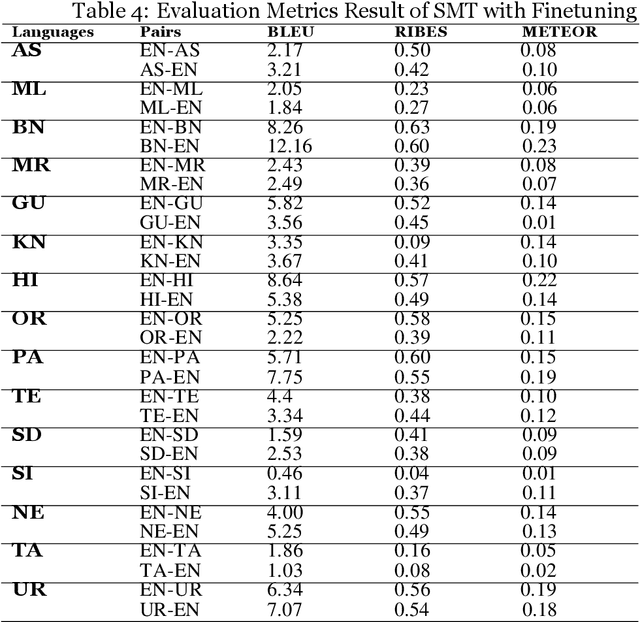
Abstract:Machine Translation (MT) system generally aims at automatic representation of source language into target language retaining the originality of context using various Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques. Among various NLP methods, Statistical Machine Translation(SMT). SMT uses probabilistic and statistical techniques to analyze information and conversion. This paper canvasses about the development of bilingual SMT models for translating English to fifteen low-resource Indian Languages (ILs) and vice versa. At the outset, all 15 languages are briefed with a short description related to our experimental need. Further, a detailed analysis of Samanantar and OPUS dataset for model building, along with standard benchmark dataset (Flores-200) for fine-tuning and testing, is done as a part of our experiment. Different preprocessing approaches are proposed in this paper to handle the noise of the dataset. To create the system, MOSES open-source SMT toolkit is explored. Distance reordering is utilized with the aim to understand the rules of grammar and context-dependent adjustments through a phrase reordering categorization framework. In our experiment, the quality of the translation is evaluated using standard metrics such as BLEU, METEOR, and RIBES
Improving Multilingual Neural Machine Translation System for Indic Languages
Sep 27, 2022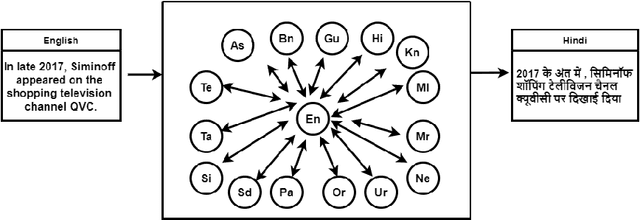
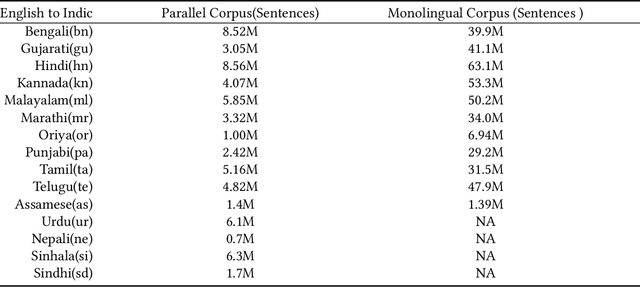
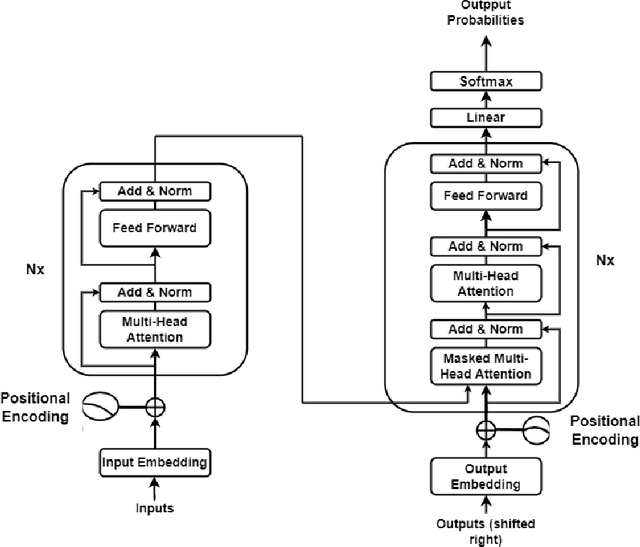
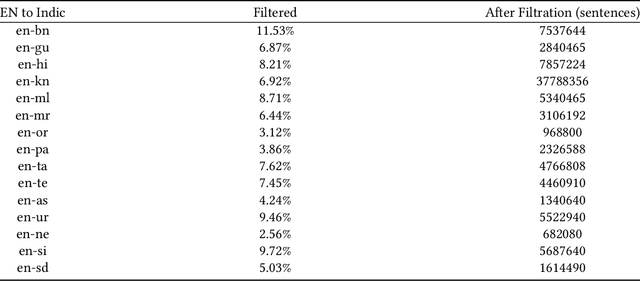
Abstract:Machine Translation System (MTS) serves as an effective tool for communication by translating text or speech from one language to another language. The need of an efficient translation system becomes obvious in a large multilingual environment like India, where English and a set of Indian Languages (ILs) are officially used. In contrast with English, ILs are still entreated as low-resource languages due to unavailability of corpora. In order to address such asymmetric nature, multilingual neural machine translation (MNMT) system evolves as an ideal approach in this direction. In this paper, we propose a MNMT system to address the issues related to low-resource language translation. Our model comprises of two MNMT systems i.e. for English-Indic (one-to-many) and the other for Indic-English (many-to-one) with a shared encoder-decoder containing 15 language pairs (30 translation directions). Since most of IL pairs have scanty amount of parallel corpora, not sufficient for training any machine translation model. We explore various augmentation strategies to improve overall translation quality through the proposed model. A state-of-the-art transformer architecture is used to realize the proposed model. Trials over a good amount of data reveal its superiority over the conventional models. In addition, the paper addresses the use of language relationships (in terms of dialect, script, etc.), particularly about the role of high-resource languages of the same family in boosting the performance of low-resource languages. Moreover, the experimental results also show the advantage of backtranslation and domain adaptation for ILs to enhance the translation quality of both source and target languages. Using all these key approaches, our proposed model emerges to be more efficient than the baseline model in terms of evaluation metrics i.e BLEU (BiLingual Evaluation Understudy) score for a set of ILs.
Design of Human Machine Interface through vision-based low-cost Hand Gesture Recognition system based on deep CNN
Jul 11, 2022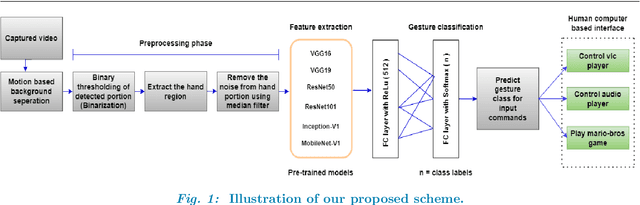
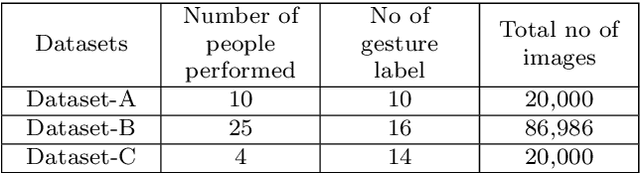


Abstract:In this work, a real-time hand gesture recognition system-based human-computer interface (HCI) is presented. The system consists of six stages: (1) hand detection, (2) gesture segmentation, (3) use of six pre-trained CNN models by using the transfer-learning method, (4) building an interactive human-machine interface, (5) development of a gesture-controlled virtual mouse, (6) use of Kalman filter to estimate the hand position, based on that the smoothness of the motion of pointer is improved. Six pre-trained convolutional neural network (CNN) models (VGG16, VGG19, ResNet50, ResNet101, Inception-V1, and MobileNet-V1) have been used to classify hand gesture images. Three multi-class datasets (two publicly and one custom) have been used to evaluate the model performances. Considering the models' performances, it has been observed that Inception-V1 has significantly shown a better classification performance compared to the other five pre-trained models in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F-score values. The gesture recognition system is expanded and used to control multimedia applications (like VLC player, audio player, file management, playing 2D Super-Mario-Bros game, etc.) with different customized gesture commands in real-time scenarios. The average speed of this system has reached 35 fps (frame per seconds), which meets the requirements for the real-time scenario.
Part-of-Speech Tagging of Odia Language Using statistical and Deep Learning-Based Approaches
Jul 07, 2022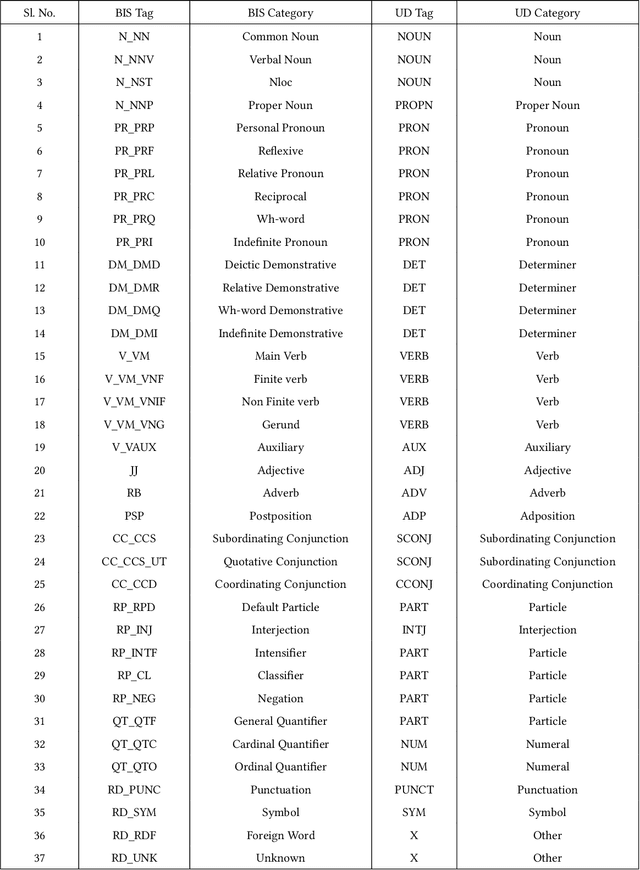
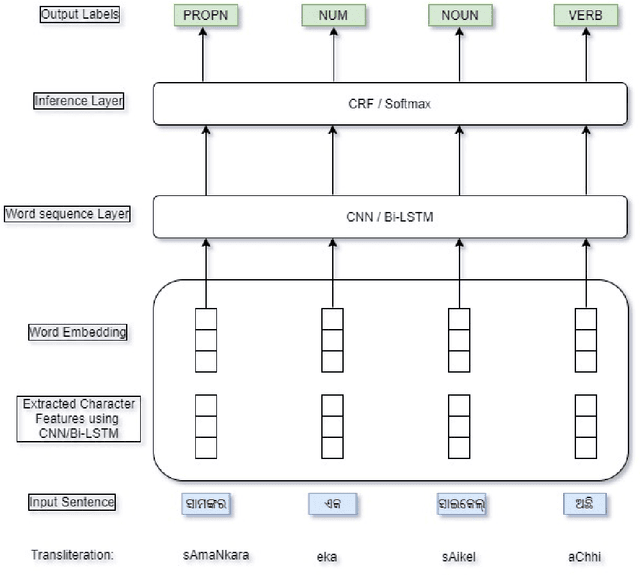

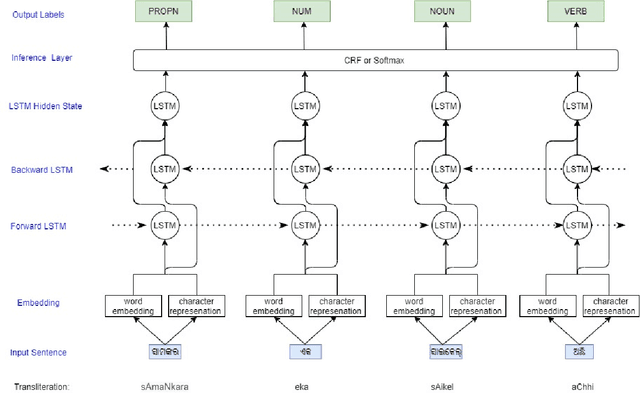
Abstract:Automatic Part-of-speech (POS) tagging is a preprocessing step of many natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as name entity recognition (NER), speech processing, information extraction, word sense disambiguation, and machine translation. It has already gained a promising result in English and European languages, but in Indian languages, particularly in Odia language, it is not yet well explored because of the lack of supporting tools, resources, and morphological richness of language. Unfortunately, we were unable to locate an open source POS tagger for Odia, and only a handful of attempts have been made to develop POS taggers for Odia language. The main contribution of this research work is to present a conditional random field (CRF) and deep learning-based approaches (CNN and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory) to develop Odia part-of-speech tagger. We used a publicly accessible corpus and the dataset is annotated with the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) tagset. However, most of the languages around the globe have used the dataset annotated with Universal Dependencies (UD) tagset. Hence, to maintain uniformity Odia dataset should use the same tagset. So we have constructed a simple mapping from BIS tagset to UD tagset. We experimented with various feature set inputs to the CRF model, observed the impact of constructed feature set. The deep learning-based model includes Bi-LSTM network, CNN network, CRF layer, character sequence information, and pre-trained word vector. Character sequence information was extracted by using convolutional neural network (CNN) and Bi-LSTM network. Six different combinations of neural sequence labelling models are implemented, and their performance measures are investigated. It has been observed that Bi-LSTM model with character sequence feature and pre-trained word vector achieved a significant state-of-the-art result.
A Novel Hand Gesture Detection and Recognition system based on ensemble-based Convolutional Neural Network
Feb 25, 2022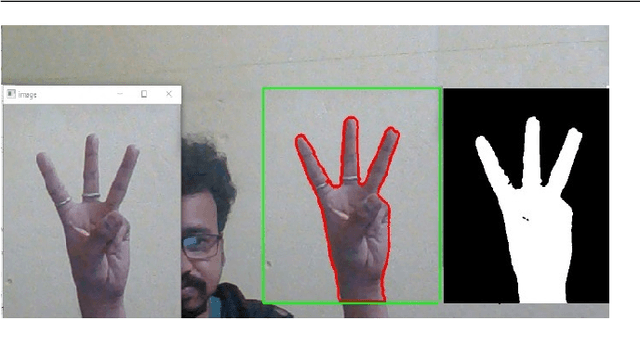
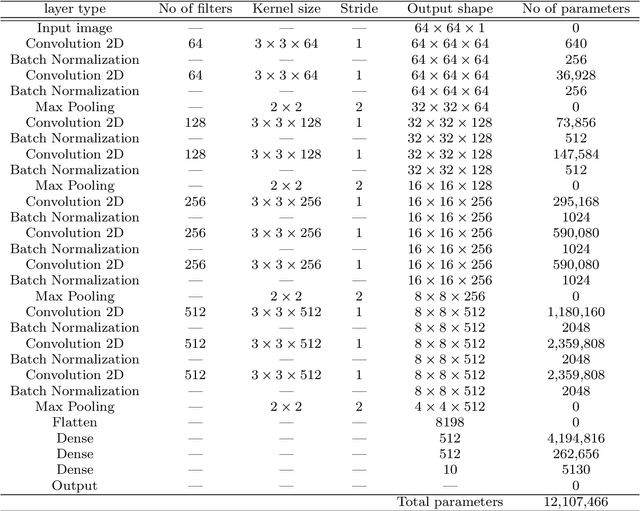
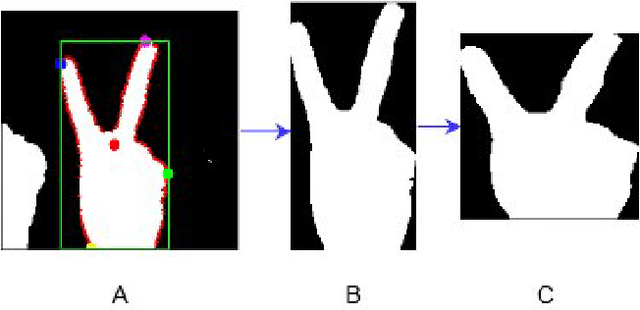
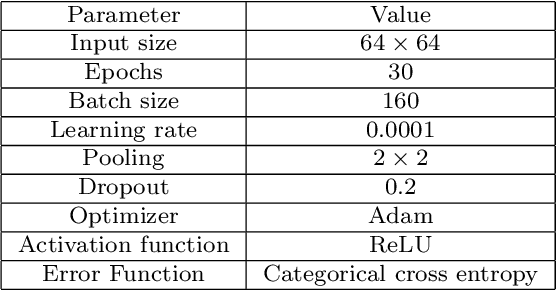
Abstract:Nowadays, hand gesture recognition has become an alternative for human-machine interaction. It has covered a large area of applications like 3D game technology, sign language interpreting, VR (virtual reality) environment, and robotics. But detection of the hand portion has become a challenging task in computer vision and pattern recognition communities. Deep learning algorithm like convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture has become a very popular choice for classification tasks, but CNN architectures suffer from some problems like high variance during prediction, overfitting problem and also prediction errors. To overcome these problems, an ensemble of CNN-based approaches is presented in this paper. Firstly, the gesture portion is detected by using the background separation method based on binary thresholding. After that, the contour portion is extracted, and the hand region is segmented. Then, the images have been resized and fed into three individual CNN models to train them in parallel. In the last part, the output scores of CNN models are averaged to construct an optimal ensemble model for the final prediction. Two publicly available datasets (labeled as Dataset-1 and Dataset-2) containing infrared images and one self-constructed dataset have been used to validate the proposed system. Experimental results are compared with the existing state-of-the-art approaches, and it is observed that our proposed ensemble model outperforms other existing proposed methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge