Part-of-Speech Tagging of Odia Language Using statistical and Deep Learning-Based Approaches
Paper and Code
Jul 07, 2022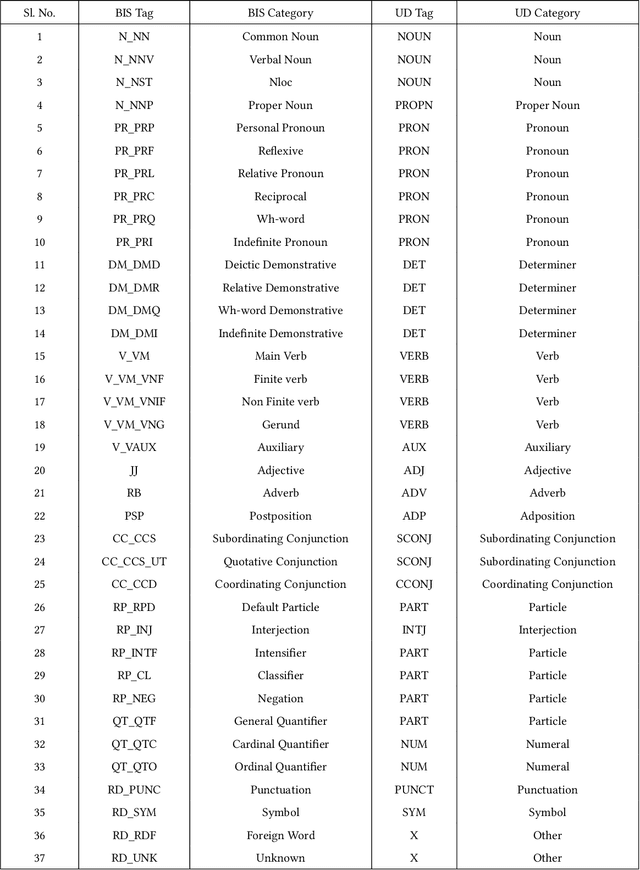
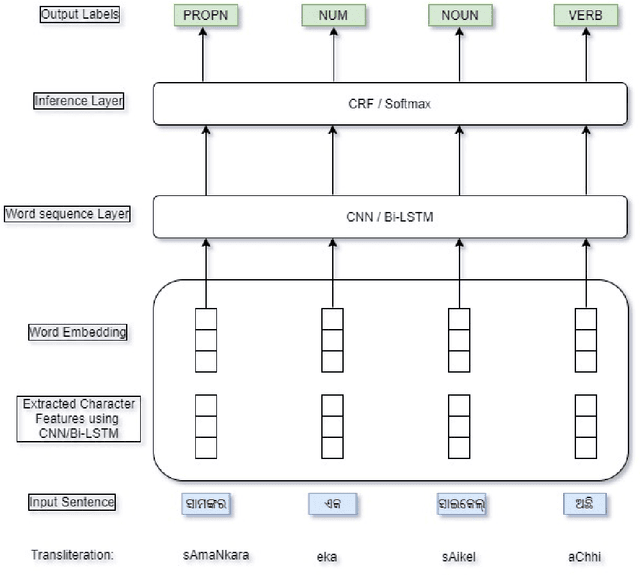

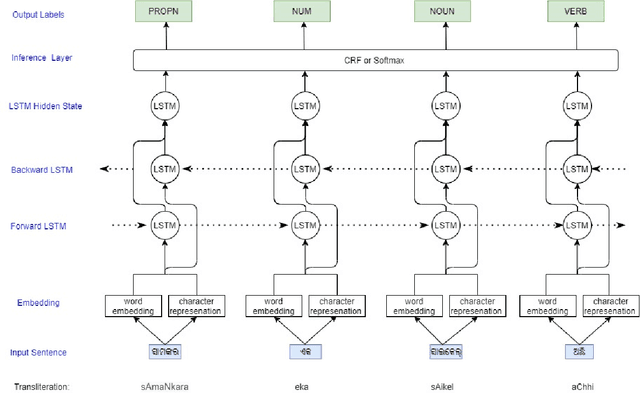
Automatic Part-of-speech (POS) tagging is a preprocessing step of many natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as name entity recognition (NER), speech processing, information extraction, word sense disambiguation, and machine translation. It has already gained a promising result in English and European languages, but in Indian languages, particularly in Odia language, it is not yet well explored because of the lack of supporting tools, resources, and morphological richness of language. Unfortunately, we were unable to locate an open source POS tagger for Odia, and only a handful of attempts have been made to develop POS taggers for Odia language. The main contribution of this research work is to present a conditional random field (CRF) and deep learning-based approaches (CNN and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory) to develop Odia part-of-speech tagger. We used a publicly accessible corpus and the dataset is annotated with the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) tagset. However, most of the languages around the globe have used the dataset annotated with Universal Dependencies (UD) tagset. Hence, to maintain uniformity Odia dataset should use the same tagset. So we have constructed a simple mapping from BIS tagset to UD tagset. We experimented with various feature set inputs to the CRF model, observed the impact of constructed feature set. The deep learning-based model includes Bi-LSTM network, CNN network, CRF layer, character sequence information, and pre-trained word vector. Character sequence information was extracted by using convolutional neural network (CNN) and Bi-LSTM network. Six different combinations of neural sequence labelling models are implemented, and their performance measures are investigated. It has been observed that Bi-LSTM model with character sequence feature and pre-trained word vector achieved a significant state-of-the-art result.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge