Taoran Wu
UR4NNV: Neural Network Verification, Under-approximation Reachability Works!
Jan 23, 2024Abstract:Recently, formal verification of deep neural networks (DNNs) has garnered considerable attention, and over-approximation based methods have become popular due to their effectiveness and efficiency. However, these strategies face challenges in addressing the "unknown dilemma" concerning whether the exact output region or the introduced approximation error violates the property in question. To address this, this paper introduces the UR4NNV verification framework, which utilizes under-approximation reachability analysis for DNN verification for the first time. UR4NNV focuses on DNNs with Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activations and employs a binary tree branch-based under-approximation algorithm. In each epoch, UR4NNV under-approximates a sub-polytope of the reachable set and verifies this polytope against the given property. Through a trial-and-error approach, UR4NNV effectively falsifies DNN properties while providing confidence levels when reaching verification epoch bounds and failing falsifying properties. Experimental comparisons with existing verification methods demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of UR4NNV, significantly reducing the impact of the "unknown dilemma".
Repairing Deep Neural Networks Based on Behavior Imitation
May 05, 2023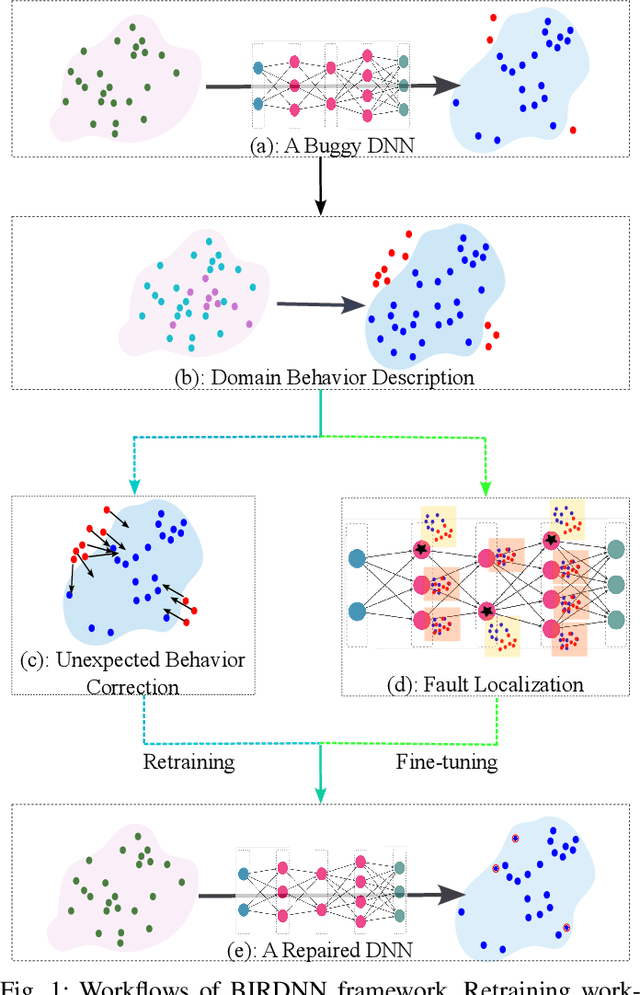
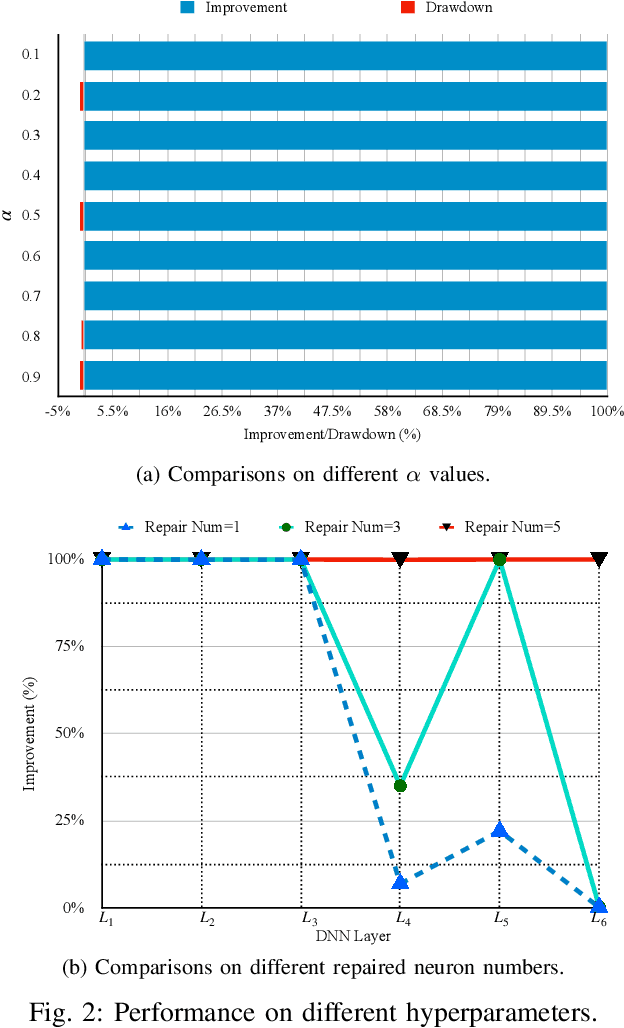
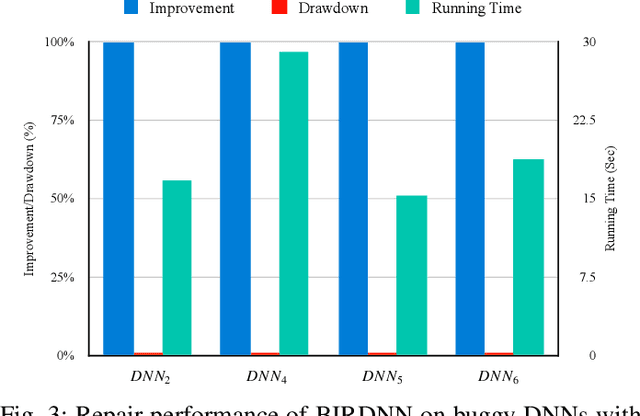
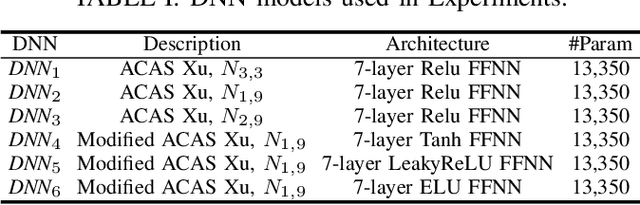
Abstract:The increasing use of deep neural networks (DNNs) in safety-critical systems has raised concerns about their potential for exhibiting ill-behaviors. While DNN verification and testing provide post hoc conclusions regarding unexpected behaviors, they do not prevent the erroneous behaviors from occurring. To address this issue, DNN repair/patch aims to eliminate unexpected predictions generated by defective DNNs. Two typical DNN repair paradigms are retraining and fine-tuning. However, existing methods focus on the high-level abstract interpretation or inference of state spaces, ignoring the underlying neurons' outputs. This renders patch processes computationally prohibitive and limited to piecewise linear (PWL) activation functions to great extent. To address these shortcomings, we propose a behavior-imitation based repair framework, BIRDNN, which integrates the two repair paradigms for the first time. BIRDNN corrects incorrect predictions of negative samples by imitating the closest expected behaviors of positive samples during the retraining repair procedure. For the fine-tuning repair process, BIRDNN analyzes the behavior differences of neurons on positive and negative samples to identify the most responsible neurons for the erroneous behaviors. To tackle more challenging domain-wise repair problems (DRPs), we synthesize BIRDNN with a domain behavior characterization technique to repair buggy DNNs in a probably approximated correct style. We also implement a prototype tool based on BIRDNN and evaluate it on ACAS Xu DNNs. Our experimental results show that BIRDNN can successfully repair buggy DNNs with significantly higher efficiency than state-of-the-art repair tools. Additionally, BIRDNN is highly compatible with different activation functions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge